
Gold (atomic radius = 0.144 nm) crystallises in a face-centred unit cell. What is the length of a side of the cell?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: FCC or face-centred cubic structure has atoms at each of the corners as well as at each of the faces of the cubical cell. These atoms that are arranged in the cell are known as lattice points.
Complete step by step solution:
An arrangement of atoms in crystals in which the atomic centres are disposed in space in such a way that one atom is located at each of the corners of the cube and one at the centre of each face is known as the face-centred unit cell. It is relatively "tightly" packed (atomic packing factor = 0.74).
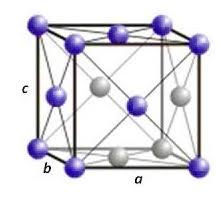
Now, in the question it is given that the atomic radius, r of gold is 0.144 nm. And the type of cubic cell is FCC. Therefore, let the length of the side of the cell be 'a'.
Thus, the diagonal of the side is given by,
$Diagonal \,of\, the\, side = 4r = a\sqrt {2}$
$\implies\,side\,length\,of \,cell, a \dfrac {4r}{\sqrt {2}} = 2\sqrt {2}r$
$\implies a = 2 \times 1.414 \times 0.144 \times {10}^{-9}$
$\implies a = 0.4073 \times {10}^{-9}m = 0.4073 nm$
Therefore, the length of the side of the cell is 0.4073 nm.
Note: It is important to note the structure of the cubic lattice before calculating the radius and side length of the cell. Each lattice has a different sort of relation between the radius and the side length.
Complete step by step solution:
An arrangement of atoms in crystals in which the atomic centres are disposed in space in such a way that one atom is located at each of the corners of the cube and one at the centre of each face is known as the face-centred unit cell. It is relatively "tightly" packed (atomic packing factor = 0.74).

Now, in the question it is given that the atomic radius, r of gold is 0.144 nm. And the type of cubic cell is FCC. Therefore, let the length of the side of the cell be 'a'.
Thus, the diagonal of the side is given by,
$Diagonal \,of\, the\, side = 4r = a\sqrt {2}$
$\implies\,side\,length\,of \,cell, a \dfrac {4r}{\sqrt {2}} = 2\sqrt {2}r$
$\implies a = 2 \times 1.414 \times 0.144 \times {10}^{-9}$
$\implies a = 0.4073 \times {10}^{-9}m = 0.4073 nm$
Therefore, the length of the side of the cell is 0.4073 nm.
Note: It is important to note the structure of the cubic lattice before calculating the radius and side length of the cell. Each lattice has a different sort of relation between the radius and the side length.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




