
Nitrobenzene on further excessive nitration gives
A. Sym-trinitrobenzne
B. M-Dinitrobenzne
C. P-Dinitrobenzene
D. All of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Nitration is a chemical process by which nitro group (s) are introduced to a chemical compound. Nitration can be done by reacting benzene with \[{\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}\] (nitric acid ) in presence of sulphuric acid (\[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\]).
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's discuss nitrobenzene first. Nitrobenzene is a chemical species possessing the chemical formula of\[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\] . It shows the insolubility in water. It is A pale yellow coloured oil possessing the odour of almond. Freezing of it gives green-yellow coloured crystals. It is manufactured in huge quantities from benzene. The structure of nitrobenzene is,
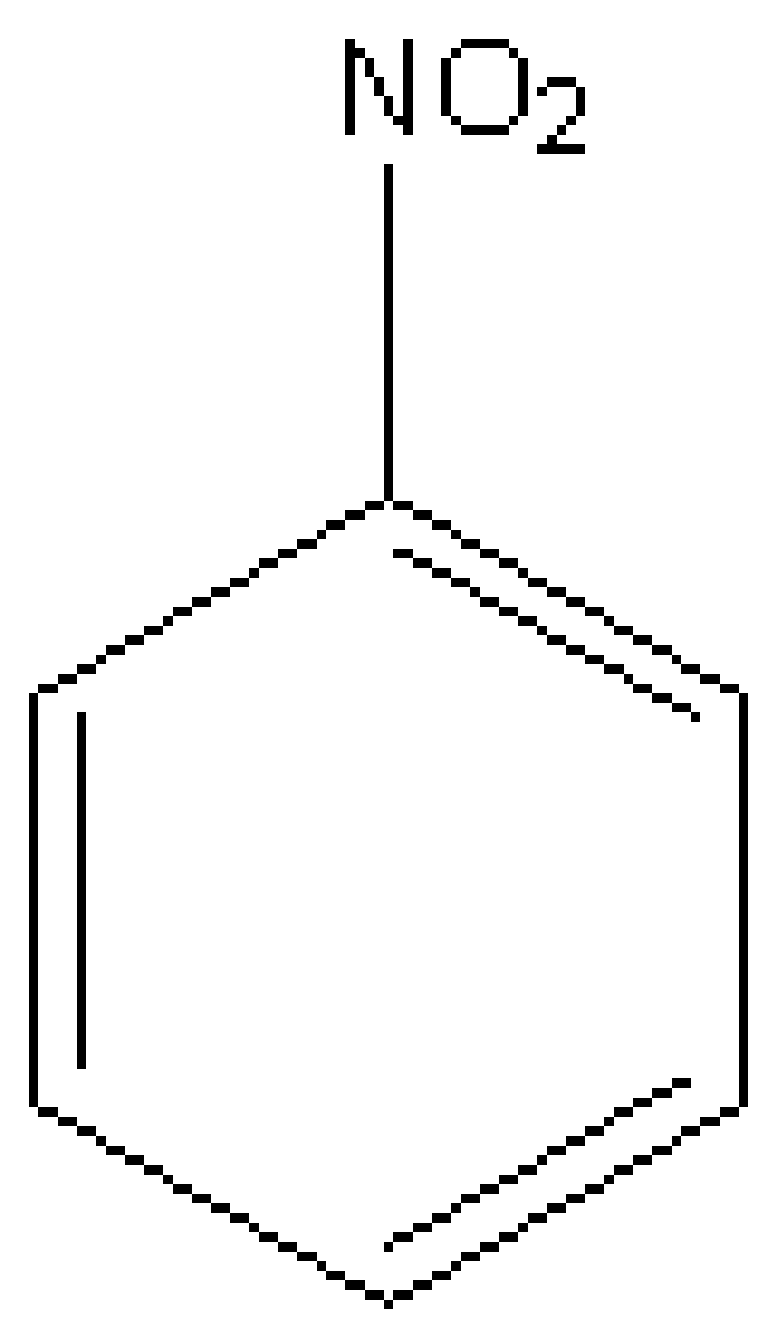
Image: Nitrobenzene
Here, we have to find out the product which is produced when excessive nitration of nitrobenzene occurs.
