
Grignard reagent adds to
A.
B.
C.
D. All of the above
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Grignard reagent is a chemical compound formed by reaction of haloalkane to magnesium present in a flask containing diethyl ether. Diethyl ether act as solvent in the reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The general formula of Grignard reagent is RMgX where X denotes the halide group and R denotes the alkyl group.
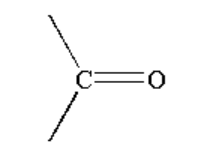
A. The reaction taking place between Grignard reagent and the ketone containing compound is shown below.
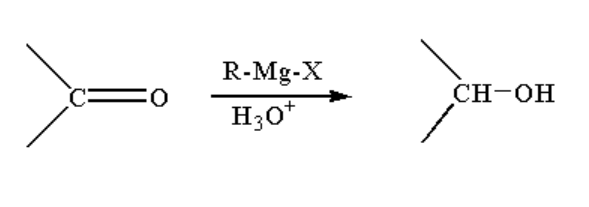
Image: Reaction of Grignard reagent with ketone
When a ketone containing compound is reacted with Grignard reagent it forms a complex which on hydrolysis forms alcohol.
Alcohol is a compound where a carbon atom is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The hydroxyl group or alcohol is represented by \[R - OH\].
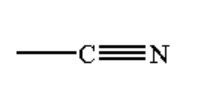
B. The reaction taking place between the Grignard reagent and nitrile-containing compound is shown below.
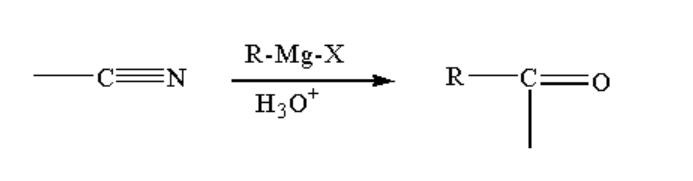
Image: Reaction of the Grignard reagent with nitrile.
When a nitrile-containing compound is reacted with Grignard reagent it forms a complex which on hydrolysis gives ketone.
Ketone is a compound where a carbon atom is bonded to one oxygen atom by a double bond and two alkyl groups by a single bond. The general formula of ketone is R-CO-R.
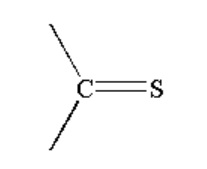
C. The reaction taking place between Grignard reagent and a compound containing \[ - C = S\] is shown below.
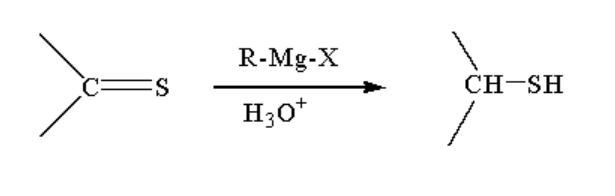
Image: Reaction of Grignard reagent with \[ - C = S\]
When a compound containing \[ - C = S\]is reacted with Grignard reagent it first forms a complex which on hydrolysis gives the thiol compound.
A thiol is a functional group where sulphur is bonded to hydrogen and an alkyl group by a single bond. The general formula of thiol is R-SH.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: A Grignard reagent act as a very strong nucleophile and act like carbonyl compounds with an electrophile.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The general formula of Grignard reagent is RMgX where X denotes the halide group and R denotes the alkyl group.
A. The reaction taking place between Grignard reagent and the ketone containing compound is shown below.
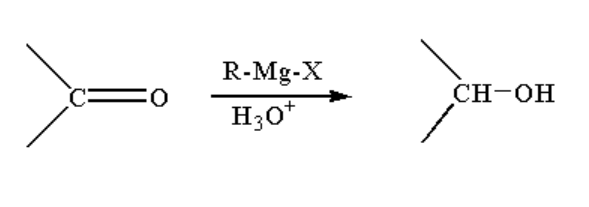
Image: Reaction of Grignard reagent with ketone
When a ketone containing compound is reacted with Grignard reagent it forms a complex which on hydrolysis forms alcohol.
Alcohol is a compound where a carbon atom is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The hydroxyl group or alcohol is represented by \[R - OH\].
B. The reaction taking place between the Grignard reagent and nitrile-containing compound is shown below.
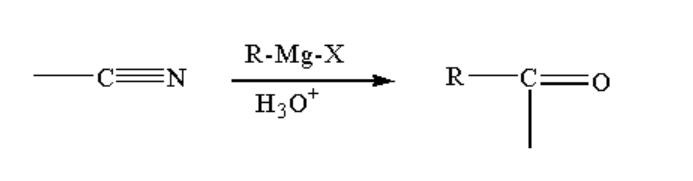
Image: Reaction of the Grignard reagent with nitrile.
When a nitrile-containing compound is reacted with Grignard reagent it forms a complex which on hydrolysis gives ketone.
Ketone is a compound where a carbon atom is bonded to one oxygen atom by a double bond and two alkyl groups by a single bond. The general formula of ketone is R-CO-R.
C. The reaction taking place between Grignard reagent and a compound containing \[ - C = S\] is shown below.
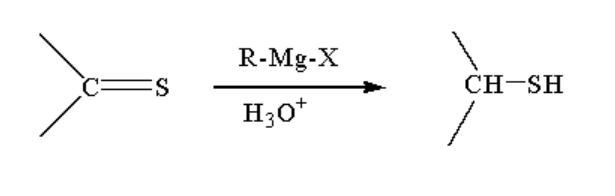
Image: Reaction of Grignard reagent with \[ - C = S\]
When a compound containing \[ - C = S\]is reacted with Grignard reagent it first forms a complex which on hydrolysis gives the thiol compound.
A thiol is a functional group where sulphur is bonded to hydrogen and an alkyl group by a single bond. The general formula of thiol is R-SH.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: A Grignard reagent act as a very strong nucleophile and act like carbonyl compounds with an electrophile.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




