
If the median of $\Delta ABC$ through $A$ is perpendicular to $AB$, then
A. $\tan A+\tan B=0$
B. $2\tan A+\tan B=0$
C. $\tan A+2\tan B=0$
D. None of these.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will first draw the diagram of triangle $ABC$ with median through $A$ perpendicular to $AB$ and a line $CN$ perpendicular to $BA$. Then by taking triangle $\Delta BCN$ and other triangle properties we will derive the value of $\tan A$ and $\tan B$ and form the relation.
Formula Used: Trigonometric ratio of tangent is $\tan A=\dfrac{P}{B}$, where $P$ is perpendicular or altitude and $B$ is base.
Complete step by step solution: We are given a triangle $ABC$ in which its median through$A$ is perpendicular to $AB$. We will draw a triangle $ABC$ with given data. We will also draw $CN$ perpendicular to $BA$.
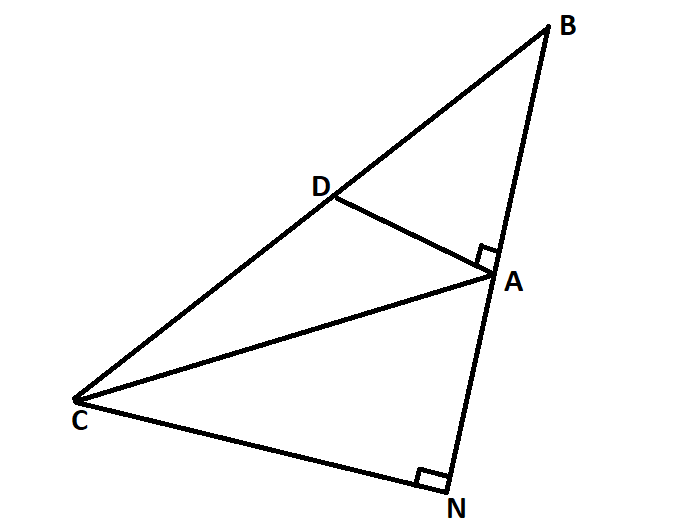
As $A$ is perpendicular to $AB$, $\angle DAB={{90}^{0}}$ and $BD=DC$.
Now in triangle $\Delta BCN$ we have,
$DA=\dfrac{1}{2}CN$ and $AB=AN$.
We will now calculate the angle $\tan A$.
Now $\tan A$ can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& \tan A=\tan (\pi -\angle CAN) \\
& =-\tan \angle CAN
\end{align}$
Using formula of trigonometric ratio of tangent,
$-\tan \angle CAN=-\dfrac{CN}{AN}$
So value of $\tan A$ will be,
$\tan A=-\dfrac{2AD}{AB}$…. (i)
If we calculate $\tan B$,
$\tan B=\dfrac{AD}{AB}$……(ii)
Now we will substitute equation (ii) in equation (i),
$\tan A=-2\tan B$
We will now simplify,
$\tan A+2\tan B=0$
When the median of a triangle $\Delta ABC$ through $A$ is perpendicular to $AB$ then $\tan A+2\tan B=0$. Hence the correct option is (C).
Note: The median of a triangle can be defined as a line segment from the vertex of a triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side of the triangle bisecting it into equal proportions.
A triangle has three medians from each of the vertices and all the three medians intersect each other at the center of the triangle which is termed as the centroid of a triangle.
Formula Used: Trigonometric ratio of tangent is $\tan A=\dfrac{P}{B}$, where $P$ is perpendicular or altitude and $B$ is base.
Complete step by step solution: We are given a triangle $ABC$ in which its median through$A$ is perpendicular to $AB$. We will draw a triangle $ABC$ with given data. We will also draw $CN$ perpendicular to $BA$.

As $A$ is perpendicular to $AB$, $\angle DAB={{90}^{0}}$ and $BD=DC$.
Now in triangle $\Delta BCN$ we have,
$DA=\dfrac{1}{2}CN$ and $AB=AN$.
We will now calculate the angle $\tan A$.
Now $\tan A$ can be written as,
$\begin{align}
& \tan A=\tan (\pi -\angle CAN) \\
& =-\tan \angle CAN
\end{align}$
Using formula of trigonometric ratio of tangent,
$-\tan \angle CAN=-\dfrac{CN}{AN}$
So value of $\tan A$ will be,
$\tan A=-\dfrac{2AD}{AB}$…. (i)
If we calculate $\tan B$,
$\tan B=\dfrac{AD}{AB}$……(ii)
Now we will substitute equation (ii) in equation (i),
$\tan A=-2\tan B$
We will now simplify,
$\tan A+2\tan B=0$
When the median of a triangle $\Delta ABC$ through $A$ is perpendicular to $AB$ then $\tan A+2\tan B=0$. Hence the correct option is (C).
Note: The median of a triangle can be defined as a line segment from the vertex of a triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side of the triangle bisecting it into equal proportions.
A triangle has three medians from each of the vertices and all the three medians intersect each other at the center of the triangle which is termed as the centroid of a triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




