
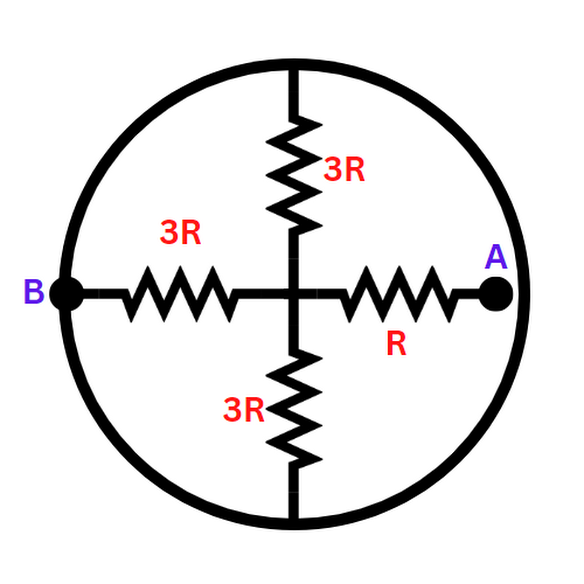
In the network shown below, the ring has zero resistance. The equivalent resistance between the point A and B is
A) 2R
B) 4R
C) 7R
D) 10R
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:The problem is from the electricity part of physics. We can apply the concept of parallel combination and series combination of resistance here. Use the equation for effective resistance in parallel and series combinations.
Formula Used:
Equivalent resistance for a series resistance circuit:
${R_E} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$
Where ${R_E}$= equivalent resistance and ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ = component resistance.
Equivalent resistance for a parallel resistance circuit:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_E}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}$
Where ${R_E}$= equivalent resistance and ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ = component resistance.
Complete answer:
The equivalent resistance is a single resistance which can replace all the component resistances in a circuit in such a manner that the current in the circuit remains unchanged.
Equivalent resistance for a series resistance circuit:
${R_E} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$
Where ${R_E}$= equivalent resistance and ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ = component resistance.
Equivalent resistance for a parallel resistance circuit:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_E}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}$
Where ${R_E}$= equivalent resistance and ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ = component resistance.
Here, in this case, the ring has zero resistance and the three $3R$resistances are in parallel connection. So the equivalent resistance will be.
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_E}}} = \dfrac{1}{{3R}} + \dfrac{1}{{3R}} + \dfrac{1}{{3R}} = \dfrac{1}{R}$
\[{R_E} = R\]
Then between points A and B, the two resistances \[{R_E}\]and \[R\]are in series combination.
Then equivalent resistance between A and B = \[R + R = 2R\]
Hence, the correct option is Option (A) 2R.
Additional Information:
Resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit. Resistance blocks the flow of current. The S.I unit of resistance is ohms. The current decreases as resistance increases. On the other hand, the current increases as the resistance decreases.
When electrons move through a conductor, like a metal wire, an electric current occurs. The ions in the metal can collide with the travelling electrons. Resistance is created as a result and makes it more difficult for the current to flow.
Note: A device created to produce resistance is called a resistor. Resistors can be used to divide voltage, limit current, or produce heat. Fixed and variable resistors are the two main types of resistors. In other words, a resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used in circuits to implement electrical resistance.
Formula Used:
Equivalent resistance for a series resistance circuit:
${R_E} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$
Where ${R_E}$= equivalent resistance and ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ = component resistance.
Equivalent resistance for a parallel resistance circuit:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_E}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}$
Where ${R_E}$= equivalent resistance and ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ = component resistance.
Complete answer:
The equivalent resistance is a single resistance which can replace all the component resistances in a circuit in such a manner that the current in the circuit remains unchanged.
Equivalent resistance for a series resistance circuit:
${R_E} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$
Where ${R_E}$= equivalent resistance and ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ = component resistance.
Equivalent resistance for a parallel resistance circuit:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_E}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}$
Where ${R_E}$= equivalent resistance and ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ = component resistance.
Here, in this case, the ring has zero resistance and the three $3R$resistances are in parallel connection. So the equivalent resistance will be.
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_E}}} = \dfrac{1}{{3R}} + \dfrac{1}{{3R}} + \dfrac{1}{{3R}} = \dfrac{1}{R}$
\[{R_E} = R\]
Then between points A and B, the two resistances \[{R_E}\]and \[R\]are in series combination.
Then equivalent resistance between A and B = \[R + R = 2R\]
Hence, the correct option is Option (A) 2R.
Additional Information:
Resistance is a measure of the opposition to current flow in an electrical circuit. Resistance blocks the flow of current. The S.I unit of resistance is ohms. The current decreases as resistance increases. On the other hand, the current increases as the resistance decreases.
When electrons move through a conductor, like a metal wire, an electric current occurs. The ions in the metal can collide with the travelling electrons. Resistance is created as a result and makes it more difficult for the current to flow.
Note: A device created to produce resistance is called a resistor. Resistors can be used to divide voltage, limit current, or produce heat. Fixed and variable resistors are the two main types of resistors. In other words, a resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used in circuits to implement electrical resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




