
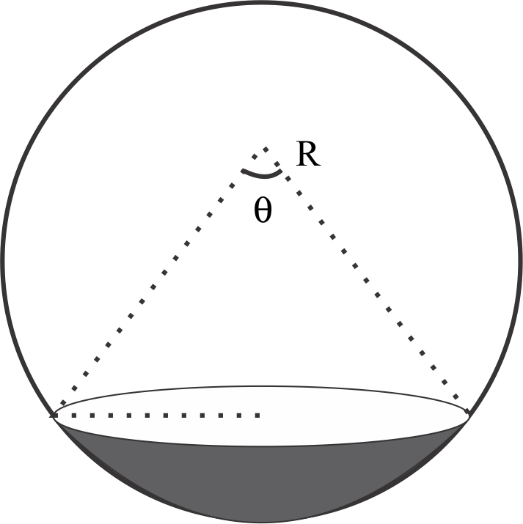
Consider a spherical drop of radius R. Surface tension of the liquid is S. Force of the surface tension on the shaded sub hemisphere due to remaining drop is $\dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2}$. The value of angle $\theta $ (angle subtended by the sub hemisphere at centre of drop) is
(A) $60^\circ $
(B) $120^\circ $
(C) $30^\circ $
(D) $90^\circ $
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint We are provided with the force of the surface tension on the shaded sub hemisphere due to the remaining drop being $\dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2}$. We can understand that statement from the diagram in the question. We have to find the angle subtended by the sub hemisphere at centre of drop. Use the surface tension formula to find the angle. Since the given surface is a sphere its radius makes an angle with the centre point. Use the given diagram for better understanding.
Complete step by step answer
Surface tension: The tendency of surfaces to shrink into the possible minimum surface area. The surface tension is the force per unit length of the surface. Surface area of an object is given by
$ \Rightarrow \gamma = \dfrac{F}{l}$
$\gamma $ is the surface tension
F is the force
L is the unit length
Given,
The radius of a spherical drop is R
Surface tension of the liquid is S
Force of the surface tension on the shaded sub hemisphere due to remaining drop is $F = \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2}$.
Angle subtended by the sub hemisphere at centre of drop $\theta = ?$
We know that
$ \Rightarrow \gamma = \dfrac{F}{l}$
$ \Rightarrow F = \gamma \times l$
Substituting the known values,
$ \Rightarrow F = \gamma \times l$
$ \Rightarrow F = S \times 2\pi R$
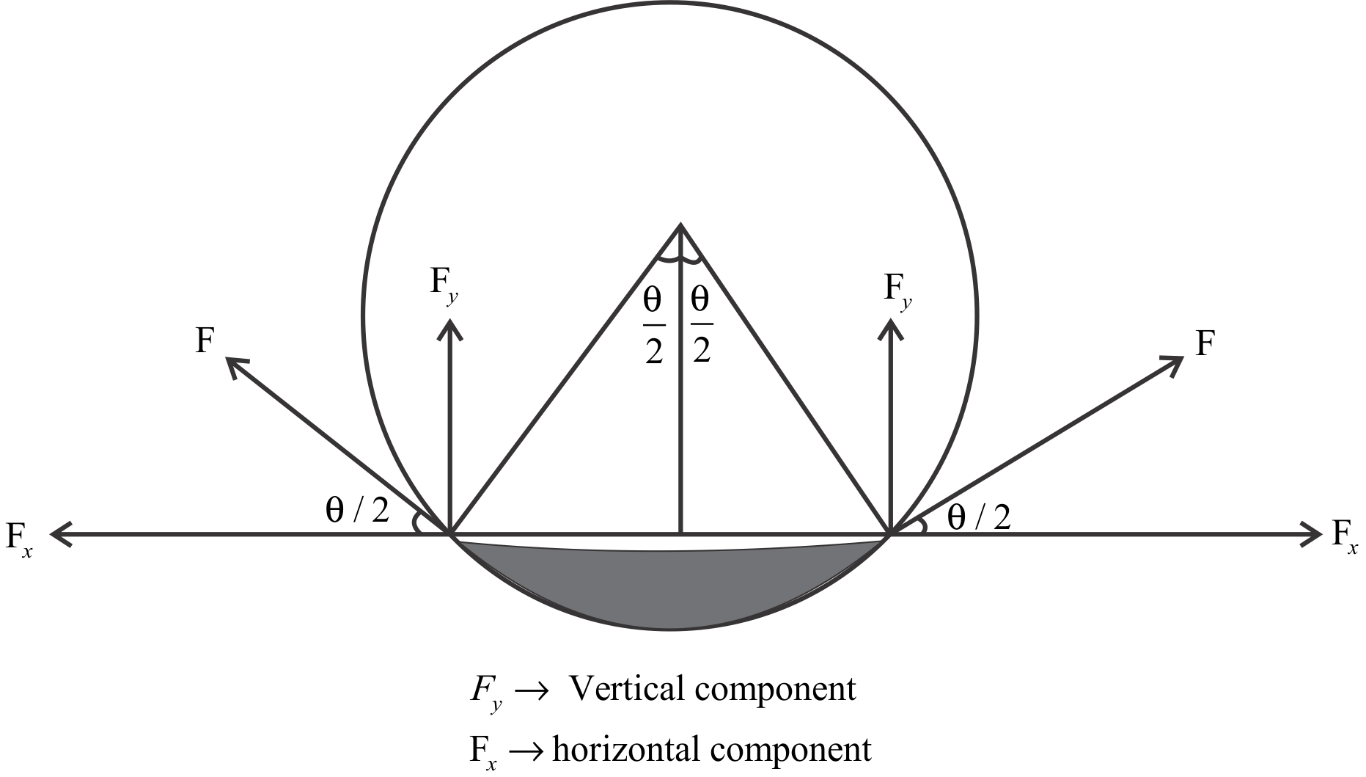
From the diagram
$ \Rightarrow F = S \times 2\pi R\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}{\text{ }} \to {\text{1}}$
From the diagram,
All the horizontal components of the force get cancelled.
The net force by vertical component of force
$ \Rightarrow F = F\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
Given $F = \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2} = F\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
From equation 1
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2} = S \times 2\pi R\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2} = S \times 2\pi R{\sin ^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \times 2{\sin ^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
Taking square root
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\theta }{2} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\theta }{2} = 30^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = 60^\circ \]
