
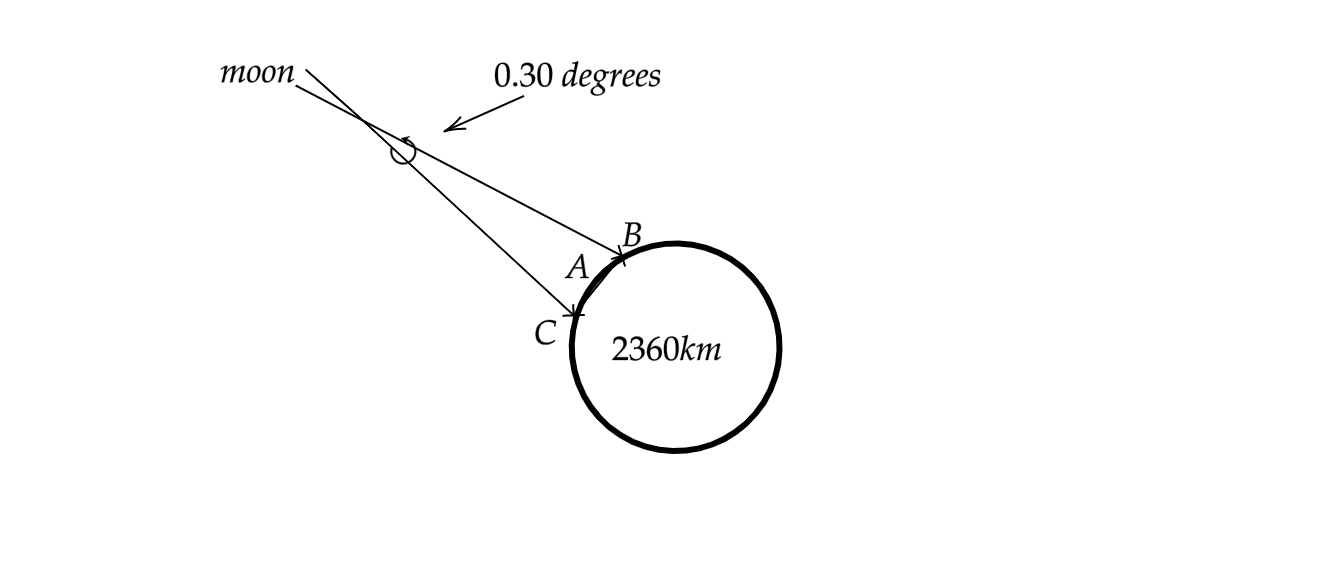
If the angular distance between the stars turns out to be approximately \[1100\] arc seconds, or \[0.30\] degrees. The moon appears to shift \[0.3\] degrees when we observe it from two vantage points \[2360km\] apart, then find the distance of the moon from the surface of the earth. Given the angular diameter of the moon is \[0.5\] degrees.
A) \[450642km\]
B) \[450392km\]
C) \[325684km\]
D) \[480264km\]
Answer
241.5k+ views
Hint: The phenomenon mentioned in the given question is parallax. Parallax is the apparent angular displacement of a celestial body due to its being observed from the surface of the earth instead of the centre of the earth. Parallax also arises due to a change in viewpoint caused by relative motion.
Complete step by step solution:
From the given question, we can say that the shift in the angular distance of the moon when viewed from two different vantage points is \[0.3\] degrees. Let this angular shift be \[\theta \].
Since angular measurements are usually made in radians, we must convert the given angular distance into radians.
\[\begin{align}
& \theta =0.3{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =0.3\times \dfrac{\pi }{180}rad \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{600}rad \\
\end{align}\]
Using the properties of circles and arcs, we can say that arc length in a circle is equal to the product of the radius and the angle subtended by the arc.
Since the distance between the moon and the earth is more than the radius of the earth, the distance between the moon and the earth, DA, is roughly equal to DC.
Now for the arc BAC, we can say that arc length will be equal to the product of the radius, DC, and the angle subtended at DC.
Mathematically, we can say that \[d=D\times \theta \] where \[d\] is the arc length.
Substituting the values, we get
\[\begin{align}
& d=D\times \theta \\
& \Rightarrow 2360=D\times \dfrac{\pi }{600}rad \\
& \Rightarrow D=\dfrac{2360\times 600}{\pi }=450642km \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:An alternative method to approach this question is using the definition of parallax. The Parallax formula states that the distance to a star is equal to the distance between the vantage points divided by the parallax angle, where the parallax angle is measured in arcseconds.
Complete step by step solution:
From the given question, we can say that the shift in the angular distance of the moon when viewed from two different vantage points is \[0.3\] degrees. Let this angular shift be \[\theta \].
Since angular measurements are usually made in radians, we must convert the given angular distance into radians.
\[\begin{align}
& \theta =0.3{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =0.3\times \dfrac{\pi }{180}rad \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{600}rad \\
\end{align}\]
Using the properties of circles and arcs, we can say that arc length in a circle is equal to the product of the radius and the angle subtended by the arc.

Since the distance between the moon and the earth is more than the radius of the earth, the distance between the moon and the earth, DA, is roughly equal to DC.
Now for the arc BAC, we can say that arc length will be equal to the product of the radius, DC, and the angle subtended at DC.
Mathematically, we can say that \[d=D\times \theta \] where \[d\] is the arc length.
Substituting the values, we get
\[\begin{align}
& d=D\times \theta \\
& \Rightarrow 2360=D\times \dfrac{\pi }{600}rad \\
& \Rightarrow D=\dfrac{2360\times 600}{\pi }=450642km \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:An alternative method to approach this question is using the definition of parallax. The Parallax formula states that the distance to a star is equal to the distance between the vantage points divided by the parallax angle, where the parallax angle is measured in arcseconds.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




