
Benzamide on reaction with \[POC{l_3}\] gives
(A) Aniline
(B) Chlorobenzene
(C) Benzylamine
(D) Benzonitrile
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The chemical name of \[POC{l_3}\] is phosphoryl chloride. It is used as a dehydrating agent in the given reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Phosphoryl chloride is a colourless liquid with the formula \[POC{l_3}\]. It hydrolyses in moist air and releases phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. Phosphoryl chloride is a commonly used dehydrating agent in chemical laboratories. It is used as a dehydrating agent for the preparation of nitriles from primary amides.
Benzamide is a white solid with chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_5}CON{H_2}\]. It is the simplest amide derived from benzoic acid. It is soluble in organic solvents and water. These are organic compounds which contain a carboxamide substituent which is attached to a benzene ring. Benzamide is an extremely weak basic compound.
When benzamide reacts with \[POC{l_3}\], a dehydration reaction takes place. The term dehydration means that \[{H_2}O\] is lost from the compound, which results in the formation of the main product that is benzonitrile. Benzonitrile is used as an intermediate for rubber manufacturing, chemicals and as a solvent for nitrile rubber.
The reaction of conversion of benzamide on treatment with \[POC{l_3}\] to give benzonitrile is given below:
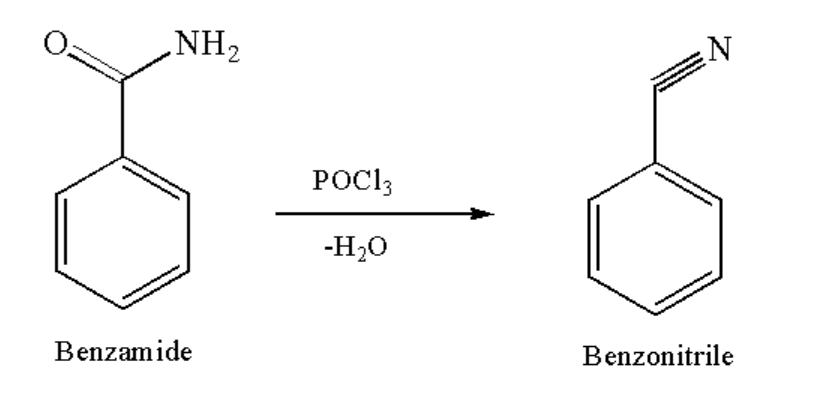
Image: Conversion of benzamide to benzonitrile
So, we can say that Benzonitrile is formed when benzamide reacts with \[POC{l_3}\].
Note: \[POC{l_3}\]is also known as phosphorous oxychloride. Phosphorus oxychloride is synthesised industrially by reacting phosphorus trichloride and oxygen atoms. It can also be prepared by reacting phosphorous trichloride with phosphorus pentachloride. It does not dissolve in water as it forms hydrogen chloride and phosphoric acid by reacting with water.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Phosphoryl chloride is a colourless liquid with the formula \[POC{l_3}\]. It hydrolyses in moist air and releases phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. Phosphoryl chloride is a commonly used dehydrating agent in chemical laboratories. It is used as a dehydrating agent for the preparation of nitriles from primary amides.
Benzamide is a white solid with chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_5}CON{H_2}\]. It is the simplest amide derived from benzoic acid. It is soluble in organic solvents and water. These are organic compounds which contain a carboxamide substituent which is attached to a benzene ring. Benzamide is an extremely weak basic compound.
When benzamide reacts with \[POC{l_3}\], a dehydration reaction takes place. The term dehydration means that \[{H_2}O\] is lost from the compound, which results in the formation of the main product that is benzonitrile. Benzonitrile is used as an intermediate for rubber manufacturing, chemicals and as a solvent for nitrile rubber.
The reaction of conversion of benzamide on treatment with \[POC{l_3}\] to give benzonitrile is given below:

Image: Conversion of benzamide to benzonitrile
So, we can say that Benzonitrile is formed when benzamide reacts with \[POC{l_3}\].
Note: \[POC{l_3}\]is also known as phosphorous oxychloride. Phosphorus oxychloride is synthesised industrially by reacting phosphorus trichloride and oxygen atoms. It can also be prepared by reacting phosphorous trichloride with phosphorus pentachloride. It does not dissolve in water as it forms hydrogen chloride and phosphoric acid by reacting with water.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




