
When acetyl chloride is heated with Na salt of carboxylic acid, the product is an :
A. Ester
B. Anhydride
C. Alkene
D. Aldehyde
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Nucleophilic substitution reactions are those reactions in which substitution is brought about by a nucleophile. These reactions are denoted by SN (S stands for substitution and N for nucleophile).
Complete step by step solution:
When acetyl chloride is heated with Na salt of carboxylic acid, the product is an acetic anhydride (which is an anhydride).
The following reaction takes place:
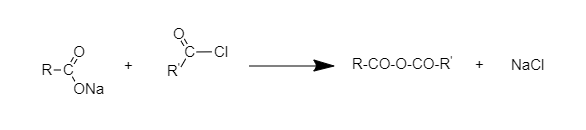
Hence, the correct option is B.
> Electrophiles and Nucleophiles are atoms, bonds, or (small or small parts of) compounds that are involved in chemical reactions.
> Electrophile may be defined as a species which are electron lovers. Such species are electron deficient in nature. It may be neutral or +ve charged.
> The nucleophile may be defined as a species, which is electron-rich in nature. Such species are neutral or –ve in charge.
> Stabilization of the negative charge on the acyl ion. The higher the stabilization through resonance, the lower will be the electrophilic nature and hence its reactivity.
> The lower the partial positive charge on the carbonyl atom, the lower will be its electrophilicity and hence reactivity.
> Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which the nucleophile substitutes the electrophile.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option C. But when acetyl chloride is heated, an anhydride is formed not an alkene.
Complete step by step solution:
When acetyl chloride is heated with Na salt of carboxylic acid, the product is an acetic anhydride (which is an anhydride).
The following reaction takes place:

Hence, the correct option is B.
> Electrophiles and Nucleophiles are atoms, bonds, or (small or small parts of) compounds that are involved in chemical reactions.
> Electrophile may be defined as a species which are electron lovers. Such species are electron deficient in nature. It may be neutral or +ve charged.
> The nucleophile may be defined as a species, which is electron-rich in nature. Such species are neutral or –ve in charge.
> Stabilization of the negative charge on the acyl ion. The higher the stabilization through resonance, the lower will be the electrophilic nature and hence its reactivity.
> The lower the partial positive charge on the carbonyl atom, the lower will be its electrophilicity and hence reactivity.
> Nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction in which the nucleophile substitutes the electrophile.
Note: The possibility to make a mistake is that you may choose option C. But when acetyl chloride is heated, an anhydride is formed not an alkene.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main Course 2026 - Important Updates and Details

JEE Main 2026 Session 1 Correction Window Started: Check Dates, Edit Link & Fees

Chemistry Question Pattern for JEE Main & Board Exams

Chemistry Question Paper PDF Download (2025, 2024) with Solutions

JEE Main Books 2026: Best JEE Main Books for Physics, Chemistry and Maths

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




