
Ascorbic acid resemble the structure of:
A. Vitamin A
B. Glucose
C. Cellulose
D. Vitamin D
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ascorbic acid is another name for vitamin C and it is also known as ascorbate. The name ‘ascorbic acid’ is always used to refer to the L – enantiomer of ascorbic acid as well as its oxidized forms.
Its molecular formula is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}$ .
Complete step by step answer:
Ascorbic acid is a vitamin which is naturally water soluble.
It is an antioxidant agent and it functions in fighting against bacterial infections, in detoxifying reactions and also in the formation of collagen in fibrous tissues.
Vitamin C is generally found in citrus and other fruits and also in some vegetables. It cannot be produced or stored by the human body and so it must be supplied in the diet.
Ascorbic acid belongs to the class of organic compounds called butenolides. These are organic compounds containing dihydrofurans with a carbonyl group present at the C-2 carbon atom. Ascorbic acid exists as a solid and is a weakly acidic compound.
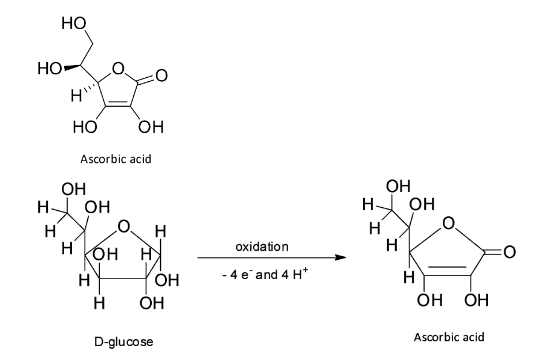
It is structurally related to glucose as it is obtained from glucose.
Thus, ascorbic acid structurally resembles glucose molecules. So, B is the correct answer.
Note:
Scurvy is a disease which is caused by the deficiency of vitamin C. Thus, scurvy can be prevented by treating with vitamin C containing foods or dietary supplements.
The intake of ascorbic acid or vitamin C on a regular basis can also reduce the severity of common cold.
However, it does not appear to prevent infection. It is also not clear if the supplementation of vitamin C affects the risk of cancer or cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Its molecular formula is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}$ .
Complete step by step answer:
Ascorbic acid is a vitamin which is naturally water soluble.
It is an antioxidant agent and it functions in fighting against bacterial infections, in detoxifying reactions and also in the formation of collagen in fibrous tissues.
Vitamin C is generally found in citrus and other fruits and also in some vegetables. It cannot be produced or stored by the human body and so it must be supplied in the diet.
Ascorbic acid belongs to the class of organic compounds called butenolides. These are organic compounds containing dihydrofurans with a carbonyl group present at the C-2 carbon atom. Ascorbic acid exists as a solid and is a weakly acidic compound.
It is structurally related to glucose as it is obtained from glucose.
Thus, ascorbic acid structurally resembles glucose molecules. So, B is the correct answer.

Note:
Scurvy is a disease which is caused by the deficiency of vitamin C. Thus, scurvy can be prevented by treating with vitamin C containing foods or dietary supplements.
The intake of ascorbic acid or vitamin C on a regular basis can also reduce the severity of common cold.
However, it does not appear to prevent infection. It is also not clear if the supplementation of vitamin C affects the risk of cancer or cardiovascular disease or dementia.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




