
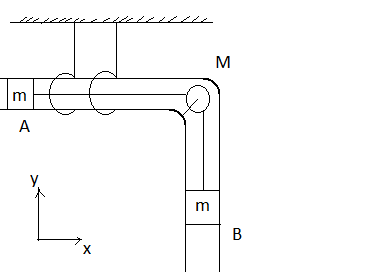
In figure, a hollow tube of mass $M$ is free in horizontal direction. The system is released from rest. There is no friction present. The tube and blocks are taken as a system.
1) Momentum of the system is conserved in x-direction.
2) Speed of $A$ with respect to $M = $ speed of $B$ with respect to $M$.
3) Trajectory of the centre of mass is $X - $ constant.
4) Centre of mass has finite acceleration.
A) Statements (1) and (2) are true and (3) and (4) are false.
B) Statements (1) and (2) are false and (3) and (4) are true.
C) All statements are true
D) All statements are false

Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: For the momentum of any system to be conserved, no external forces can be acting on it. Find the external forces on the system and find out what direction they’re acting in. For trajectory also, find out if momentum is conserved or not.
Complete step by step solution:
1. To find out if momentum of a system is conserved in any direction, we find out the forces acting on the system in that direction. In this case, the only forces acting on the system are gravitational force and tension force. But the tension force is an internal force therefore the only external force acting on it is the gravitational force. Gravitational force acts in $Y - $ direction therefore momentum is conserved in $X - $ direction where no external force is acting. Therefore, this statement is true.
2. Since the strings are inextensible, with respect to $M$ , both blocks move with the same speed but not velocity. Therefore this statement is true also.
3. There is no external force acting in $X - $ direction leading to momentum being conserved. As the system was originally at rest, therefore the velocity of centre of mass of In $X - $ direction ( ${v_{xcm}} = 0$ ) also remains zero. Hence the trajectory of the system is $X - $ constant . Hence this statement is true.
4. In $Y - $ direction , the centre of mass has a finite acceleration due to the finite gravitational force acting on it. That is
$mg - T = m{a_y}$
Where ${a_y}$ is the final acceleration in y direction and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity acting on a string with tension $T$ and block of mass $m$ . This statement is also true.
Since all statements are true, the correct option is ( C ) All statements are true.
Note: Remember that even if the speed of the blocks can be the same around the axis of rotation, velocity need not be the same. Also, don’t forget all the forces acting on the system, external and internal both.
Complete step by step solution:
1. To find out if momentum of a system is conserved in any direction, we find out the forces acting on the system in that direction. In this case, the only forces acting on the system are gravitational force and tension force. But the tension force is an internal force therefore the only external force acting on it is the gravitational force. Gravitational force acts in $Y - $ direction therefore momentum is conserved in $X - $ direction where no external force is acting. Therefore, this statement is true.
2. Since the strings are inextensible, with respect to $M$ , both blocks move with the same speed but not velocity. Therefore this statement is true also.
3. There is no external force acting in $X - $ direction leading to momentum being conserved. As the system was originally at rest, therefore the velocity of centre of mass of In $X - $ direction ( ${v_{xcm}} = 0$ ) also remains zero. Hence the trajectory of the system is $X - $ constant . Hence this statement is true.
4. In $Y - $ direction , the centre of mass has a finite acceleration due to the finite gravitational force acting on it. That is
$mg - T = m{a_y}$
Where ${a_y}$ is the final acceleration in y direction and $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity acting on a string with tension $T$ and block of mass $m$ . This statement is also true.
Since all statements are true, the correct option is ( C ) All statements are true.
Note: Remember that even if the speed of the blocks can be the same around the axis of rotation, velocity need not be the same. Also, don’t forget all the forces acting on the system, external and internal both.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




