
How to convert ethanoic acid to 2-chloroethanoic acid?
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: Chloroacetic acid, industrially known as monochloroacetic acid is an organochlorine compound. It has the formula \[C{H_2}\left( {Cl} \right)COOH\]. Ethanoic acid is converted to 2-chloroethanoic acid by a reaction called the Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Acetic acid is the common name for ethanoic acid.
It is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the structural formula \[C{H_3}COOH\].
It is a carboxylic acid and has a -COOH group or carboxyl group attached to the methyl group.
The carbon attached to the carboxyl group is called the \[\alpha \]-carbon. The hydrogen atoms attached to this carbon are \[\alpha \]-hydrogen.
The Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction is a chemical conversion that concerns the halogenation of a carboxylic acid at the α-carbon.
For this reaction, a \[\alpha \]-carbon must carry a minimum of one proton.
Phosphorus trichloride or \[PC{l_3}\] is used as a catalyst in this reaction.
This reaction occurs in two steps.
In the first step, \[PC{l_3}\]takes the place of the carboxylic OH group with a chloride, forming a carboxylic acid chloride.
Then the acyl chloride undergoes tautomerization to form an enol.
This enol reacts with the \[B{r_2}\]and undergoes bromination at the α position.
The mono-chlorinated compound is slightly nucleophilic, and the reaction ceases at this phase.
This acyl intermediate compound can go through chloride exchange with unreacted carboxylic acid through the anhydride, which permits the reaction to proceed until the reaction is finished.
The mechanism is as follows:-
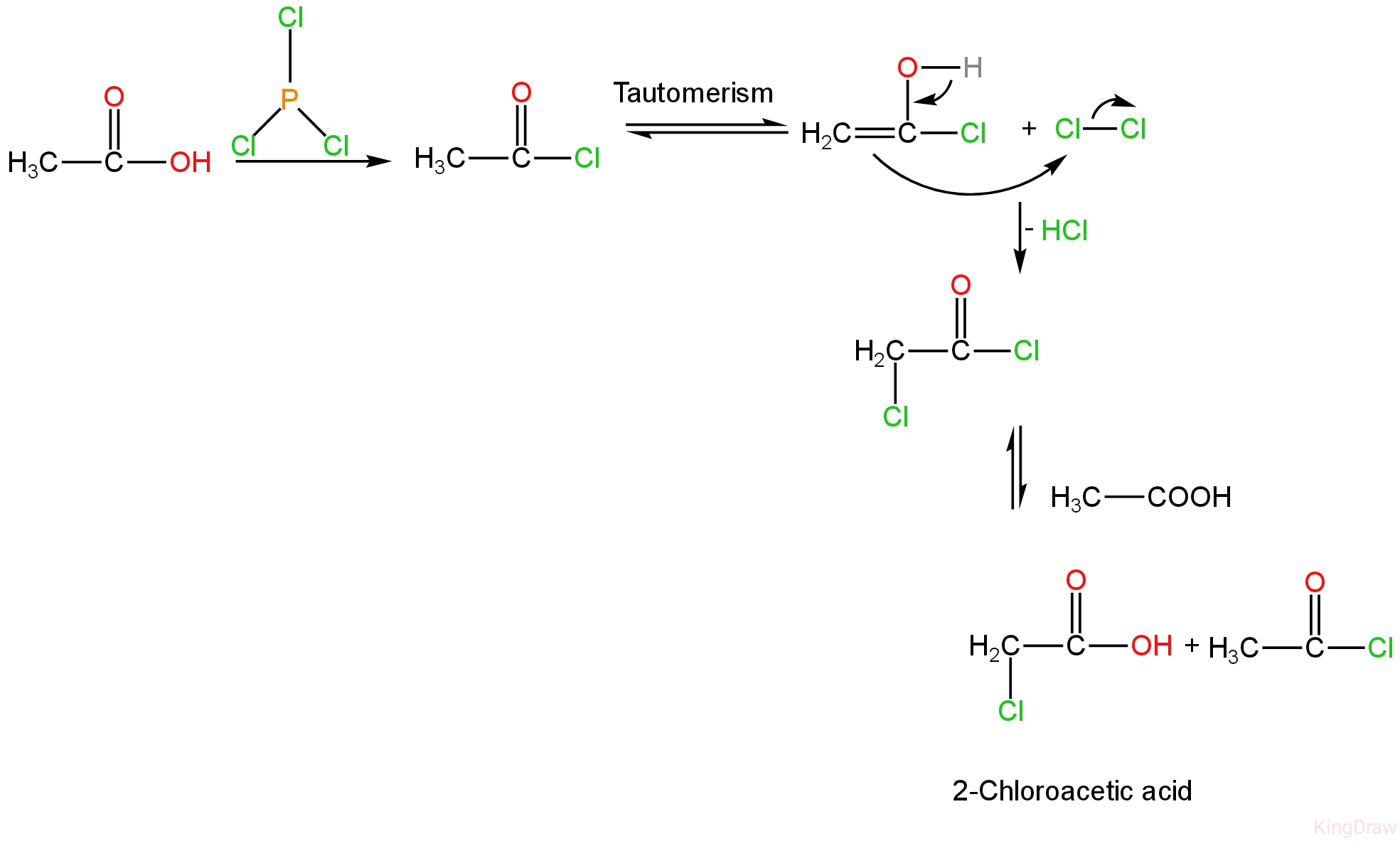
Image: Mechanism of Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.
So, ethanoic acid can be converted to 2-chloroacetic acid in the presence of phosphorus chloride.
Note: In a neutral to the mildly acidic aqueous solution, hydrolysis of the \[\alpha \]-Chloro acyl bromide ensues spontaneously, generating the \[\alpha \]-Chloro carboxylic acid. It is an instance of a nucleophilic acyl substitution. If a mildly nucleophilic solvent is present, the reaction of the \[\alpha \]-Chloro acyl bromide with the carboxylic acid generates the \[\alpha \]-Chloro carboxylic acid and again forms the acyl chloride intermediate.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Acetic acid is the common name for ethanoic acid.
