
Consider the arrangement of three plates X, Y and Z each of the area A and separation d. The energy stored when the plates are fully charged is: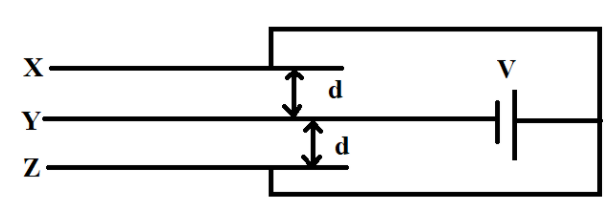
A) ${\varepsilon _0}A\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{{2d}}$
B) ${\varepsilon _0}A\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{d}$
C) $2{\varepsilon _0}A\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{d}$
D) $3{\varepsilon _0}A\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{d}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:Work has to be done to store energy in the plates. This work is converted into electrostatic potential energy and stored in the plates of the capacitor. To find the energy stored in the plates, we have to consider the plates as the plates of a capacitor and use the formula for the energy stored in the plates of a capacitor.
Formula used:
i) $C = \dfrac{{A{\varepsilon _0}}}{d}$ (Where C stands for the capacitance of the capacitor, A stands for the area of the plates, ${\varepsilon _0}$stands for the dielectric constant of free space, d stands for the distance between two plates)
ii) $U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$ (Where U stands for the energy stored in the capacitor, V stands for the potential difference)
Complete step by step solution:
In the diagram, the three plates can be considered as two capacitors.
Hence the capacitance is,
${C_{net}} = C + C = 2C$
We know that the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor is $C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}$
Since the net capacitance is given by 2C, we can write
${C_{net}} = \dfrac{{2{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}$
Now we have to find the energy stored in the plates by using the formula, $U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$
Here, $U = \dfrac{1}{2}{C_{net}}{V^2}$
Substituting the value of ${C_{net}}$in the equation
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{2{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}} \right){V^2}$
$U = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A{V^2}}}{d}$
The correct answer is option(B), ${\varepsilon _0}A\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{d}$.
Note:Capacitors store electrical energy in an electrical field. According to the law of conservation of energy, the work done in storing the energy is converted into energy. To find the energy stored in the plates of a capacitor, two more formulae can be used.
If the charge Q and the capacitance C is given in the question we can use the equation, $U = \dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{2C}}$.
If the charge Q and potential difference V is given, then use the equation, $U = \dfrac{1}{2}QV$.
Formula used:
i) $C = \dfrac{{A{\varepsilon _0}}}{d}$ (Where C stands for the capacitance of the capacitor, A stands for the area of the plates, ${\varepsilon _0}$stands for the dielectric constant of free space, d stands for the distance between two plates)
ii) $U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$ (Where U stands for the energy stored in the capacitor, V stands for the potential difference)
Complete step by step solution:
In the diagram, the three plates can be considered as two capacitors.
Hence the capacitance is,
${C_{net}} = C + C = 2C$
We know that the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor is $C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}$
Since the net capacitance is given by 2C, we can write
${C_{net}} = \dfrac{{2{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}$
Now we have to find the energy stored in the plates by using the formula, $U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$
Here, $U = \dfrac{1}{2}{C_{net}}{V^2}$
Substituting the value of ${C_{net}}$in the equation
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\dfrac{{2{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}} \right){V^2}$
$U = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A{V^2}}}{d}$
The correct answer is option(B), ${\varepsilon _0}A\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{d}$.
Note:Capacitors store electrical energy in an electrical field. According to the law of conservation of energy, the work done in storing the energy is converted into energy. To find the energy stored in the plates of a capacitor, two more formulae can be used.
If the charge Q and the capacitance C is given in the question we can use the equation, $U = \dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{2C}}$.
If the charge Q and potential difference V is given, then use the equation, $U = \dfrac{1}{2}QV$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




