
What is the correct Fischer projection of (R) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid?
(A)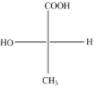
(B)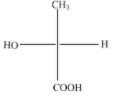
(C)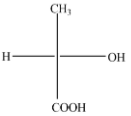
(D)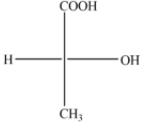
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The right hand and left-hand nomenclature are used to name the enantiomers of a chiral compound. The stereo centres are labelled as R or S. the D-L system corresponds to the configuration of the molecule with spatial arrangements of its atoms around the chiral centre.
Complete step by step solution:
The structure of 2- hydroxy propanoic acid which is IUPAC name of the given structure,
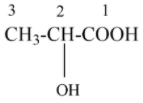
Based on R and S rotation, a curved arrow is shown in a clockwise direction, then denotes S configuration, similarly, it shows anti-clockwise direction, it denotes R configuration. In a Fischer projection molecule, a curve arrow is drawn based on the priority of the functional groups around the chiral centre. In the given 2-hydroxy propanoic acid, the priority order as follows,
$-OH>-COOH>-C{{H}_{3}}>-H$
Let us take options given fischer projection formula and find out which is (R) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid?
(A)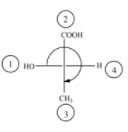
The above diagram indicates that curved arrow shows clockwise direction, it should be R-configuration, but 4th priority group on the horizontal line, then the above fischer projection is (S) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
(B)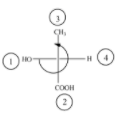
The above diagram indicates that curved arrow shows anti clockwise direction, the configuration should be S. but the 4th priority group on the horizontal line, then the above fischer projection is (R) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
(C)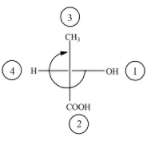
The above diagram indicates that curved arrow shows clockwise direction, the configuration should be R. but the 4th priority group on horizontal line then the above fischer projection is (S) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
(D)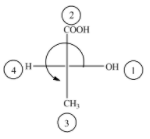
The above diagram indicates that curved arrow shows anti clockwise direction, the configuration should be S. but the 4th priority group on the horizontal line, then the above fischer projection is (R) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
Hence, option B and D are R-configuration for 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
Note: A dextrorotatory compound is often prefixed with (+)- or d-, similarly, a levorotatory compound is often prefixed with (-)- or l-. These lowercase are different from D and L prefixes, which are used to distinguish chiral configuration with organic compounds.
Complete step by step solution:
The structure of 2- hydroxy propanoic acid which is IUPAC name of the given structure,

Based on R and S rotation, a curved arrow is shown in a clockwise direction, then denotes S configuration, similarly, it shows anti-clockwise direction, it denotes R configuration. In a Fischer projection molecule, a curve arrow is drawn based on the priority of the functional groups around the chiral centre. In the given 2-hydroxy propanoic acid, the priority order as follows,
$-OH>-COOH>-C{{H}_{3}}>-H$
Let us take options given fischer projection formula and find out which is (R) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid?
(A)

The above diagram indicates that curved arrow shows clockwise direction, it should be R-configuration, but 4th priority group on the horizontal line, then the above fischer projection is (S) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
(B)

The above diagram indicates that curved arrow shows anti clockwise direction, the configuration should be S. but the 4th priority group on the horizontal line, then the above fischer projection is (R) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
(C)

The above diagram indicates that curved arrow shows clockwise direction, the configuration should be R. but the 4th priority group on horizontal line then the above fischer projection is (S) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
(D)

The above diagram indicates that curved arrow shows anti clockwise direction, the configuration should be S. but the 4th priority group on the horizontal line, then the above fischer projection is (R) 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
Hence, option B and D are R-configuration for 2-hydroxy propanoic acid.
Note: A dextrorotatory compound is often prefixed with (+)- or d-, similarly, a levorotatory compound is often prefixed with (-)- or l-. These lowercase are different from D and L prefixes, which are used to distinguish chiral configuration with organic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




