
Images are inverted in a pinhole camera because:
(A) Light travels in a straight line
(B) Images are always inverted
(C) Images get inverted when light travel through a hole
(D) There is no specific reason
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint An image formed by reflection can be real or virtual. A real image occurs when light rays actually intersect at the image, and become inverted, or turned upside down. A virtual image occurs when light rays do not actually meet at the image but appear to be met.
Complete step by step answer:
The light rays that come from the object get reflected from the plane mirror and reach our eyes. As they touch eyes our brain feels that the reflected ray is coming from inside the mirror. That is why the image of the object seems to be laterally inverted.
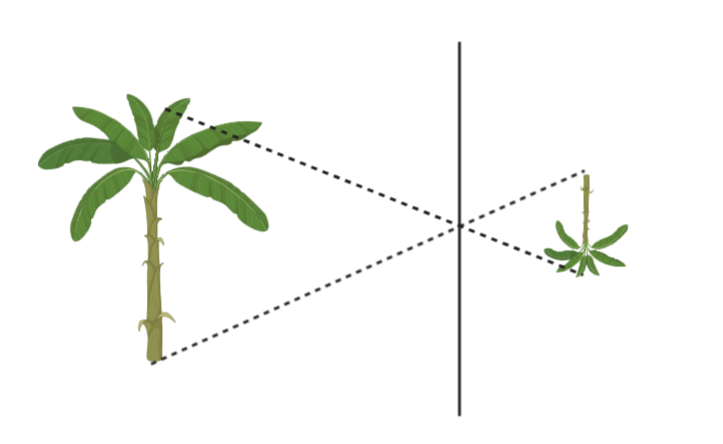
Such upside down inversion also occurs when you see yourself in a spoon on the concave side.
This phenomenon occurs obeying laws of reflection and laws of rectilinear propagation; which is light travels in a straight line.
Hence option A is correct.
Note Magnifying glasses are made of convex lenses. A convex lens can make objects look larger because it disperses the light. When objects are magnified, they are within the focal length of the magnifying glass. The focal length is defined as the distance between the center of the lens and its focus, the point where an object can be viewed clearly through a lens.
Complete step by step answer:
The light rays that come from the object get reflected from the plane mirror and reach our eyes. As they touch eyes our brain feels that the reflected ray is coming from inside the mirror. That is why the image of the object seems to be laterally inverted.

Such upside down inversion also occurs when you see yourself in a spoon on the concave side.
This phenomenon occurs obeying laws of reflection and laws of rectilinear propagation; which is light travels in a straight line.
Hence option A is correct.
Note Magnifying glasses are made of convex lenses. A convex lens can make objects look larger because it disperses the light. When objects are magnified, they are within the focal length of the magnifying glass. The focal length is defined as the distance between the center of the lens and its focus, the point where an object can be viewed clearly through a lens.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

CBSE Class 10 Sanskrit Set 4 52 Question Paper 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




