
ASSERTION
Among the carbon allotropes diamond is an insulator, whereas graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
REASON
Hybridization of carbon in diamond and graphite are \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{{\text{3\;}}}}\]and \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\]respectively.
A. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
C. Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
D. Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Presence of unpaired electrons make the compound a good conductor. This is determined from the structure.
Complete step by step answer: There are two major allotropes of carbon, diamond and graphite. In case conductivity, diamond is an insulator, whereas graphite is a good conductor of electricity. This is due to hybridisation and structure of carbon present in it.
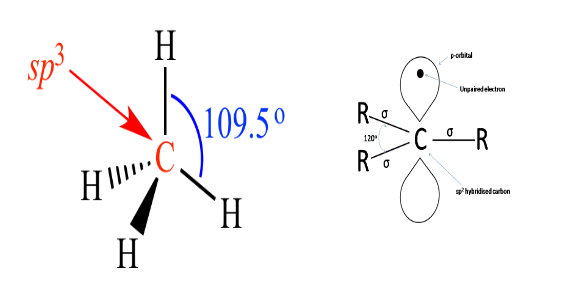
In diamond, the carbon atoms are \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{{\text{3\;}}}}\]hybridised, the electrons are present in 1s and 3p orbitals with no presence of unpaired electrons. Absence of unpaired electrons makes it an insulator.
In graphite the hybridisation of carbon is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\]thus we can see that in the below structure of \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\]carbon there is an availability of one unpaired electron in p orbital this helps in the conduction of electricity thus they are regarded as good conductor of electricity.
Hence, both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion. So, the correct option is A.
Note: Availability of free unpaired electrons is must for conductivity. Graphite is used in pencils and lubricants. Its high conductivity makes it useful in electronic products such as electrodes, batteries, and solar panels. Diamonds are used to make fine jewellery because diamonds are so they are extremely effective at polishing, cutting, and drilling.
Complete step by step answer: There are two major allotropes of carbon, diamond and graphite. In case conductivity, diamond is an insulator, whereas graphite is a good conductor of electricity. This is due to hybridisation and structure of carbon present in it.
In diamond, the carbon atoms are \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{{\text{3\;}}}}\]hybridised, the electrons are present in 1s and 3p orbitals with no presence of unpaired electrons. Absence of unpaired electrons makes it an insulator.
In graphite the hybridisation of carbon is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\]thus we can see that in the below structure of \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\]carbon there is an availability of one unpaired electron in p orbital this helps in the conduction of electricity thus they are regarded as good conductor of electricity.

Hence, both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion. So, the correct option is A.
Note: Availability of free unpaired electrons is must for conductivity. Graphite is used in pencils and lubricants. Its high conductivity makes it useful in electronic products such as electrodes, batteries, and solar panels. Diamonds are used to make fine jewellery because diamonds are so they are extremely effective at polishing, cutting, and drilling.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




