
Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids:
A. ${\rm{Mg}}$and ${\rm{Zn}}$
B. ${\rm{Cu}}$and ${\rm{Au}}$
C. ${\rm{Cu}}$and ${\rm{Mg}}$
D. ${\rm{Zn}}$and ${\rm{Cu}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We know that a reaction where displacement of a less reactive metal from its compound occurs by a more reactive metal is termed as displacement reaction. The reactivity of metals is decided by the reactivity series of metals.
Complete step-by step answer:
Now, we discuss the condition in which displacement of hydrogen from dilute acids takes place. From dilute acids like hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid, hydrogen is replaced by metals which are more reactive than hydrogen. The reactivity series of metals is given as follows:
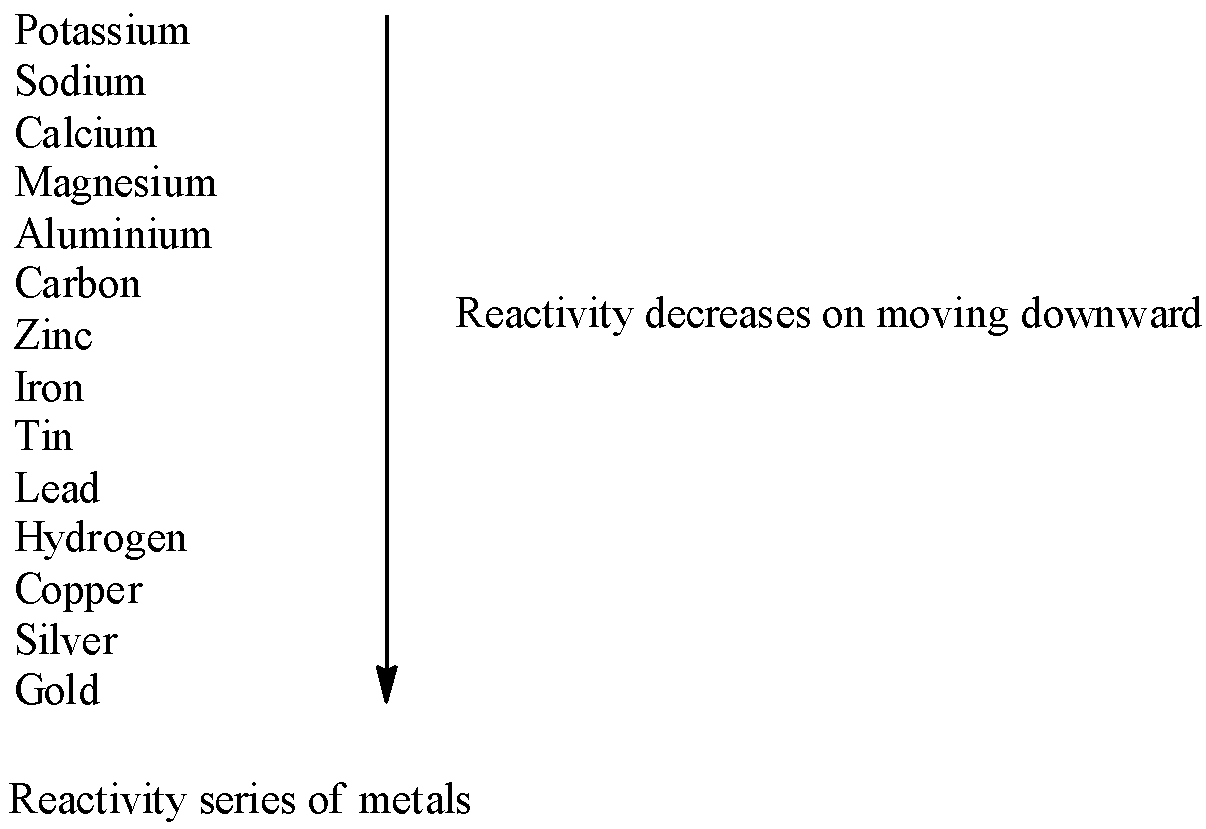
Let’s find the correct option.
Option A contains ${\rm{Mg}}$(Magnesium) and ${\rm{Zn}}$(zinc). Both magnesium and zinc are more reactive than hydrogen in the activity series. So, they displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Option B contains ${\rm{Cu}}$(copper) and ${\rm{Au}}$(gold). Copper and gold both are less reactive than hydrogen. So, they do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Option C contains ${\rm{Cu}}$(copper) and ${\rm{Mg}}$(magnesium). Copper is less reactive than hydrogen but magnesium is more reactive than hydrogen. So, displacement of hydrogen from dilute acid is possible in case of magnesium but not possible in case of copper.
Option D contains ${\rm{Zn}}$(zinc) and ${\rm{Cu}}$(copper). Copper is less reactive than hydrogen but zinc is more reactive than hydrogen. So, displacement of hydrogen from dilute acid is possible in case of zinc but not possible in case of copper.
Hence, correct option is A, that is, ${\rm{Mg}}$and ${\rm{Zn}}$
Note: Highly reactive metal like potassium, sodium and calcium displaces hydrogen from dilute acids with explosive violence, moderately reactive metals like magnesium, aluminium and zinc displaces hydrogen vigorously and metals such as copper, gold, mercury and silver do not displaces hydrogen from dilute acids.
Complete step-by step answer:
Now, we discuss the condition in which displacement of hydrogen from dilute acids takes place. From dilute acids like hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid, hydrogen is replaced by metals which are more reactive than hydrogen. The reactivity series of metals is given as follows:

Let’s find the correct option.
Option A contains ${\rm{Mg}}$(Magnesium) and ${\rm{Zn}}$(zinc). Both magnesium and zinc are more reactive than hydrogen in the activity series. So, they displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Option B contains ${\rm{Cu}}$(copper) and ${\rm{Au}}$(gold). Copper and gold both are less reactive than hydrogen. So, they do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Option C contains ${\rm{Cu}}$(copper) and ${\rm{Mg}}$(magnesium). Copper is less reactive than hydrogen but magnesium is more reactive than hydrogen. So, displacement of hydrogen from dilute acid is possible in case of magnesium but not possible in case of copper.
Option D contains ${\rm{Zn}}$(zinc) and ${\rm{Cu}}$(copper). Copper is less reactive than hydrogen but zinc is more reactive than hydrogen. So, displacement of hydrogen from dilute acid is possible in case of zinc but not possible in case of copper.
Hence, correct option is A, that is, ${\rm{Mg}}$and ${\rm{Zn}}$
Note: Highly reactive metal like potassium, sodium and calcium displaces hydrogen from dilute acids with explosive violence, moderately reactive metals like magnesium, aluminium and zinc displaces hydrogen vigorously and metals such as copper, gold, mercury and silver do not displaces hydrogen from dilute acids.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




