
Benzyl chloride when oxidised by Lead nitrate solution gives
A. Benzoic acid
B. Benzaldehyde
C. Benzene
D. None
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: Oxidation is the addition of oxygen to a compound.
It involves the loss of electrons increasing the oxidation state of a compound.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here, we are given lead nitrate solution, a mild oxidising agent. It is not as powerful as potassium permanganate.
Lead nitrate solution when treated with benzyl chloride acts as an oxidising agent.
Benzyl chloride undergoes oxidation.
A. Benzoic acid
Lead nitrate solution is a mild oxidising agent. It can't convert benzyl chloride directly into benzoic acid.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Lead nitrate solution oxides benzyl chloride into benzaldehyde.
Benzaldehyde does not undergo further oxidation in the presence of a mild oxidizing agent like lead nitrate.
So, B is correct.
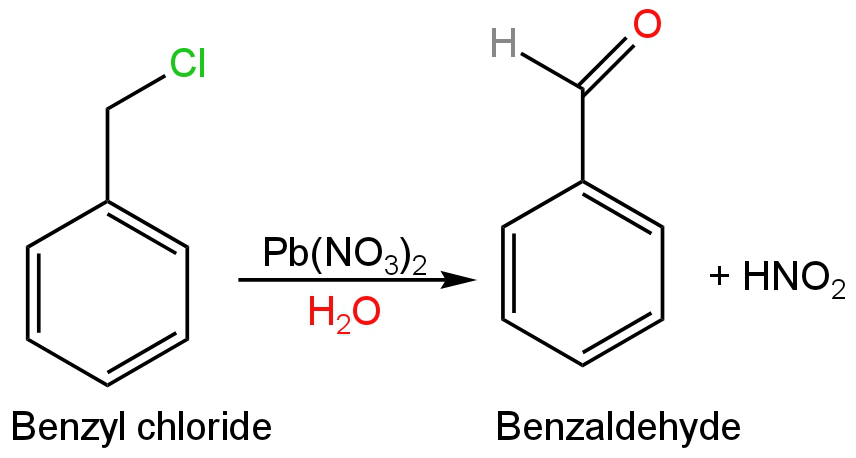
Image: Oxidation of benzyl chloride.
C. Lead nitrate is an oxidising agent that cannot convert benzyl alcohol to benzene.
It is only capable of oxidation.
So, C is incorrect.
So, option B is correct.
Additional Information: Benzyl chloride is a colourless organochlorine compound.
It is prepared by the photochemical reaction of chlorine with benzene.
This reaction follows a free radical mechanism.
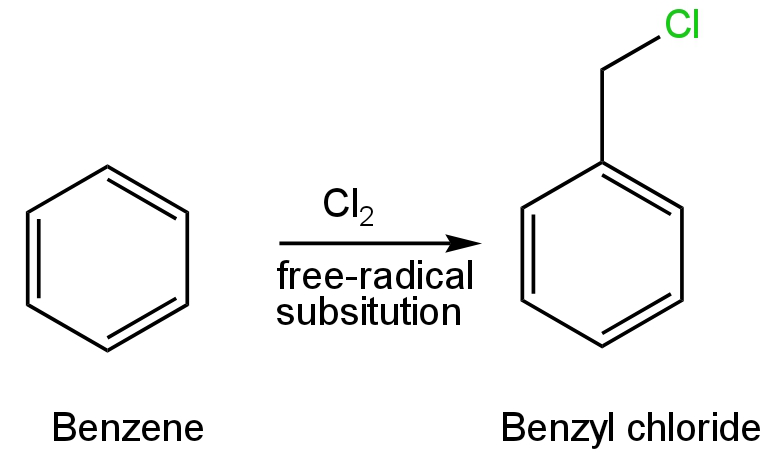
Image: Formation of benzyl chloride
Note: While attempting the question, one must retain in mind that lead nitrate is a mild oxidising agent. When benzyl chloride reacts with alkaline potassium permanganate solution, it undergoes oxidation to form benzoic acid. This happens because of the presence of potassium permanganate which is a powerful oxidising agent. Benzyl chloride in the presence of mild oxidising agents like lead nitrate forms benzaldehyde.
It involves the loss of electrons increasing the oxidation state of a compound.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here, we are given lead nitrate solution, a mild oxidising agent. It is not as powerful as potassium permanganate.
Lead nitrate solution when treated with benzyl chloride acts as an oxidising agent.
Benzyl chloride undergoes oxidation.
A. Benzoic acid
Lead nitrate solution is a mild oxidising agent. It can't convert benzyl chloride directly into benzoic acid.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Lead nitrate solution oxides benzyl chloride into benzaldehyde.
Benzaldehyde does not undergo further oxidation in the presence of a mild oxidizing agent like lead nitrate.
So, B is correct.

Image: Oxidation of benzyl chloride.
C. Lead nitrate is an oxidising agent that cannot convert benzyl alcohol to benzene.
It is only capable of oxidation.
So, C is incorrect.
So, option B is correct.
Additional Information: Benzyl chloride is a colourless organochlorine compound.
It is prepared by the photochemical reaction of chlorine with benzene.
This reaction follows a free radical mechanism.

Image: Formation of benzyl chloride
Note: While attempting the question, one must retain in mind that lead nitrate is a mild oxidising agent. When benzyl chloride reacts with alkaline potassium permanganate solution, it undergoes oxidation to form benzoic acid. This happens because of the presence of potassium permanganate which is a powerful oxidising agent. Benzyl chloride in the presence of mild oxidising agents like lead nitrate forms benzaldehyde.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




