
Iso-propyl bromide on Wurtz reaction gives:
A. Hexane
B. Propane
C. 2, 3-dimethylbutane
D. Neo-hexane
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The compound formed is a saturated hydrocarbon. Saturated hydrocarbons are the type of hydrocarbon where the carbon-carbon single bond is present.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Wurtz reaction is a type of coupling reaction where sodium metal undergoes a reaction with 2 molecules of an alkyl halide in presence of dry ether to form a higher alkane. In the given reaction dry ether is used as a solvent.
When 2 molecules of iso-propyl bromide react with sodium metal in presence of dry ether 2, 3-dimethylbutane is obtained as the main product.
The reaction of Isopropyl bromide with sodium is shown below.
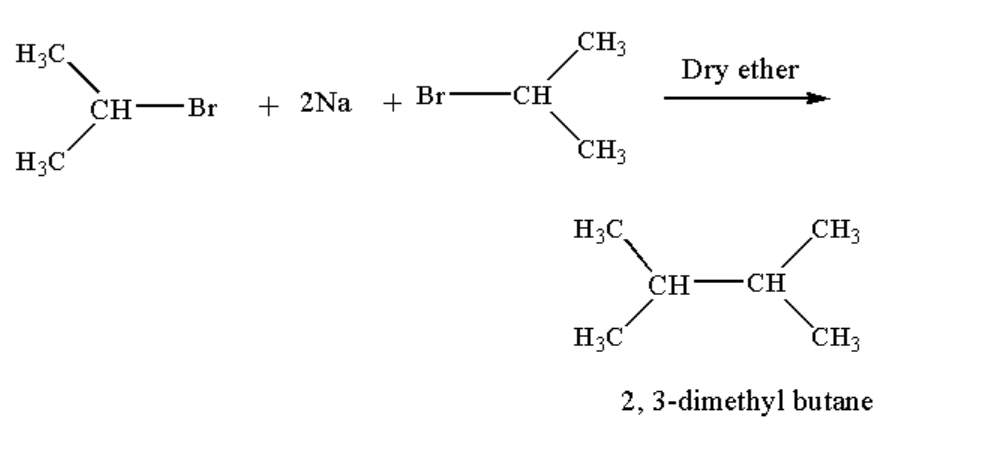
Image: Reaction of Isopropyl bromide with sodium
In the general reaction, the first electron transfer takes place from the sodium metal to the halogen group which results in the formation of the alkyl radical and metal halide. After that, another electron from other sodium attacks the alkyl radical to form an alkyl anion. The nucleophilic carbon of the alkyl anion replaces the halogen of an alkyl halide by nucleophilic substitution reaction and leads to the formation of a carbon-carbon covalent bond.
In the free radical mechanism for the preparation of alkanes by Wurtz reaction, there is a possibility that alkene is also produced as a side product.
Thus iso-propyl bromide on Wurtz reaction gives 2, 3-dimethylbutane. Therefore, option C is correct.
Note: In the Wurtz reaction, only symmetric alkanes are produced as a mixture of alkanes as products are produced on the reaction of different alkanes and hence these mixtures are very difficult to separate.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Wurtz reaction is a type of coupling reaction where sodium metal undergoes a reaction with 2 molecules of an alkyl halide in presence of dry ether to form a higher alkane. In the given reaction dry ether is used as a solvent.
When 2 molecules of iso-propyl bromide react with sodium metal in presence of dry ether 2, 3-dimethylbutane is obtained as the main product.
The reaction of Isopropyl bromide with sodium is shown below.

Image: Reaction of Isopropyl bromide with sodium
In the general reaction, the first electron transfer takes place from the sodium metal to the halogen group which results in the formation of the alkyl radical and metal halide. After that, another electron from other sodium attacks the alkyl radical to form an alkyl anion. The nucleophilic carbon of the alkyl anion replaces the halogen of an alkyl halide by nucleophilic substitution reaction and leads to the formation of a carbon-carbon covalent bond.
In the free radical mechanism for the preparation of alkanes by Wurtz reaction, there is a possibility that alkene is also produced as a side product.
Thus iso-propyl bromide on Wurtz reaction gives 2, 3-dimethylbutane. Therefore, option C is correct.
Note: In the Wurtz reaction, only symmetric alkanes are produced as a mixture of alkanes as products are produced on the reaction of different alkanes and hence these mixtures are very difficult to separate.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




