
What is electromagnet? Draw a circuit diagram to show how a soft iron piece can be transformed into an electromagnet.
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: An electromagnet is a non-permanent magnet formed when the current passes through a solenoid and a material like the soft iron core gets magnetized. The magnetic properties are present only when the current passes through the insulated copper wire surrounding the solenoid.
Complete step by step solution:
Electromagnet is a magnet where the magnetic field is produced by electric current. It is known that when a current passes through a coil, it generates a magnetic field around it. This property of electromagnetism is applied in electromagnetics.
To create an solenoid, an insulated copper wire is used, this wire is wound around a soft iron core and both the ends of this wire are connected to a battery, and the switch is closed. When the current flows through the wire loop, it generates a small magnetic field around it. Many such loops are formed when the wire is wound around the metal core. Thus the intensity of the magnetic field is increased .All the magnetic field lines created by the wire loops pass through the soft iron core. Thus it gets magnetized as well, this results in formation of an electromagnet, or a solenoid.
This diagram shows how a soft iron piece can be transformed into an electromagnet-
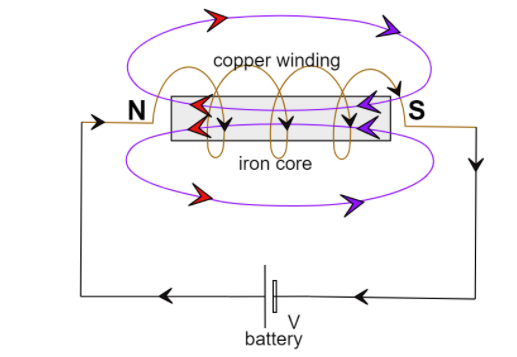
The iron core behaves like a bar magnet, and has a North pole where the magnetic field lines come out and a south pole where the field lines go back into the core.
Note: The direction of winding of the insulated copper wire is given by the right hand thumb rule. The polarity of the magnet can be reversed by reversing the direction of current. This is either done by changing the polarity of the magnet or by changing the direction of winding, from clockwise to anticlockwise.
Complete step by step solution:
Electromagnet is a magnet where the magnetic field is produced by electric current. It is known that when a current passes through a coil, it generates a magnetic field around it. This property of electromagnetism is applied in electromagnetics.
To create an solenoid, an insulated copper wire is used, this wire is wound around a soft iron core and both the ends of this wire are connected to a battery, and the switch is closed. When the current flows through the wire loop, it generates a small magnetic field around it. Many such loops are formed when the wire is wound around the metal core. Thus the intensity of the magnetic field is increased .All the magnetic field lines created by the wire loops pass through the soft iron core. Thus it gets magnetized as well, this results in formation of an electromagnet, or a solenoid.
This diagram shows how a soft iron piece can be transformed into an electromagnet-

The iron core behaves like a bar magnet, and has a North pole where the magnetic field lines come out and a south pole where the field lines go back into the core.
Note: The direction of winding of the insulated copper wire is given by the right hand thumb rule. The polarity of the magnet can be reversed by reversing the direction of current. This is either done by changing the polarity of the magnet or by changing the direction of winding, from clockwise to anticlockwise.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 1 (55/1/1) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Marking Scheme




