
Ammonia molecule is:
(A) A nucleophile
(B) An electron deficient molecule
(C) A homolytic molecule
(D) An acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ammonia is a volatile trihydride of the element nitrogen of group 15. It has the formula \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\] . Nucleophiles or nucleophilic reagents are attracted to the nucleus or are nucleus loving or positive charge loving. Thus, the nucleophiles can be said to be the type of reagent species which are rich in electrons. Thus, the nucleophiles are negatively charged species.
Nucleophiles are of two types, negative nucleophiles or neutral nucleophiles. According to the Lewis concept, a nucleophile can donate an electron pair and hence it acts as a Lewis base.
Complete step by step answer:
The negative nucleophiles are those nucleophiles which have an excess electron pair and carry a negative charge. For example, carbanions have an unshared electron pair and a negative charge and hence they are negative nucleophiles. Another example of negative nucleophile is the bromide ion.
The neutral nucleophiles are those nucleophiles which have an unshared pair of electrons but do not carry any charge. Now, let us see the structure of the ammonia molecule. The valence shell configuration of nitrogen is ${\text{2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ and it undergoes ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridization. Three of the four ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybrid orbitals overlap with 1s orbitals of 3 hydrogen atoms to form 3 ${\text{N - H}}$ sigma bonds while the fourth contains the lone pair of electrons. It has pyramidal structure.
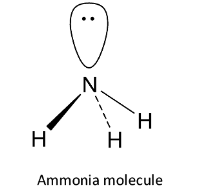
Thus ammonia contains a lone pair of electrons but has no charge. Hence, it is a neutral nucleophile. So, option A is correct.
An electron deficient molecule will try to take electrons from other sources and thus it is electron loving. Therefore, it will be an electrophile. So, option B is wrong.
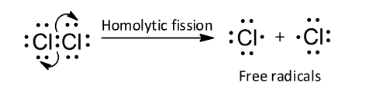
A homolytic molecule undergoes homolytic fission to give free radicals. In homolytic bond fission, the shared pair of electrons is distributed equally between two bonded atoms. So, option C is wrong.
According to the Lewis concept, an electrophile accepts an electron pair and hence it acts as a Lewis acid and a nucleophile can donate an electron pair and hence it acts as a Lewis base. Thus ammonia is a base and not an acid.
So, option D is wrong.
Note: Another type of reagent is free radical. It is a neutral species carrying an unpaired electron and it is formed by the homolytic bond fission of a covalent bond. Due to the presence of unpaired electrons, free radicals are paramagnetic.
Nucleophiles are of two types, negative nucleophiles or neutral nucleophiles. According to the Lewis concept, a nucleophile can donate an electron pair and hence it acts as a Lewis base.
Complete step by step answer:
The negative nucleophiles are those nucleophiles which have an excess electron pair and carry a negative charge. For example, carbanions have an unshared electron pair and a negative charge and hence they are negative nucleophiles. Another example of negative nucleophile is the bromide ion.
The neutral nucleophiles are those nucleophiles which have an unshared pair of electrons but do not carry any charge. Now, let us see the structure of the ammonia molecule. The valence shell configuration of nitrogen is ${\text{2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ and it undergoes ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybridization. Three of the four ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}$ hybrid orbitals overlap with 1s orbitals of 3 hydrogen atoms to form 3 ${\text{N - H}}$ sigma bonds while the fourth contains the lone pair of electrons. It has pyramidal structure.

Thus ammonia contains a lone pair of electrons but has no charge. Hence, it is a neutral nucleophile. So, option A is correct.
An electron deficient molecule will try to take electrons from other sources and thus it is electron loving. Therefore, it will be an electrophile. So, option B is wrong.
A homolytic molecule undergoes homolytic fission to give free radicals. In homolytic bond fission, the shared pair of electrons is distributed equally between two bonded atoms. So, option C is wrong.
According to the Lewis concept, an electrophile accepts an electron pair and hence it acts as a Lewis acid and a nucleophile can donate an electron pair and hence it acts as a Lewis base. Thus ammonia is a base and not an acid.
So, option D is wrong.
Note: Another type of reagent is free radical. It is a neutral species carrying an unpaired electron and it is formed by the homolytic bond fission of a covalent bond. Due to the presence of unpaired electrons, free radicals are paramagnetic.

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




