
Most important energy carrier in living cells is:
(A) ADP
(B) TTP
(C) ATP
(D) GTP
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The phosphate which can store maximum amount of energy in its bonds and can release maximum amount of energy when these bonds are broken (when cell needs energy) is the best and most important energy carrier in living cells.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The process of synthesis of the carrier of energy in living cells is known as cellular respiration, the first step of cellular respiration that is glycolysis is common in all living organisms even bacteria, this step occurs in cytosol or cytoplasm of the cell. Further steps occur in mitochondria of the cell (also known as powerhouse of cell). In the process of cellular respiration glucose is converted into carbon dioxide and water along with evolution of energy, this energy is not released in a single step (as that may lead to excessive heat in the cell), this evolved energy is trapped in the form of energy currency that is ATP ( adenosine triphosphate), it contains adenosine (adenine + pentose sugar) which is a nucleoside and three phosphate groups. During cellular respiration, inorganic phosphate is added to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) it also as adenosine nucleoside and two phosphate groups, amd ATP is formed. $ADP+iP\to ATP$
In conversion of one molecule of glucose into carbon dioxide and water 36/38 molecule of ATP is formed: ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}+6{{O}_{2}}\to 6C{{O}_{2}}+6{{H}_{2}}0+36/38ATP$
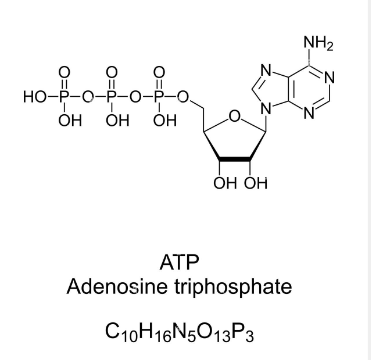
Image Caption: Structure of ATP.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: You may think that cellular respiration is a catabolic pathway so how is ATP made, so make it clear that it is said to be catabolic because here glucose is catabolized and energy released and this energy is trapped in the form of ATP which is also known as energy currency of the cell.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The process of synthesis of the carrier of energy in living cells is known as cellular respiration, the first step of cellular respiration that is glycolysis is common in all living organisms even bacteria, this step occurs in cytosol or cytoplasm of the cell. Further steps occur in mitochondria of the cell (also known as powerhouse of cell). In the process of cellular respiration glucose is converted into carbon dioxide and water along with evolution of energy, this energy is not released in a single step (as that may lead to excessive heat in the cell), this evolved energy is trapped in the form of energy currency that is ATP ( adenosine triphosphate), it contains adenosine (adenine + pentose sugar) which is a nucleoside and three phosphate groups. During cellular respiration, inorganic phosphate is added to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) it also as adenosine nucleoside and two phosphate groups, amd ATP is formed. $ADP+iP\to ATP$
In conversion of one molecule of glucose into carbon dioxide and water 36/38 molecule of ATP is formed: ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}+6{{O}_{2}}\to 6C{{O}_{2}}+6{{H}_{2}}0+36/38ATP$

Image Caption: Structure of ATP.
Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: You may think that cellular respiration is a catabolic pathway so how is ATP made, so make it clear that it is said to be catabolic because here glucose is catabolized and energy released and this energy is trapped in the form of ATP which is also known as energy currency of the cell.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




