
Aluminium has FCC structure. The edge length of the unit cell is 404pm If the density of the metal is $2.7gc{m^{ - 3}}$ , the molar mass (in $gmo{l^{ - 1}}$ ) of Al atom is:
A.28.20
B.30.40
C.26.80
D.25.20
Answer
239.7k+ views
Hint: An FCC unit cell contains atoms at all the corners of the crystal lattice and at the center of all the faces of the cube. Basically, the atom present at the face-centered is shared between two adjacent unit cells and only $\dfrac{1}{2}$ of each atom belongs to an individual cell.
Formula used:
$d = \dfrac{{zM}}{{{N_A}{a^3}}}$
Where d is the density
M is molar mass
a is edge length
${N_A}$ is Avogadro’s number
Z is the number of formula units in the unit cell.
Complete step by step answer:
In FCC unit cells, the atoms are present in all the corners of the crystal lattice. Moreover, there is an atom present at the center of every face of the cube. The structure is as shown:
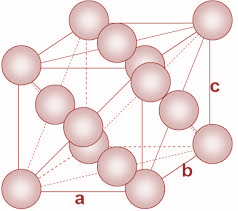
Now, in the given question, we have to calculate the molar mass Al atom. We have been given the density and the edge length of the unit cell.
Now, density is $2.7gc{m^{ - 3}}$
Edge length i.e. a is 404pm
${N_A}$ i.e. Avogadro number is $6.023 \times {10^{23}}$
And z for FCC is $4$
So, according to the given formula,
$d = \dfrac{{zM}}{{{N_A}{a^3}}}$
By substituting the values, we get
$d = \dfrac{{4 \times M}}{{6.023 \times {{10}^{23}} \times {{(404 \times {{10}^{ - 10}})}^3}}}$
$2.7 = \dfrac{{4 \times M}}{{6.023 \times {{10}^{23}} \times {{(404 \times {{10}^{ - 10}})}^3}}}$
Therefore, $M = 26.80gmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Hence, option C is correct.
Note:The smallest replicating portion of a crystal lattice is known as a unit cell. They further exist in many types. The cubic crystal structure for example, consists of three distinct unit cell types i.e. plain cubic, face centered cubic and body centered cubic.
Formula used:
$d = \dfrac{{zM}}{{{N_A}{a^3}}}$
Where d is the density
M is molar mass
a is edge length
${N_A}$ is Avogadro’s number
Z is the number of formula units in the unit cell.
Complete step by step answer:
In FCC unit cells, the atoms are present in all the corners of the crystal lattice. Moreover, there is an atom present at the center of every face of the cube. The structure is as shown:

Now, in the given question, we have to calculate the molar mass Al atom. We have been given the density and the edge length of the unit cell.
Now, density is $2.7gc{m^{ - 3}}$
Edge length i.e. a is 404pm
${N_A}$ i.e. Avogadro number is $6.023 \times {10^{23}}$
And z for FCC is $4$
So, according to the given formula,
$d = \dfrac{{zM}}{{{N_A}{a^3}}}$
By substituting the values, we get
$d = \dfrac{{4 \times M}}{{6.023 \times {{10}^{23}} \times {{(404 \times {{10}^{ - 10}})}^3}}}$
$2.7 = \dfrac{{4 \times M}}{{6.023 \times {{10}^{23}} \times {{(404 \times {{10}^{ - 10}})}^3}}}$
Therefore, $M = 26.80gmo{l^{ - 1}}$
Hence, option C is correct.
Note:The smallest replicating portion of a crystal lattice is known as a unit cell. They further exist in many types. The cubic crystal structure for example, consists of three distinct unit cell types i.e. plain cubic, face centered cubic and body centered cubic.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26




