
Formula for the following compound Tin (IV) oxide is $SnO_2$:
(A) True
(B) False
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We should know that Tin dioxide is a tin oxide compound which consists of Tin (IV) covalently bound to two oxygen atoms. The chemical formula of Tin (IV) oxide, will further be understood from the structure of Tin (IV) oxide.
Complete step by step answer:
> Tin (IV) oxide is also known as Stannic Oxide. We know that the symbol of Tin is Sn.
Here is the structure of Tin (IV) oxide, for better understanding of the formula:
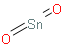
> The Tin (IV) crystallizes with the rutile structure. As such the Tin atoms are 6 coordinate and the oxygen atoms are 3 coordinate. ${\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is usually regarded as an oxygen deficient n type semiconductor. Hydrous forms of ${\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ has been described as stannic acid.
> The bond formation of Tin and the two oxygen atoms are known as just polar covalent. This is because of the electronegativity difference between Tin (1.8) and that of Oxygen (3.5). So, with a difference of only 1.7 in electronegativity, ionic bonds cannot be formed.
> The chemical formula of Tin (IV) oxide is ${\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Therefore, the answer to the question that the formula for the following compound Tin (IV) oxide is True.
So Option A is the correct answer to the mentioned question.
- Tin (IV) oxide appears as white or off white crystalline solid or powder. It is insoluble in water and soluble in concentrated sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid. It occurs in nature as a mineral cassiterite. It is used as a catalyst in putty as a polishing powder for steel and glass, in ceramic places and colours.
Note: As mentioned earlier ${\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is insoluble in water. But it is also amphoteric in nature. By amphoteric we mean, it dissolves in acids and bases. It is also diamagnetic in nature.
Complete step by step answer:
> Tin (IV) oxide is also known as Stannic Oxide. We know that the symbol of Tin is Sn.
Here is the structure of Tin (IV) oxide, for better understanding of the formula:
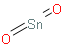
> The Tin (IV) crystallizes with the rutile structure. As such the Tin atoms are 6 coordinate and the oxygen atoms are 3 coordinate. ${\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is usually regarded as an oxygen deficient n type semiconductor. Hydrous forms of ${\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ has been described as stannic acid.
> The bond formation of Tin and the two oxygen atoms are known as just polar covalent. This is because of the electronegativity difference between Tin (1.8) and that of Oxygen (3.5). So, with a difference of only 1.7 in electronegativity, ionic bonds cannot be formed.
> The chemical formula of Tin (IV) oxide is ${\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Therefore, the answer to the question that the formula for the following compound Tin (IV) oxide is True.
So Option A is the correct answer to the mentioned question.
- Tin (IV) oxide appears as white or off white crystalline solid or powder. It is insoluble in water and soluble in concentrated sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid. It occurs in nature as a mineral cassiterite. It is used as a catalyst in putty as a polishing powder for steel and glass, in ceramic places and colours.
Note: As mentioned earlier ${\text{Sn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is insoluble in water. But it is also amphoteric in nature. By amphoteric we mean, it dissolves in acids and bases. It is also diamagnetic in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




