
In the arrangement shown a solid cylinder of mass $M$ and radius $R$ is suspended with the help of an ideal string, and the lift is moving upward with acceleration $g/3$. The tension in the string is
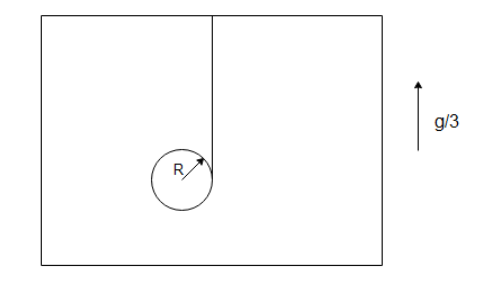
A) $\dfrac{{5mg}}{{12}}$
B) $\dfrac{{4mg}}{3}$
C) $\dfrac{{3mg}}{4}$
D) $\dfrac{{4mg}}{9}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The tension in the string can be determined from the force balance of the string. It can also be determined from the angular motion of the solid cylinder on the string. We will equate these two equations to determine the tension in the string.
Formula used: In this solution, we will use the following formulae:
Torque on the cylinder: $\tau = F.R = I.\alpha $ where $F$ is the force or the tension in the string, $R$ is the radius of the pulley, $I$ is the moment of inertia of the rod, and $\alpha $ is the angular acceleration of the cylinder.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us start by drawing a free body diagram of the situation described:
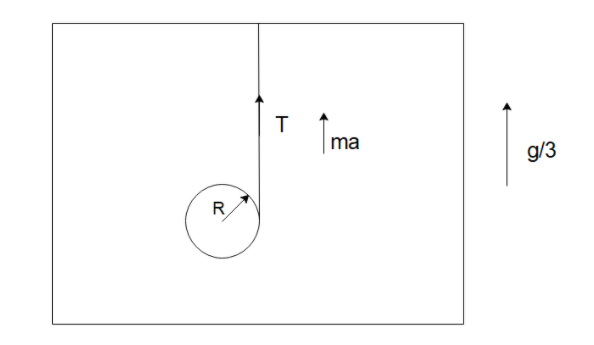
We can see that the net acceleration experienced by the system will be due to gravity and the acceleration of the lift as $a = g + \dfrac{g}{3} = \dfrac{{4g}}{3}$.
Then the force balance of the diagram in the vertical direction will be
$\dfrac{{4mg}}{3} - T = ma$
where $a$ is the net acceleration of the object.
Now looking at the angular motion of the cylinder, we know that the moment of inertia of a solid cylinder is calculated as $\dfrac{{m{R^2}}}{2}$. Then the torque acting on the cylinder due to the unrolling of the string will be
$TR = \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{2}\alpha $
As the angular acceleration is the product of the linear acceleration and the radius of the sphere, we have $\alpha = aR$. Then the above equation can be written as
$ma = 2T$
Equating equation (1) and (2), we get
$\dfrac{{4mg}}{3} - T = 2T$
Which gives us the tension as
$T = \dfrac{{4mg}}{9}$ which corresponds to option (D).
Note: Such questions always require knowledge of the translational dynamics as well as the rotational dynamics of the object. We should also know the moment of inertia of certain objects like cylinders about different axes as these objects are frequently encountered in such questions.
Formula used: In this solution, we will use the following formulae:
Torque on the cylinder: $\tau = F.R = I.\alpha $ where $F$ is the force or the tension in the string, $R$ is the radius of the pulley, $I$ is the moment of inertia of the rod, and $\alpha $ is the angular acceleration of the cylinder.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us start by drawing a free body diagram of the situation described:

We can see that the net acceleration experienced by the system will be due to gravity and the acceleration of the lift as $a = g + \dfrac{g}{3} = \dfrac{{4g}}{3}$.
Then the force balance of the diagram in the vertical direction will be
$\dfrac{{4mg}}{3} - T = ma$
where $a$ is the net acceleration of the object.
Now looking at the angular motion of the cylinder, we know that the moment of inertia of a solid cylinder is calculated as $\dfrac{{m{R^2}}}{2}$. Then the torque acting on the cylinder due to the unrolling of the string will be
$TR = \dfrac{{M{R^2}}}{2}\alpha $
As the angular acceleration is the product of the linear acceleration and the radius of the sphere, we have $\alpha = aR$. Then the above equation can be written as
$ma = 2T$
Equating equation (1) and (2), we get
$\dfrac{{4mg}}{3} - T = 2T$
Which gives us the tension as
$T = \dfrac{{4mg}}{9}$ which corresponds to option (D).
Note: Such questions always require knowledge of the translational dynamics as well as the rotational dynamics of the object. We should also know the moment of inertia of certain objects like cylinders about different axes as these objects are frequently encountered in such questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




