
The resultant of $\vec A$ and $\vec B$ is perpendicular to $\vec A$. What is the angle between $\vec A$ and $\vec B$?
A) ${\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{A}{B}} \right)$
B) ${\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( { - \dfrac{A}{B}} \right)$
C) ${\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{A}{B}} \right)$
D) ${\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( { - \dfrac{A}{B}} \right)$
Answer
239.1k+ views
Hint: The resultant of two vectors is the vector addition of two vectors. Vectors can be added following two rules of addition: triangle law of addition or parallelogram law of addition. We can draw the vectors with co-initial points to illustrate the parallelogram law of vectors.
Formulae used:
The formula for the angle between resultant vector $\left( {\vec A + \vec B} \right)$ and a vector $\vec A$ is
$\tan \alpha = \dfrac{{b\sin \theta }}{{a + b\cos \theta }}$
Where $\alpha $ is the angle between resultant and the original vector and $\theta $ is the angle between the two vectors.
Complete step by step solution:
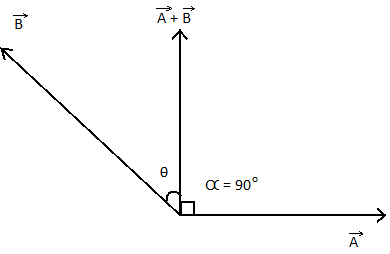
In the question it is given that the angle between resultant vector $\left( {\vec A + \vec B} \right)$ and a vector $\vec A$ is ${90^\circ }$ , that is, the resultant vector is perpendicular to the original vector.
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = {90^\circ }$
This means that
$\tan {90^\circ } = \dfrac{{B\sin \theta }}{{A + B\cos \theta }}$
As $\tan {90^\circ } \approx \infty $, for a fraction to approach infinity, the denominator of the fraction has to be zero
$A + B\cos \theta = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = - \dfrac{B}{A}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = - \dfrac{B}{A}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {\cos ^{ - 1}}( - \dfrac{B}{A})$
So the angle between the vectors is (B), ${\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( { - \dfrac{A}{B}} \right)$.
Additional information:
To derive the formula for the angle between the vectors we use the parallelogram law of vector addition. If $\vec A$ and $\vec B$ are vectors acting simultaneously from a point, representing both the magnitude and direction of the vectors, and $\theta $ is the angle between them then, then the diagonal of the parallelogram passing through the common vertices is the resultant. The angle between resultant and base is found by extending the base until a right angled triangle is formed and using Pythagoras and basic trigonometry to find the formula
Note: To solve such questions, we can also look at it from the point of view of triangle addition of vectors but that would make the formula more complicated. In parallelogram law of additions, both vectors and resultant share a common origin point, hence making the angle between the vectors more evident.
Formulae used:
The formula for the angle between resultant vector $\left( {\vec A + \vec B} \right)$ and a vector $\vec A$ is
$\tan \alpha = \dfrac{{b\sin \theta }}{{a + b\cos \theta }}$
Where $\alpha $ is the angle between resultant and the original vector and $\theta $ is the angle between the two vectors.
Complete step by step solution:

In the question it is given that the angle between resultant vector $\left( {\vec A + \vec B} \right)$ and a vector $\vec A$ is ${90^\circ }$ , that is, the resultant vector is perpendicular to the original vector.
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = {90^\circ }$
This means that
$\tan {90^\circ } = \dfrac{{B\sin \theta }}{{A + B\cos \theta }}$
As $\tan {90^\circ } \approx \infty $, for a fraction to approach infinity, the denominator of the fraction has to be zero
$A + B\cos \theta = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = - \dfrac{B}{A}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = - \dfrac{B}{A}$
$ \Rightarrow \theta = {\cos ^{ - 1}}( - \dfrac{B}{A})$
So the angle between the vectors is (B), ${\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( { - \dfrac{A}{B}} \right)$.
Additional information:
To derive the formula for the angle between the vectors we use the parallelogram law of vector addition. If $\vec A$ and $\vec B$ are vectors acting simultaneously from a point, representing both the magnitude and direction of the vectors, and $\theta $ is the angle between them then, then the diagonal of the parallelogram passing through the common vertices is the resultant. The angle between resultant and base is found by extending the base until a right angled triangle is formed and using Pythagoras and basic trigonometry to find the formula
Note: To solve such questions, we can also look at it from the point of view of triangle addition of vectors but that would make the formula more complicated. In parallelogram law of additions, both vectors and resultant share a common origin point, hence making the angle between the vectors more evident.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Other Pages
JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

Understanding the Electric Field of a Charged Spherical Shell

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

JEE Main Correction Window 2026 Session 1 Dates Announced - Edit Form Details, Dates and Link

Understanding the Electric Field Due to Infinite Linear Charge and Cylinders

JEE Main Colleges 2026: Complete List of Participating Institutes




