
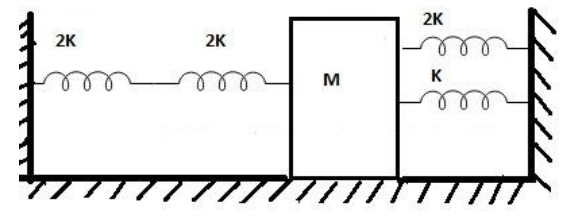
Four massless springs whose force constants are 2k, 2k, k and 2k respectively are attached to a mass M kept on a frictionless plane as shown in the figure. If the mass M is displaced in the horizontal direction, then the frequency of the system is:
A) $\dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{k}{{4M}}} $
B) $\dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{4k}}{M}} $
C) $\dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{k}{{7M}}} $
D) $\dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{7k}}{{7M}}} $
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Formula for frequency is:
$\dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{{LC}}} $ (L is the inductor, C is the capacitor)
As per electrical and mechanical analogy conversion, in force current analogy M is the capacitor (C) and k is the reciprocal of the inductor (1/L).
Let’s find the value of k using series and parallel connections (using 1/L = k, in series connections are added with their direct connections and the parallel connection have reciprocal addition).
Complete step by step solution:
As we are provided with an inductor and capacitor in the system then we will add the reciprocal of the inductor for the series connection.
$K = {K_1} + {K_2}$
First, we will do the calculation for series connection:
$
\Rightarrow {K_1} = \dfrac{1}{{2k}} + \dfrac{1}{{2k}} \\
\Rightarrow {K_1} = \dfrac{{2k \times 2k}}{{2k + 2k}}
$ (Taking LCM)
$ \Rightarrow {K_1} = \dfrac{{2k}}{{2k}} = 1k$
Now, we will calculate for the springs in parallel:
$
\Rightarrow {K_2} = \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{1}{{2k}}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{1}{k}}} \\
\Rightarrow {K_2} = 2k + k = 3k$ (in parallel connection we have to take the reciprocal of the spring constants)
Total value of K comes out to be:
$
\Rightarrow K = {K_1} + {K_2} \\
\Rightarrow K = k + 3k = 4k $
From the equation of frequency:
$
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{{M\dfrac{1}{K}}}} \\
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{K}{M}} $ (We have substituted the value of LC as per formula of frequency)
$ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{4k}}{M}} $ (We have substituted the values M and K).
Hence, Option B is correct.
Note: In the question above we have used electrical to mechanical equivalent system of force current, where current is acting as the force in a mechanical system, mass as capacitor, frictional coefficient as reciprocal of R resistor, spring constant as reciprocal of L inductor, displacement as magnetic flux and velocity as voltage.
$\dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{{LC}}} $ (L is the inductor, C is the capacitor)
As per electrical and mechanical analogy conversion, in force current analogy M is the capacitor (C) and k is the reciprocal of the inductor (1/L).
Let’s find the value of k using series and parallel connections (using 1/L = k, in series connections are added with their direct connections and the parallel connection have reciprocal addition).
Complete step by step solution:
As we are provided with an inductor and capacitor in the system then we will add the reciprocal of the inductor for the series connection.
$K = {K_1} + {K_2}$
First, we will do the calculation for series connection:
$
\Rightarrow {K_1} = \dfrac{1}{{2k}} + \dfrac{1}{{2k}} \\
\Rightarrow {K_1} = \dfrac{{2k \times 2k}}{{2k + 2k}}
$ (Taking LCM)
$ \Rightarrow {K_1} = \dfrac{{2k}}{{2k}} = 1k$
Now, we will calculate for the springs in parallel:
$
\Rightarrow {K_2} = \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{1}{{2k}}}} + \dfrac{1}{{\dfrac{1}{k}}} \\
\Rightarrow {K_2} = 2k + k = 3k$ (in parallel connection we have to take the reciprocal of the spring constants)
Total value of K comes out to be:
$
\Rightarrow K = {K_1} + {K_2} \\
\Rightarrow K = k + 3k = 4k $
From the equation of frequency:
$
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{{M\dfrac{1}{K}}}} \\
\Rightarrow f = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{K}{M}} $ (We have substituted the value of LC as per formula of frequency)
$ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt {\dfrac{{4k}}{M}} $ (We have substituted the values M and K).
Hence, Option B is correct.
Note: In the question above we have used electrical to mechanical equivalent system of force current, where current is acting as the force in a mechanical system, mass as capacitor, frictional coefficient as reciprocal of R resistor, spring constant as reciprocal of L inductor, displacement as magnetic flux and velocity as voltage.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