Angle subtended by the sub hemisphere at centre of drop, \[\theta = 60^\circ \]
Hence the correct answer is option (A) \[60^\circ \]
Note We can notice that we have used $2\pi R$ in place of L while solving. Surface tension is the force per unit length. Here we are provided with a sphere. To find the surface tension on the sphere we have to use the circumference of the sphere. Circumference of the sphere is $2\pi R$.
Complete step by step answer
Surface tension: The tendency of surfaces to shrink into the possible minimum surface area. The surface tension is the force per unit length of the surface. Surface area of an object is given by
$ \Rightarrow \gamma = \dfrac{F}{l}$
$\gamma $ is the surface tension
F is the force
L is the unit length
Given,
The radius of a spherical drop is R
Surface tension of the liquid is S
Force of the surface tension on the shaded sub hemisphere due to remaining drop is $F = \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2}$.
Angle subtended by the sub hemisphere at centre of drop $\theta = ?$

We know that
$ \Rightarrow \gamma = \dfrac{F}{l}$
$ \Rightarrow F = \gamma \times l$
Substituting the known values,
$ \Rightarrow F = \gamma \times l$
$ \Rightarrow F = S \times 2\pi R$
From the diagram
$ \Rightarrow F = S \times 2\pi R\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}{\text{ }} \to {\text{1}}$
From the diagram,
All the horizontal components of the force get cancelled.
The net force by vertical component of force
$ \Rightarrow F = F\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
Given $F = \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2} = F\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
From equation 1
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2} = S \times 2\pi R\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} \times \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{S\pi R}}{2} = S \times 2\pi R{\sin ^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \times 2{\sin ^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
Taking square root
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \dfrac{\theta }{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\theta }{2} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{\theta }{2} = 30^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = 60^\circ \]
Angle subtended by the sub hemisphere at centre of drop, \[\theta = 60^\circ \]
Hence the correct answer is option (A) \[60^\circ \]
Note We can notice that we have used $2\pi R$ in place of L while solving. Surface tension is the force per unit length. Here we are provided with a sphere. To find the surface tension on the sphere we have to use the circumference of the sphere. Circumference of the sphere is $2\pi R$.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




