
Arrange the following phenols in increasing order of ${\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{{\text{a1}}}}$ value.
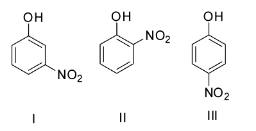
A. IB. IIIC. IIID. I
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Electron donating substituents tend to decrease the acidic strength while electron withdrawing substituents tend to increase the acidic strength of substituted phenols relative to phenol.
The acid strengthening effect of the electron withdrawing substituents and the acid weakening effect of the electron donating substituents are more pronounced at the ortho and the para positions.
Complete step by step answer:
Nitro group has a powerful electron withdrawing resonance effect or –R effect as well as an electron withdrawing inductive effect or –I effect. As a result, all the nitrophenols are stronger acids than phenol.
Therefore, the acid strengthening effect of the electron withdrawing nitro group will be less pronounced at the meta position of the ring in comparison to that at the ortho and para positions. So, the nitro group will decrease the electron density more at the ortho and para positions than at the meta position.
Thus, the conjugate base nitro phenoxide ion will have lesser stabilization in case of the meta isomer than in the case of ortho and para isomers. So, only the weaker –I effect will be responsible for electron withdrawing at meta position. Thus, meta nitrophenol will be the weakest acid among the three.
Now, we are left with ortho- and para- nitrophenol. In case of ortho nitrophenol, intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs between the adjacent hydroxyl and the nitro group. Thus, the removal of a proton is difficult in the ortho isomer and so it is a weaker acid than the para isomer.
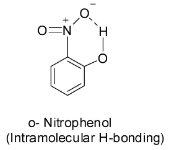
Thus, the acidic strength increases in the order: meta< ortho< para.
Since higher ${\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}$ value indicates a weaker acid, thus the order of ${\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}$ values will be para< ortho< meta or III< II< I.
So the correct option is C.
Note:
Ortho effect is the effect which makes the ortho substituted benzoic acids stronger acids than benzoic acid regardless of the nature of the substituent.
In case of nitrobenzoic acid, the ortho nitrobenzoic acid will be the strongest acid due to ortho effect while the meta isomer will be now a weaker acid only in comparison to the para isomer.
Thus, the acidic strength of nitrobenzoic acids will be: meta< para< ortho.
The acid strengthening effect of the electron withdrawing substituents and the acid weakening effect of the electron donating substituents are more pronounced at the ortho and the para positions.
Complete step by step answer:
Nitro group has a powerful electron withdrawing resonance effect or –R effect as well as an electron withdrawing inductive effect or –I effect. As a result, all the nitrophenols are stronger acids than phenol.
Therefore, the acid strengthening effect of the electron withdrawing nitro group will be less pronounced at the meta position of the ring in comparison to that at the ortho and para positions. So, the nitro group will decrease the electron density more at the ortho and para positions than at the meta position.
Thus, the conjugate base nitro phenoxide ion will have lesser stabilization in case of the meta isomer than in the case of ortho and para isomers. So, only the weaker –I effect will be responsible for electron withdrawing at meta position. Thus, meta nitrophenol will be the weakest acid among the three.
Now, we are left with ortho- and para- nitrophenol. In case of ortho nitrophenol, intramolecular hydrogen bonding occurs between the adjacent hydroxyl and the nitro group. Thus, the removal of a proton is difficult in the ortho isomer and so it is a weaker acid than the para isomer.

Thus, the acidic strength increases in the order: meta< ortho< para.
Since higher ${\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}$ value indicates a weaker acid, thus the order of ${\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}$ values will be para< ortho< meta or III< II< I.
So the correct option is C.
Note:
Ortho effect is the effect which makes the ortho substituted benzoic acids stronger acids than benzoic acid regardless of the nature of the substituent.
In case of nitrobenzoic acid, the ortho nitrobenzoic acid will be the strongest acid due to ortho effect while the meta isomer will be now a weaker acid only in comparison to the para isomer.
Thus, the acidic strength of nitrobenzoic acids will be: meta< para< ortho.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