It is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the structural formula \[C{H_3}COOH\].
It is a carboxylic acid and has a -COOH group or carboxyl group attached to the methyl group.
The carbon attached to the carboxyl group is called the \[\alpha \]-carbon. The hydrogen atoms attached to this carbon are \[\alpha \]-hydrogen.
The Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction is a chemical conversion that concerns the halogenation of a carboxylic acid at the α-carbon.
For this reaction, a \[\alpha \]-carbon must carry a minimum of one proton.
Phosphorus trichloride or \[PC{l_3}\] is used as a catalyst in this reaction.
This reaction occurs in two steps.
In the first step, \[PC{l_3}\]takes the place of the carboxylic OH group with a chloride, forming a carboxylic acid chloride.
Then the acyl chloride undergoes tautomerization to form an enol.
This enol reacts with the \[B{r_2}\]and undergoes bromination at the α position.
The mono-chlorinated compound is slightly nucleophilic, and the reaction ceases at this phase.
This acyl intermediate compound can go through chloride exchange with unreacted carboxylic acid through the anhydride, which permits the reaction to proceed until the reaction is finished.
The mechanism is as follows:-

Image: Mechanism of Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.
So, ethanoic acid can be converted to 2-chloroacetic acid in the presence of phosphorus chloride.
Note: In a neutral to the mildly acidic aqueous solution, hydrolysis of the \[\alpha \]-Chloro acyl bromide ensues spontaneously, generating the \[\alpha \]-Chloro carboxylic acid. It is an instance of a nucleophilic acyl substitution. If a mildly nucleophilic solvent is present, the reaction of the \[\alpha \]-Chloro acyl bromide with the carboxylic acid generates the \[\alpha \]-Chloro carboxylic acid and again forms the acyl chloride intermediate.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