Here, nitrobenzene undergoes excessive nitration. When nitrobenzene undergoes a reaction with nitric acid in presence of sulphuric acid, the following reaction occurs.
\[{\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}} + {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}} \to {\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}^ + + {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} + {\rm{HS}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}^ - \]
Although \[{\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}\] is an acid, in the above reaction, it acts as a base and \[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\] acts as an acid. And we know, nitro group is an meta directing and deactivating group. Therefore, the product obtained is,
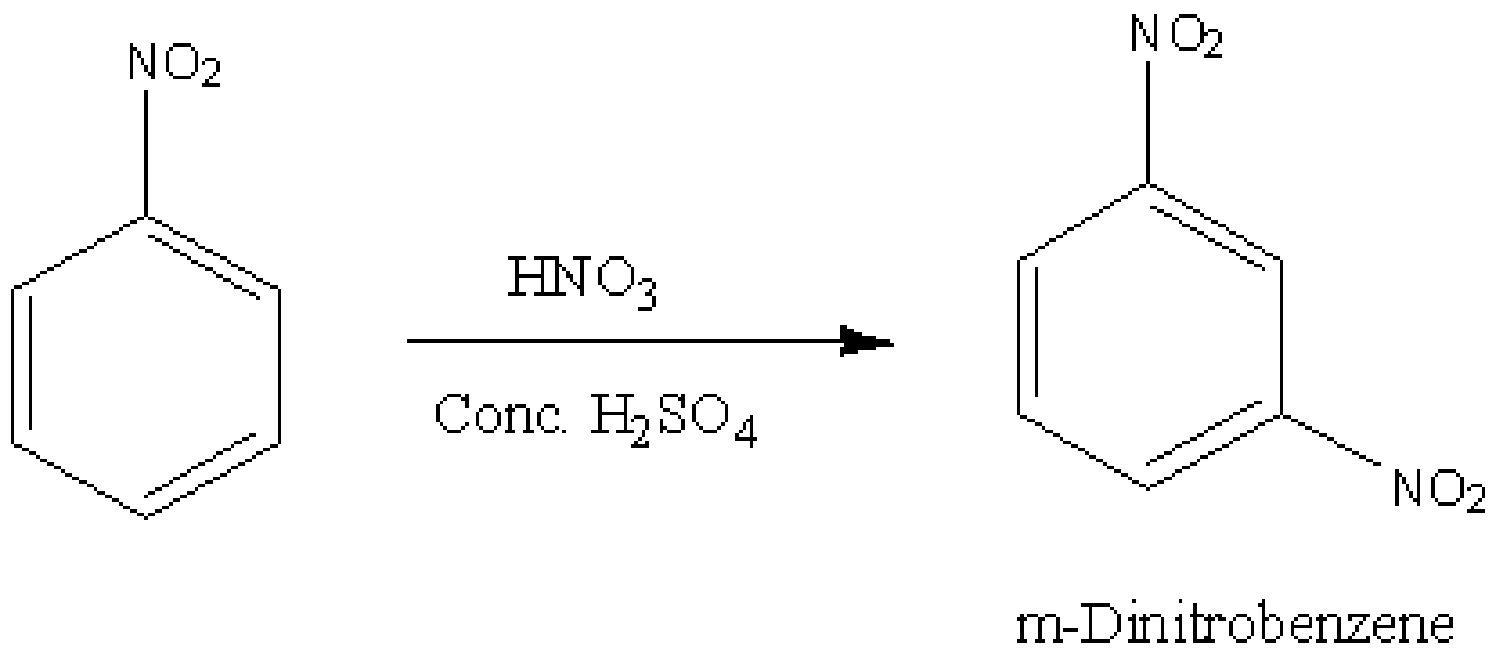
Image: Nitration of nitrobenzene
Further nitration of nitration is not possible because of the deactivating nitro group.
Hence, the option B is right.
Note: Nitration of benzene takes place in three steps, First step is, Activation of the electrophile by the acid. Second step is an attack of the activated electrophile by benzene and the last step is deprotonation to restore the aromatic ring and regeneration of the acidic catalyst.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's discuss nitrobenzene first. Nitrobenzene is a chemical species possessing the chemical formula of\[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\] . It shows the insolubility in water. It is A pale yellow coloured oil possessing the odour of almond. Freezing of it gives green-yellow coloured crystals. It is manufactured in huge quantities from benzene. The structure of nitrobenzene is,

Image: Nitrobenzene
Here, we have to find out the product which is produced when excessive nitration of nitrobenzene occurs.
Here, nitrobenzene undergoes excessive nitration. When nitrobenzene undergoes a reaction with nitric acid in presence of sulphuric acid, the following reaction occurs.
\[{\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}} + {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}} \to {\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}^ + + {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} + {\rm{HS}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}^ - \]
Although \[{\rm{HN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}\] is an acid, in the above reaction, it acts as a base and \[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\] acts as an acid. And we know, nitro group is an meta directing and deactivating group. Therefore, the product obtained is,

Image: Nitration of nitrobenzene
Further nitration of nitration is not possible because of the deactivating nitro group.
Hence, the option B is right.
Note: Nitration of benzene takes place in three steps, First step is, Activation of the electrophile by the acid. Second step is an attack of the activated electrophile by benzene and the last step is deprotonation to restore the aromatic ring and regeneration of the acidic catalyst.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




