
If d is the distance between the source of sound and reflector \[{{\text{t}}_{\text{1}}}\] , \[{{\text{t}}_{\text{2}}}\] are times at which echoes are heard, the expression for determination of velocity of sound in air by echo method is:
(A) \[\dfrac{{{\text{2d}}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}}\]
(B) \[\dfrac{{{\text{2d}}}}{{{t_1} - {t_2}}}\]
(C) \[\dfrac{{{\text{4d}}}}{{{t_1} - {t_2}}}\]
(D) \[\dfrac{{{\text{2d}}}}{{{t_1} + {t_2}}}\]
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: We will find the total distance travelled and total time taken by the echo to reach the source. Then, we will substitute it in the formula for finding the speed of any object.
Complete step by step answer
An echo is the repetition of sound waves, after reflection from any obstacle.
We are already familiar with the formula for calculating the speed, i.e.,
Speed \[{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{time}}}}\]…………………………………(i)
We use the Echo method to find the large distances of objects like Hill or a mountain.
Now, let’s consider a man standing at a point A x meters away from a hill situated at point B as shown in the figure.
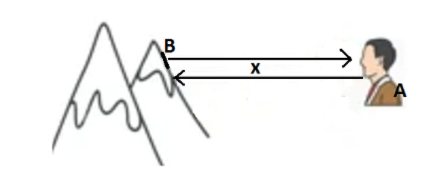
So, the sound wave will travel from point A to point B. Here it will reflect back by touching the mountain and again travel back from point B to A. Suppose that \[{{\text{t}}_{\text{1}}}\] is the time at which the man produces the sound and \[{{\text{t}}_{\text{2}}}\] be the time at which the man heard the echo of the sound produced by him.
This means the total time taken for the echo to be heard will be, \[t = {t_2} - {t_1}\]
Now, the total distance travelled by the sound wave is, \[{\text{AB + BA = x + x = 2x}}\]
We will apply the formula of speed given in Eq.(i),
speed\[{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{2x}}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}}\](on substituting the values of distance and time)
In the question, the total distance travelled by the wave is given as ‘d’. Substitute this value in place of x.
Speed\[{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{2d}}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}}\]
This is the speed of the sound wave after an echo.
So option (a.) is the correct option.
Note Since we are calculating the distance for an echo, it is important to consider both the distances (i.e., distance travelled by the sound wave before and after the reflection). Forgetting even one might result in getting a wrong answer.
Complete step by step answer
An echo is the repetition of sound waves, after reflection from any obstacle.
We are already familiar with the formula for calculating the speed, i.e.,
Speed \[{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{time}}}}\]…………………………………(i)
We use the Echo method to find the large distances of objects like Hill or a mountain.
Now, let’s consider a man standing at a point A x meters away from a hill situated at point B as shown in the figure.

So, the sound wave will travel from point A to point B. Here it will reflect back by touching the mountain and again travel back from point B to A. Suppose that \[{{\text{t}}_{\text{1}}}\] is the time at which the man produces the sound and \[{{\text{t}}_{\text{2}}}\] be the time at which the man heard the echo of the sound produced by him.
This means the total time taken for the echo to be heard will be, \[t = {t_2} - {t_1}\]
Now, the total distance travelled by the sound wave is, \[{\text{AB + BA = x + x = 2x}}\]
We will apply the formula of speed given in Eq.(i),
speed\[{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{2x}}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}}\](on substituting the values of distance and time)
In the question, the total distance travelled by the wave is given as ‘d’. Substitute this value in place of x.
Speed\[{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{2d}}}}{{{t_2} - {t_1}}}\]
This is the speed of the sound wave after an echo.
So option (a.) is the correct option.
Note Since we are calculating the distance for an echo, it is important to consider both the distances (i.e., distance travelled by the sound wave before and after the reflection). Forgetting even one might result in getting a wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




