
An alkene on ozonolysis gives formaldehyde and. The alkene is
A. Ethene
B. Propene
C. 1-butene
D. 2-butene
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ozonolysis of alkene is the oxidation of alkenes with the help of ozone which gives aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acid as the products. This is a redox reaction in organic chemistry one or more than one product can be formed due to this reaction.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Ozonolysis of alkene goes through the process of oxidative cleavage. Ozonide is formed when ozone attacks the alkene and ozone breaks the π-bond as well as the σ-bond between the carbon and to break the sigma(σ) bond between the carbons high amount of energy and a very reactive species is required and Ozone is a very strong oxidising agent. Ozonolysis of an alkene with no alkyl substituent will produce aldehyde. When one carbon of alkene has both alkyl substituents it will produce ketone and aldehyde and ketones, and further oxidation will produce carboxylic acid.
The give compounds on ozonolysis will produce the following products:
$CH_2=CH_2\ +\ O_3 \longrightarrow \ 2HCHO$
$CH_3CH=CH_2\ +\ O_3 \longrightarrow \ CH_3CHO\ +\ HCHO$
$CH_3CH_2CH=CH_2\ +\ O_3 \longrightarrow \ CH_3CH_2CHO\ +\ HCHO$
$CH_3CH=CHCH_3+ \ O_3 \longrightarrow \ 2CH_3CHO$
As we can see, propene on ozonolysis produces formaldehyde and acetaldehyde as the product.
The reaction of ozonolysis of alkene proceeds through the following mechanism:
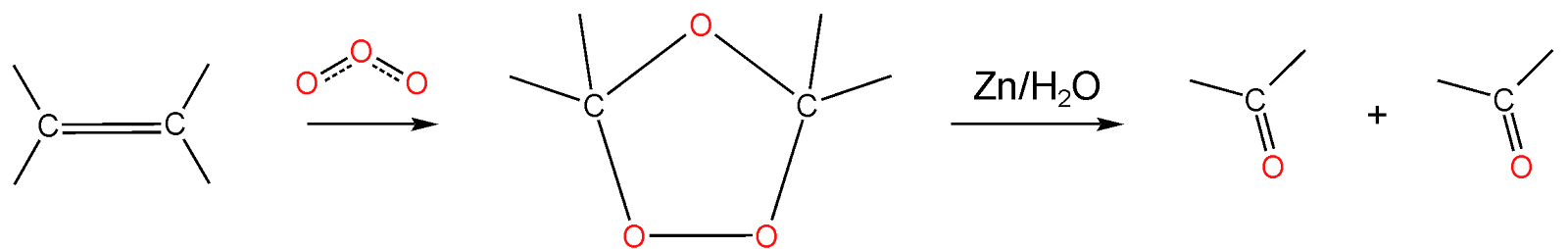
Alkene reacts with the ozone and forms ozonide then the ozonide is further hydrolyzed in presence of Zn to produce aldehydes, ketone, or carboxylic acid. The five-membered heterocyclic ring formed in the reaction is called ozonide.
Thus, Option (B) is correct
Note: Alkenes are also known as olefins. Ozonides are generally formed by alkenes and they are very reactive species; they decompose rapidly into aldehydes, ketone, and peroxide. During the hydrolysis of ozonide hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is generated to reduce the H2O2. Zinc dust is used as a catalyst in the reaction.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Ozonolysis of alkene goes through the process of oxidative cleavage. Ozonide is formed when ozone attacks the alkene and ozone breaks the π-bond as well as the σ-bond between the carbon and to break the sigma(σ) bond between the carbons high amount of energy and a very reactive species is required and Ozone is a very strong oxidising agent. Ozonolysis of an alkene with no alkyl substituent will produce aldehyde. When one carbon of alkene has both alkyl substituents it will produce ketone and aldehyde and ketones, and further oxidation will produce carboxylic acid.
The give compounds on ozonolysis will produce the following products:
$CH_2=CH_2\ +\ O_3 \longrightarrow \ 2HCHO$
$CH_3CH=CH_2\ +\ O_3 \longrightarrow \ CH_3CHO\ +\ HCHO$
$CH_3CH_2CH=CH_2\ +\ O_3 \longrightarrow \ CH_3CH_2CHO\ +\ HCHO$
$CH_3CH=CHCH_3+ \ O_3 \longrightarrow \ 2CH_3CHO$
As we can see, propene on ozonolysis produces formaldehyde and acetaldehyde as the product.
The reaction of ozonolysis of alkene proceeds through the following mechanism:

Alkene reacts with the ozone and forms ozonide then the ozonide is further hydrolyzed in presence of Zn to produce aldehydes, ketone, or carboxylic acid. The five-membered heterocyclic ring formed in the reaction is called ozonide.
Thus, Option (B) is correct
Note: Alkenes are also known as olefins. Ozonides are generally formed by alkenes and they are very reactive species; they decompose rapidly into aldehydes, ketone, and peroxide. During the hydrolysis of ozonide hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is generated to reduce the H2O2. Zinc dust is used as a catalyst in the reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




