
In a monoclinic unit cell, the relation of sides and angles are, respectively:
(A) \[{{a = b }} \ne {{ c \quad and \quad \alpha = \beta = \gamma = 9}}{{{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]
(B) \[{{a }} \ne {{ b }} \ne {{ c \quad and \quad \alpha = \beta = \gamma = 9}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]
(C) \[{{a }} \ne {{ b }} \ne {{ c \quad and \quad \beta = \gamma = 9}}{{{0}}^{{o}}} \ne {{\alpha }}\]
(D) \[{{a}} \ne {{ b}} \ne {{ c \quad and \quad \alpha }} \ne {{\beta }} \ne {{\gamma }} \ne {{ 9}}{{{0}}^{{o}}}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Monoclinic crystal system has a restriction on two of the angles. It forms a rectangular prism having a base of parallelogram.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In crystallography, the crystal system is classified into seven groups on the basis of structures of the crystal. Symmetry here describes the relationship between the sides of the unit cell a, b and c and angles $\alpha$, $\beta$ and $\gamma$. These are- Triclinic, Monoclinic, Orthorhombic, Tetragonal, Trigonal, Hexagonal and Cubic.
As per question, in a monoclinic system, all three axes are unequal in length and any two axes are perpendicular to each other and the third is inclined between them forming an oblique angle \[{{\alpha }}\]. Rest of the two angles are \[{\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]each.
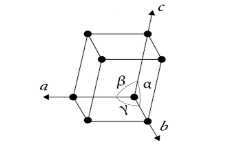
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Additional information: It is also known as sphenoidal because its general form is sphenoid. But it also exists in domatic and prismatic form. It depicts a 2-fold rotation axis and a single mirror plane.
Note: We can also understand it by the meaning of the term ‘monoclinic’. It means single inclination i.e., one axis of the unit cell is inclined at an angle greater than \[{\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]. They can perform perfect cleavage in at least one direction.
Complete step-by-step solution:
In crystallography, the crystal system is classified into seven groups on the basis of structures of the crystal. Symmetry here describes the relationship between the sides of the unit cell a, b and c and angles $\alpha$, $\beta$ and $\gamma$. These are- Triclinic, Monoclinic, Orthorhombic, Tetragonal, Trigonal, Hexagonal and Cubic.
As per question, in a monoclinic system, all three axes are unequal in length and any two axes are perpendicular to each other and the third is inclined between them forming an oblique angle \[{{\alpha }}\]. Rest of the two angles are \[{\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]each.

Hence, the correct option is (C).
Additional information: It is also known as sphenoidal because its general form is sphenoid. But it also exists in domatic and prismatic form. It depicts a 2-fold rotation axis and a single mirror plane.
Note: We can also understand it by the meaning of the term ‘monoclinic’. It means single inclination i.e., one axis of the unit cell is inclined at an angle greater than \[{\text{9}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]. They can perform perfect cleavage in at least one direction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




