
An electron gun is placed inside a long solenoid of radius R on its axis. The solenoid has n turns/length and carries a current i. The electron gun shoots an electron along the radius of solenoid with speed If the electron does not hit the surface of the solenoid, maximum possible value of v is (all symbols have their standard meaning):
A. $\dfrac{\operatorname{Re}{{\mu }_{0}}in}{2m}$
B. $\dfrac{2\operatorname{Re}{{\mu }_{0}}in}{m}$
C. $\dfrac{\operatorname{Re}{{\mu }_{0}}in}{m}$
D. $\dfrac{\operatorname{Re}{{\mu }_{0}}in}{4m}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Recall the equation of magnetic field inside the solenoid. We have to find the maximum possible velocity. The varying quantity is radius. So, the condition for maximum velocity depends on radius. We just have to find that condition to find the maximum velocity. We also know that the force due to the magnetic field inside should be equal to centripetal force.
Formula used:
The expression of maximum velocity is,
$evB=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{R}$
Here, $B$ is the magnetic field, $m$ is the mass of the charged particle, $e$ is the charge of the particle and $R$ is the radius of the curved path.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, an electron gun shoots electrons perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. If the electron enters at different angles, then the trajectory is different. If an electron is entering at an angle, then the trajectory of the electron will be helix.
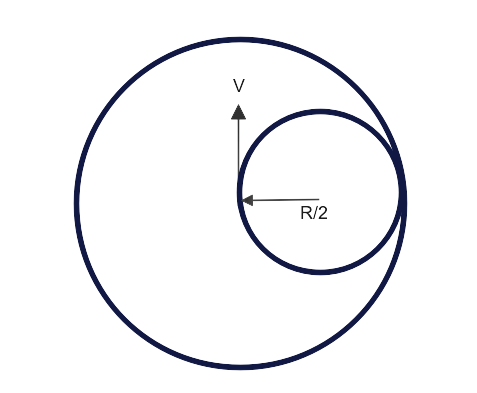
When we look at the cross-section of solenoid, we can see that: electrons are moving perpendicular to the magnetic field inside the solenoid. As it is moving perpendicular to the magnetic field, its trajectory is circular. Therefore, the maximum value of the radius of path taken by the electron so that it does not collide with the walls of the solenoid happens when the radius is $\dfrac{R}{2}$ .
We also have, the force due to magnetic field is equal to centripetal force to satisfy the maximum velocity condition:
$evB=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{R}$
We have the equation for magnetic field inside the solenoid with n number of turns is
$B={{\mu }_{0}}ni$
${{R}_{\max }}=\dfrac{R}{2}=\dfrac{m{{v}_{\max }}}{ein{{\mu }_{0}}}$
Maximum velocity is:
$\therefore {{v}_{\max }}=\dfrac{\operatorname{Re}in{{\mu }_{0}}}{2m}$
Therefore, the answer is option A.
Note: Here you should remember that we should find the velocity for which it should not hit the wall of solenoid. You should also take care of the number of turns in solenoid. Also, we should take care of the direction in which the electron enters the magnetic field since it affects the trajectory of electron
Formula used:
The expression of maximum velocity is,
$evB=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{R}$
Here, $B$ is the magnetic field, $m$ is the mass of the charged particle, $e$ is the charge of the particle and $R$ is the radius of the curved path.
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, an electron gun shoots electrons perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. If the electron enters at different angles, then the trajectory is different. If an electron is entering at an angle, then the trajectory of the electron will be helix.

When we look at the cross-section of solenoid, we can see that: electrons are moving perpendicular to the magnetic field inside the solenoid. As it is moving perpendicular to the magnetic field, its trajectory is circular. Therefore, the maximum value of the radius of path taken by the electron so that it does not collide with the walls of the solenoid happens when the radius is $\dfrac{R}{2}$ .
We also have, the force due to magnetic field is equal to centripetal force to satisfy the maximum velocity condition:
$evB=\dfrac{m{{v}^{2}}}{R}$
We have the equation for magnetic field inside the solenoid with n number of turns is
$B={{\mu }_{0}}ni$
${{R}_{\max }}=\dfrac{R}{2}=\dfrac{m{{v}_{\max }}}{ein{{\mu }_{0}}}$
Maximum velocity is:
$\therefore {{v}_{\max }}=\dfrac{\operatorname{Re}in{{\mu }_{0}}}{2m}$
Therefore, the answer is option A.
Note: Here you should remember that we should find the velocity for which it should not hit the wall of solenoid. You should also take care of the number of turns in solenoid. Also, we should take care of the direction in which the electron enters the magnetic field since it affects the trajectory of electron
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




