
Leucine amino acid is the
(A) Essential
(B) Non-essential
(C) Aromatic
(D) Basic
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Amino acids which our body synthesis on its own are not required from outside the body in the form of food but the amino acids which are not synthesised by our own body cells (but body need these amino acids to function normally) then we need this from various food sources. The amino acids which the body can synthesise itself are known are non essential amino acids and the ones which the body cannot synthesise and are taken from outside sources are known as essential amino acids.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Amino acid is the monomeric unit for synthesis of proteins (which are basic building blocks of the body). Amino acids have two functional groups one is amino group and the other one carboxylic acid group, they are divided into various categories based on various broad headings. On the basis of abundance of amino or carboxyl groups they are divided into basic and acidic. If the structure has an aromatic ring then amino acid becomes aromatic and if no aromatic ring is present in the structure then amino acid becomes non aromatic.
Essential amino acids are histidine, arginine, lysine, leucine, valine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, methionine, tryptophan, threonine,
Aromatic amino acids are phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
Basic amino acids are histidine, lysine, arginine and asparagine
Therefore from above data we can conclude that leucine is an essential amino acid.
Hence option (A) is correct.
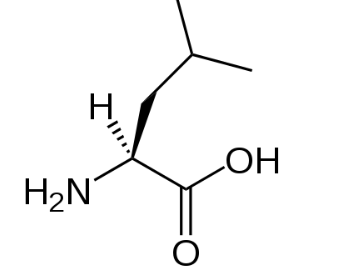
Image Caption: Structure of leucine.
Note: Make structure and check whether the amino acid contains an aromatic ring or not, if it does then it is an aromatic amino acid and if not then it is non aromatic amino acid. Leucine is a non aromatic amino acid as no aromatic ring is present in its structure.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Amino acid is the monomeric unit for synthesis of proteins (which are basic building blocks of the body). Amino acids have two functional groups one is amino group and the other one carboxylic acid group, they are divided into various categories based on various broad headings. On the basis of abundance of amino or carboxyl groups they are divided into basic and acidic. If the structure has an aromatic ring then amino acid becomes aromatic and if no aromatic ring is present in the structure then amino acid becomes non aromatic.
Essential amino acids are histidine, arginine, lysine, leucine, valine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, methionine, tryptophan, threonine,
Aromatic amino acids are phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
Basic amino acids are histidine, lysine, arginine and asparagine
Therefore from above data we can conclude that leucine is an essential amino acid.
Hence option (A) is correct.

Image Caption: Structure of leucine.
Note: Make structure and check whether the amino acid contains an aromatic ring or not, if it does then it is an aromatic amino acid and if not then it is non aromatic amino acid. Leucine is a non aromatic amino acid as no aromatic ring is present in its structure.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




