
If work done by string on block A is W. shown in the given arrangement, then the work done by the string on block B is
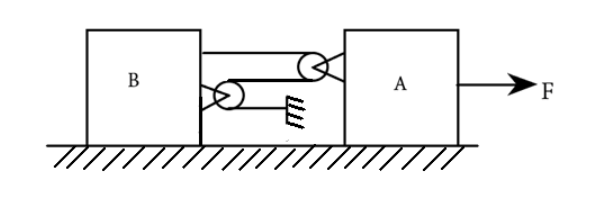
(A) \[ - W\]
(B) \[\dfrac{{ - 2W}}{3}\]
(C) \[\dfrac{{2W}}{3}\]
(D) \[\dfrac{{ - 3W}}{2}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The total length of the string is constant. The distance increase from the fixed point of one will result in a corresponding decrease in the other.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[W = Fd\] where \[W\] is the work done by a force on a body, \[F\] is the force acting on a body and \[d\] is the distance moved by the body while the body acts on it.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
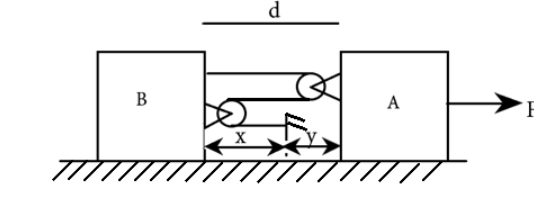
Let the distance between the two blocks be \[d\]. The let the distance of the left block to the fixed point be \[x\], and the distance of the right block to fix point be \[y\] such that their sum is the distance from each other
Hence, if the block A is pulled, then the distance \[y\] changes. But since the total length of the string is constant, the distance \[x\] must reduce correspondingly.
Then \[\Delta y = - \Delta x\]
Now, since it’s the same string, the tensions in each line of the string are all equal to say \[T\]. This means that the total tension acting on block A will be \[2T\] (because the lines connected to A are 2).
Similarity, the tension on the block B will be \[3T\]
Work done on an object is \[W = Fd\] where \[F\] is the force acting on a body and \[d\] is the distance moved by the body while the body acts on it.
Work done on A is
\[W = 2T \times \Delta y\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta y = \dfrac{W}{{2T}}\]
Then the work done on B would be
\[W = 3T \times \Delta x = 3T \times - \Delta y\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3T \times - \left( {\dfrac{W}{{2T}}} \right) = - \dfrac{{3W}}{2}\]
Hence the correct option is C
Note: For clarity, we can prove that \[\Delta y = - \Delta x\] as follows.
The distance between the blocks is the sum of \[x\] and \[y\] as in
\[d = x + y\]
By finding the derivative (which gives the instantaneous change of the quantities), we get
\[0 = dx + dy\] (since the length of the string is constant, the distance between the blocks cannot increase)
\[dy= - dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta y = - \Delta x\]
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[W = Fd\] where \[W\] is the work done by a force on a body, \[F\] is the force acting on a body and \[d\] is the distance moved by the body while the body acts on it.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:

Let the distance between the two blocks be \[d\]. The let the distance of the left block to the fixed point be \[x\], and the distance of the right block to fix point be \[y\] such that their sum is the distance from each other
Hence, if the block A is pulled, then the distance \[y\] changes. But since the total length of the string is constant, the distance \[x\] must reduce correspondingly.
Then \[\Delta y = - \Delta x\]
Now, since it’s the same string, the tensions in each line of the string are all equal to say \[T\]. This means that the total tension acting on block A will be \[2T\] (because the lines connected to A are 2).
Similarity, the tension on the block B will be \[3T\]
Work done on an object is \[W = Fd\] where \[F\] is the force acting on a body and \[d\] is the distance moved by the body while the body acts on it.
Work done on A is
\[W = 2T \times \Delta y\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta y = \dfrac{W}{{2T}}\]
Then the work done on B would be
\[W = 3T \times \Delta x = 3T \times - \Delta y\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3T \times - \left( {\dfrac{W}{{2T}}} \right) = - \dfrac{{3W}}{2}\]
Hence the correct option is C
Note: For clarity, we can prove that \[\Delta y = - \Delta x\] as follows.
The distance between the blocks is the sum of \[x\] and \[y\] as in
\[d = x + y\]
By finding the derivative (which gives the instantaneous change of the quantities), we get
\[0 = dx + dy\] (since the length of the string is constant, the distance between the blocks cannot increase)
\[dy= - dx\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta y = - \Delta x\]
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Law of Motion (2025-26)

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




