
In acidic and alkaline solution amino acid exists as a-
(A) Positive and negative ion respectively
(B) Negative and positive ion respectively
(C) Neutral in both medium
(D) None of these.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In acidic conditions, the amino acid acts as a base and accepts a proton at the amino group. In alkaline conditions, the amino acid acts as an acid and donates a proton from its carboxyl group.
Complete step by step solution:
-The structure of an amino acid allows it to act as both an acid and a base. This is because at a certain pH value (different for each amino acid) nearly all the amino acid molecules exist as zwitterions.
-If acid is added to a solution containing the zwitterion, the carboxylate group captures a hydrogen $\left(\mathrm{H}^{+}\right)$ ion and the amino acid becomes positively charged.
-If base is added, ion removal of the $\mathrm{H}^{+}$ ion from the amino group of the zwitterion produces a negatively charged amino acid.
In both circumstances, the amino acid acts to maintain the $\mathrm{pH}$ of the system- that is, to remove the added acid ( $\mathrm{H}^{+}$ ) or base ( $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$ ) from solution.
-Thus, in acidic medium, the amino acid has a positive charge, thus a positive charge. In a basic medium, it possesses a negative charge.
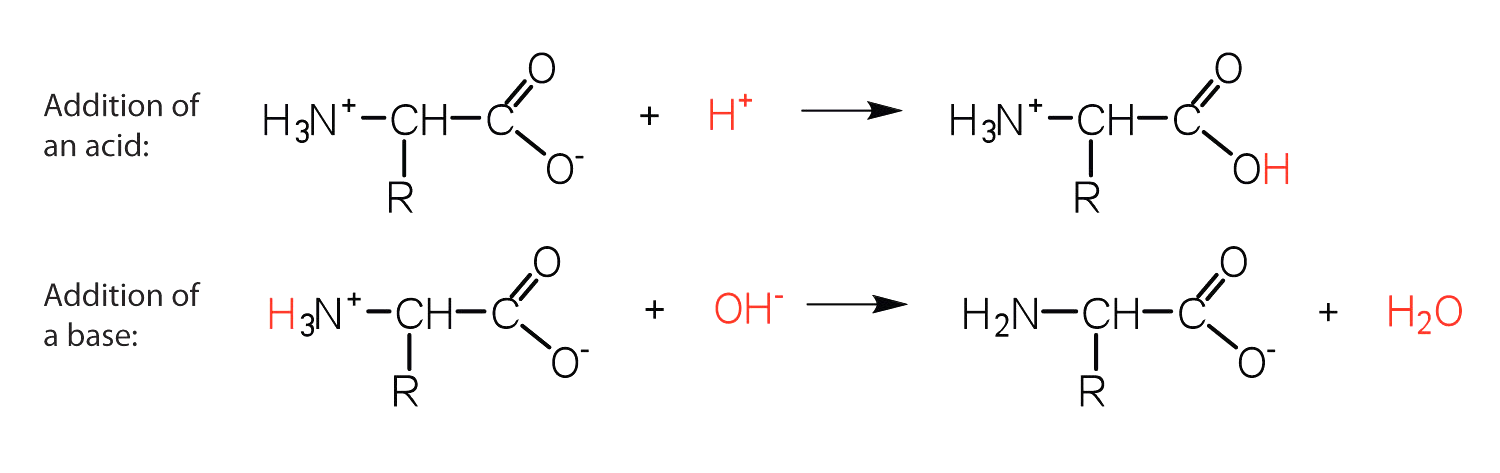
Clearly, the answer is A.
Note: Zwitterion is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively- and negatively-charged functional groups. In an acidic and basic medium, it possesses a charge and becomes ions.
Complete step by step solution:
-The structure of an amino acid allows it to act as both an acid and a base. This is because at a certain pH value (different for each amino acid) nearly all the amino acid molecules exist as zwitterions.
-If acid is added to a solution containing the zwitterion, the carboxylate group captures a hydrogen $\left(\mathrm{H}^{+}\right)$ ion and the amino acid becomes positively charged.
-If base is added, ion removal of the $\mathrm{H}^{+}$ ion from the amino group of the zwitterion produces a negatively charged amino acid.
In both circumstances, the amino acid acts to maintain the $\mathrm{pH}$ of the system- that is, to remove the added acid ( $\mathrm{H}^{+}$ ) or base ( $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$ ) from solution.
-Thus, in acidic medium, the amino acid has a positive charge, thus a positive charge. In a basic medium, it possesses a negative charge.

Clearly, the answer is A.
Note: Zwitterion is a molecule that contains an equal number of positively- and negatively-charged functional groups. In an acidic and basic medium, it possesses a charge and becomes ions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




