
How many equivalents of CH3MgBr are required to make 2-methylpropan-2-ol from ethyl ethanoate?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: To convert ethyl ethanoate into 2-methylpropan-2-ol, two extra C-C bonds must be created. Therefore, a Grignard’s reagent such as \[C{H_3}MgBr\] is used.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this question, we are asked the number of equivalents\[C{H_3}MgBr\]required to convert ethyl ethanoate (more commonly known as ethyl acetate) into 2-methylpropan-2-ol. So, let’s look at the conversion itself first.

Image: Conversion of ethyl acetate to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
It can be seen above that 2-methylpropan-2-ol has three carbon atoms attached to the blue-coloured carbon atom while ethyl acetate has only one. Thus, we must use a reagent that can construct C-C bonds in esters. Grignard’s reagents are fit for this purpose. Also, notice that the groups attached to the blue-coloured carbon atom are methyl groups (\[ - C{H_3}\]). So, we require a Grignard’s reagent that can supply methyl groups as well as form C-C bonds in esters. Therefore, methyl magnesium bromide (\[C{H_3}MgBr\]) is used as Grignard’s reagent here.
Grignard’s reagents have the general formula \[R - MgBr\]in which the R group may be a methyl group, ethyl group, propyl group etc. Since magnesium is a metal, it possesses a partial positive charge in Grignard’s reagent. To balance this partial positive charge, the R group carries a partial negative charge and thus, behaves like a nucleophile (\[{R^ - }\]).
When ethyl acetate reacts with one equivalent \[C{H_3}MgBr\], the \[C{H_3}\] group acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electron-deficient carbonyl carbon. The \[ - OC{H_2}C{H_3}\]group leaves and the product formed is acetone.
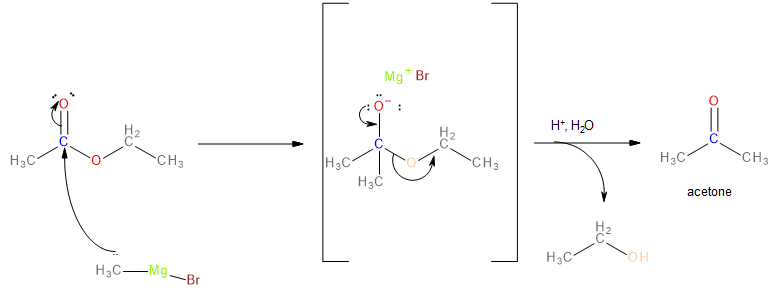
Image: Reaction of Ethyl Acetate with equation (1) with CH3MgBr
Acetone must be reacted with another equivalent\[C{H_3}MgBr\]to obtain 2-methylpropan-2-ol. The reaction proceeds comparably as shown earlier except, unlike the previous reaction, acid hydrolysis yields alcohol instead of a ketone.
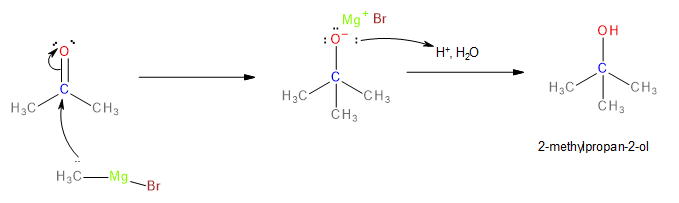
Image: Formation of 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Thus, to convert ethyl ethanoate to 2-methylpropan-2-ol, two equivalents \[C{H_3}MgBr\]must be used
Note: The base catalysis of an ester is a reaction irreversible as the end products are alcohol and carboxylate ion which is resonance stabilised and thus stable and does not react with alcohol.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this question, we are asked the number of equivalents\[C{H_3}MgBr\]required to convert ethyl ethanoate (more commonly known as ethyl acetate) into 2-methylpropan-2-ol. So, let’s look at the conversion itself first.

Image: Conversion of ethyl acetate to 2-methylpropan-2-ol
It can be seen above that 2-methylpropan-2-ol has three carbon atoms attached to the blue-coloured carbon atom while ethyl acetate has only one. Thus, we must use a reagent that can construct C-C bonds in esters. Grignard’s reagents are fit for this purpose. Also, notice that the groups attached to the blue-coloured carbon atom are methyl groups (\[ - C{H_3}\]). So, we require a Grignard’s reagent that can supply methyl groups as well as form C-C bonds in esters. Therefore, methyl magnesium bromide (\[C{H_3}MgBr\]) is used as Grignard’s reagent here.
Grignard’s reagents have the general formula \[R - MgBr\]in which the R group may be a methyl group, ethyl group, propyl group etc. Since magnesium is a metal, it possesses a partial positive charge in Grignard’s reagent. To balance this partial positive charge, the R group carries a partial negative charge and thus, behaves like a nucleophile (\[{R^ - }\]).
When ethyl acetate reacts with one equivalent \[C{H_3}MgBr\], the \[C{H_3}\] group acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electron-deficient carbonyl carbon. The \[ - OC{H_2}C{H_3}\]group leaves and the product formed is acetone.

Image: Reaction of Ethyl Acetate with equation (1) with CH3MgBr
Acetone must be reacted with another equivalent\[C{H_3}MgBr\]to obtain 2-methylpropan-2-ol. The reaction proceeds comparably as shown earlier except, unlike the previous reaction, acid hydrolysis yields alcohol instead of a ketone.

Image: Formation of 2-methylpropan-2-ol
Thus, to convert ethyl ethanoate to 2-methylpropan-2-ol, two equivalents \[C{H_3}MgBr\]must be used
Note: The base catalysis of an ester is a reaction irreversible as the end products are alcohol and carboxylate ion which is resonance stabilised and thus stable and does not react with alcohol.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




