
In acidic medium amino acid exists as:
A. \[R-CH\left( N{{H}_{2}} \right)COOH\]
B. \[R-CH{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}^{+}}COOH\]
C. \[R-CH\left( N{{H}_{2}} \right)CO{{O}^{-}}\]
D. \[R-CH{{\left( NH{}_{3} \right)}^{+}}CO{{O}^{-}}\]
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint: As we know, reactions are carried out in aqueous solutions and when the concentration of hydrogen ion is more in the solution then it is called as acidic medium and similarly when the concentration of hydroxyl ion is more in the solution then it is termed as basic medium.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Based on the definition of the acidic medium, in acidic conditions the amino acid acts as a base and accepts a proton at the amino group which results into positive charge whereas, in alkaline conditions, the amino acid acts as an acid donate a proton from its carboxyl group which results into negative charge.
All amino acids have amino groups \[\left( -N{{H}_{2}} \right)\] which is a basic and carboxyl group \[\left( { - COOH} \right)\] which is acidic. The acidic and basic nature of amino acid depends on the pH of the solution. As stated above, free amino acids can behave as cations and anions depending on the protonation state of their amino group, carboxyl group, and lateral chain ionizable group.
In acidic conditions, by donating an \[{{H}^{+}}ion\], the amino acid act as an acid while in basic condition, \[ - COOH\] group loses \[{{H}^{+}}ion\] to become \[CO{O^ - }\].
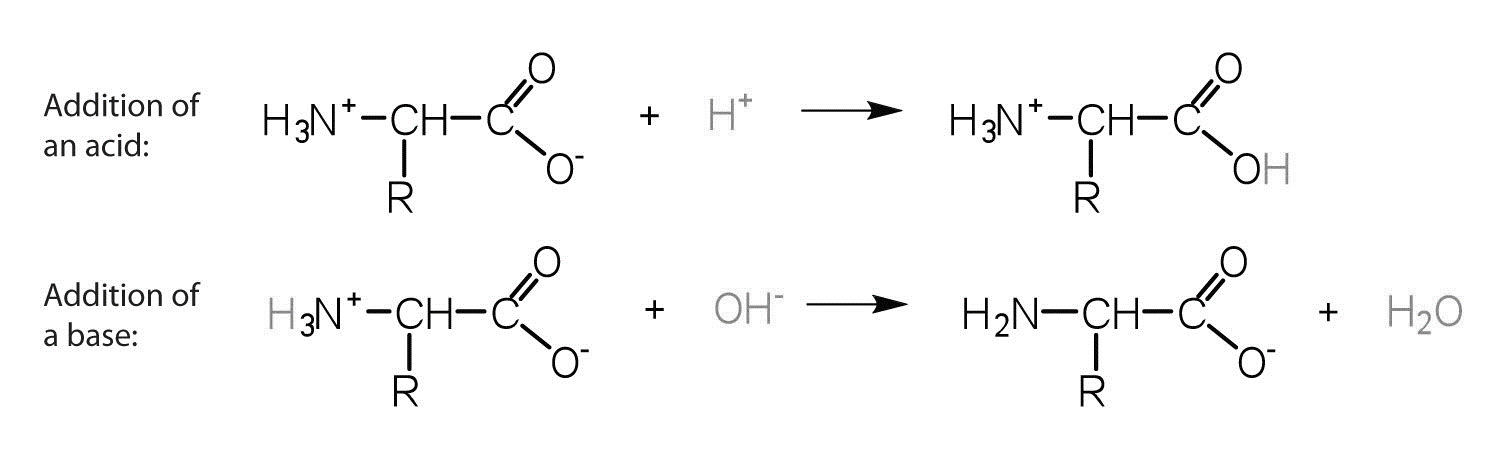
\[N{{H}_{2}}\] group receives \[{{H}^{+}}ion\] and therefore becomes \[N{{H}_{3}}^{+}\]. A chemical which behaves both acidic and basic is termed as amphoteric. At intermediate pH (the isoelectric point) both groups are ionized, and the molecules exist as a dipolar zwitterion.
Hence, from the above, it is concluded that the correct option is (B).
Let us see why other examples are incorrect:
As we can see the first option amino acid neither accept nor donates a proton
In the third option, an amino acid that acts as an acid donates protons from the carboxyl group and becomes a negative charge in alkaline conditions.
Whereas in the last option, both amino group and carboxyl group carry positive and negative charge respectively, that is both groups are ionized and molecules act as a zwitterion.
Note: Sometimes zwitterion is confused with isoelectric point (isoelectric point or pI of an amino acid is the pH at which amino acid has net charge zero).
Complete step-by-step answer:
Based on the definition of the acidic medium, in acidic conditions the amino acid acts as a base and accepts a proton at the amino group which results into positive charge whereas, in alkaline conditions, the amino acid acts as an acid donate a proton from its carboxyl group which results into negative charge.
All amino acids have amino groups \[\left( -N{{H}_{2}} \right)\] which is a basic and carboxyl group \[\left( { - COOH} \right)\] which is acidic. The acidic and basic nature of amino acid depends on the pH of the solution. As stated above, free amino acids can behave as cations and anions depending on the protonation state of their amino group, carboxyl group, and lateral chain ionizable group.
In acidic conditions, by donating an \[{{H}^{+}}ion\], the amino acid act as an acid while in basic condition, \[ - COOH\] group loses \[{{H}^{+}}ion\] to become \[CO{O^ - }\].

\[N{{H}_{2}}\] group receives \[{{H}^{+}}ion\] and therefore becomes \[N{{H}_{3}}^{+}\]. A chemical which behaves both acidic and basic is termed as amphoteric. At intermediate pH (the isoelectric point) both groups are ionized, and the molecules exist as a dipolar zwitterion.
Hence, from the above, it is concluded that the correct option is (B).
Let us see why other examples are incorrect:
As we can see the first option amino acid neither accept nor donates a proton
In the third option, an amino acid that acts as an acid donates protons from the carboxyl group and becomes a negative charge in alkaline conditions.
Whereas in the last option, both amino group and carboxyl group carry positive and negative charge respectively, that is both groups are ionized and molecules act as a zwitterion.
Note: Sometimes zwitterion is confused with isoelectric point (isoelectric point or pI of an amino acid is the pH at which amino acid has net charge zero).
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




