
How many ions are produced by ${{K}_{4}}[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]$ in an aqueous solution?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The number of ions produced by the inorganic coordination complex is going to depend on the solubility of the inorganic coordination complex. The number of ions produced by an inorganic complex is going to decide by the outer sphere complex.
Complete step by step solution:
-There are two spheres in inorganic coordination complexes.
-One is the outer sphere and second is inner-sphere complex.
-We can see the outer sphere and inner-sphere complex clearly by the below image.
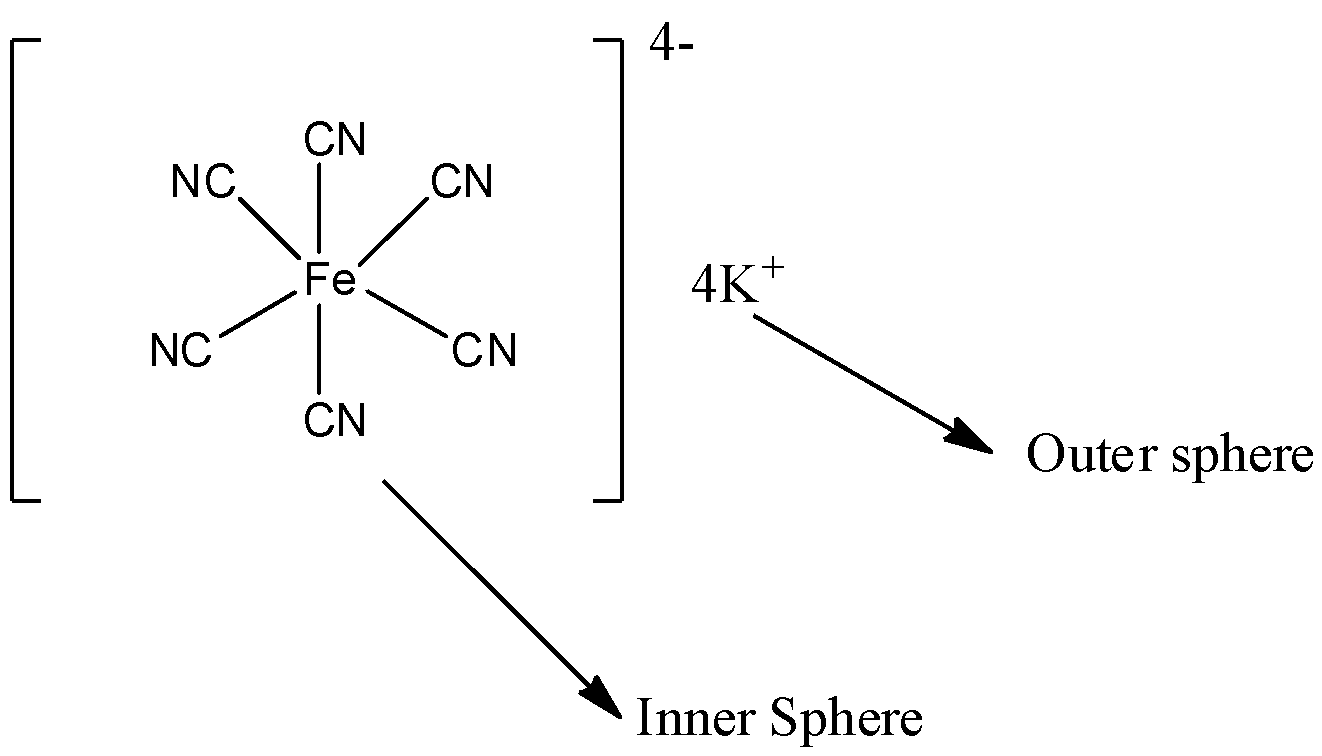
-The ligands inside the inner sphere won’t come out when dissolved in water.
-The ligands present in the outer sphere are going to release into the water when the inorganic coordination complex is added to water.
-Coming to the given complex, ${{K}_{4}}[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]$.
-From the above structure, we can see clearly that potassium hexacyanoferrate has two spheres.
-In the outer sphere there are four potassium ions and total inner sphere is one ion is going to form when ${{K}_{4}}[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]$is going to be added to water.
-Thus the number of ions produced by ${{K}_{4}}[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]$is = 4+1 = 5.
Therefore the number of ions produced by ${{K}_{4}}[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]$ is 5.
Note: The solubility of the inorganic coordination complex is going to depend on the composition of the coordination complex. If the coordination complex does not contain any ligands in the outer sphere then the coordination complex is very less soluble in water. It means the solubility of the complexes is going to be depending on the ligands present in the outer sphere of the complex. Once the coordination complex is dissolved in water, only the ligands present in the outer sphere are going to be released into the water and the ligands present in the inner sphere stay with the central metal ion.
Complete step by step solution:
-There are two spheres in inorganic coordination complexes.
-One is the outer sphere and second is inner-sphere complex.
-We can see the outer sphere and inner-sphere complex clearly by the below image.

-The ligands inside the inner sphere won’t come out when dissolved in water.
-The ligands present in the outer sphere are going to release into the water when the inorganic coordination complex is added to water.
-Coming to the given complex, ${{K}_{4}}[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]$.
-From the above structure, we can see clearly that potassium hexacyanoferrate has two spheres.
-In the outer sphere there are four potassium ions and total inner sphere is one ion is going to form when ${{K}_{4}}[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]$is going to be added to water.
-Thus the number of ions produced by ${{K}_{4}}[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]$is = 4+1 = 5.
Therefore the number of ions produced by ${{K}_{4}}[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]$ is 5.
Note: The solubility of the inorganic coordination complex is going to depend on the composition of the coordination complex. If the coordination complex does not contain any ligands in the outer sphere then the coordination complex is very less soluble in water. It means the solubility of the complexes is going to be depending on the ligands present in the outer sphere of the complex. Once the coordination complex is dissolved in water, only the ligands present in the outer sphere are going to be released into the water and the ligands present in the inner sphere stay with the central metal ion.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




