
Which of the following will not undergo H V Z reaction?
a. Propanoic acid
b. Ethanoic acid
c. 2-methyl propanoic acid
d. 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid
Answer
531k+ views
Hint: Hell- Volhard- Zelinsky reaction is a type of odd substitution reaction in which carboxylic acid which contains $\alpha $hydrogen gets converted to $\alpha $ halo carboxylic acid.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, let us understand what the Hell- Volhard- Zelinsky [H V Z] reaction?
Hell- Volhard- Zelinsky [H V Z] reaction is also known as H V Z reaction. It is a type of substitution reaction in which carboxylic acids are converted to $\alpha $halo carboxylic acid. The reaction is initiated by the addition of phosphorus tribromide [Catalytic amount] and the further addition of one molar equivalent of di-atomic bromine.
Since, it is clear that $\alpha $hydrogen present in carboxylic acid is substituted by a halo group so the presence of $\alpha $hydrogen in the corresponding carboxylic acid is very important.
Let us draw the structure of four carboxylic acids given to us in the question.
(a) Propanoic acid
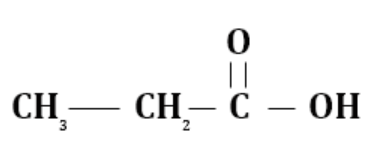
$(2 \propto \, - H)$
(b) Ethanoic acid
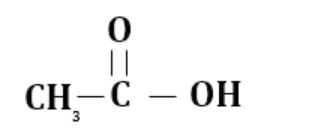
$(3 \propto \, - H)$
(c) 2-methyl propanoic acid
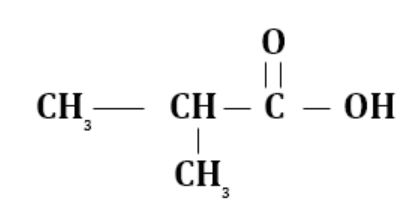
$(1 \propto \,H)$
(d) 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid

$(no \propto \, - H)$
Thus, 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid does not contain any $\alpha $hydrogen. Hence it will not participate in Hell- Volhard- Zelinsky [H V Z] reaction.
Option (d) is the correct answer.
Note:
Students should note that the H V Z reaction generally accomplishes bromination but fails in case of fluorination and iodination of carboxylic acid. The following reaction is not conducted at extremely high temperature, as there may be an elimination of hydrogen halide from the product thereby resulting in the formation of beta unsaturated carboxylic acid.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all, let us understand what the Hell- Volhard- Zelinsky [H V Z] reaction?
Hell- Volhard- Zelinsky [H V Z] reaction is also known as H V Z reaction. It is a type of substitution reaction in which carboxylic acids are converted to $\alpha $halo carboxylic acid. The reaction is initiated by the addition of phosphorus tribromide [Catalytic amount] and the further addition of one molar equivalent of di-atomic bromine.
Since, it is clear that $\alpha $hydrogen present in carboxylic acid is substituted by a halo group so the presence of $\alpha $hydrogen in the corresponding carboxylic acid is very important.
Let us draw the structure of four carboxylic acids given to us in the question.
(a) Propanoic acid
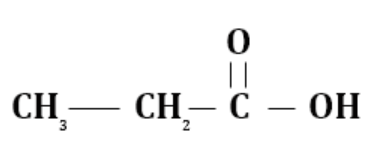
$(2 \propto \, - H)$
(b) Ethanoic acid
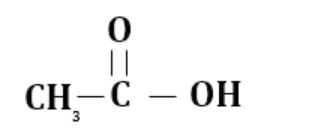
$(3 \propto \, - H)$
(c) 2-methyl propanoic acid

$(1 \propto \,H)$
(d) 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid

$(no \propto \, - H)$
Thus, 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid does not contain any $\alpha $hydrogen. Hence it will not participate in Hell- Volhard- Zelinsky [H V Z] reaction.
Option (d) is the correct answer.
Note:
Students should note that the H V Z reaction generally accomplishes bromination but fails in case of fluorination and iodination of carboxylic acid. The following reaction is not conducted at extremely high temperature, as there may be an elimination of hydrogen halide from the product thereby resulting in the formation of beta unsaturated carboxylic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




