
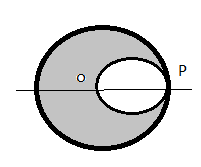
A transparent sphere of radius R has a cavity of radius $\dfrac{R}{2}$ as shown in Fig. The refractive index of the sphere if a parallel beam of light falling on the left surface focuses at point P is $\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{x}$. Find out the value of X?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:We have to find the refractive index of the sphere if a parallel beam of light falling on the left surface focuses on a point. It is given that this transparent sphere of radius R has a cavity of radius $\dfrac{R}{2}$ . Using the equation connecting image distance, refractive index and radius we can find the value of x.
Formula used:
Let refractive index be μ and v be image distance and if the light is falling parallel then we have the equation as:
$\dfrac{\mu }{v}-\dfrac{1}{\infty }=\dfrac{\mu }{\mu -1}$
Complete step by step solution:
We have a transparent sphere of radius R and it has a cavity with radius $\dfrac{R}{2}$. Refractive index of the sphere is given as $\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{x}$. This refractive index is measured when a parallel beam of light falling on the left surface focuses at point P. All conditions are given and we have to find the value of x. That is, we have to find a refractive index. When a parallel beam of light is falling on the left surface, then object distance will be infinity.
Let refractive index be μ and v be image distance and if the light is falling parallel then we have the equation as:
$\dfrac{\mu }{v}-\dfrac{1}{\infty }=\dfrac{\mu }{\mu -1}$
That is,
$v=\dfrac{\mu R}{\mu -1}$
For finding object distance at second boundary, we have:
$u=\dfrac{\mu R}{\mu -1}-R=\dfrac{R}{\mu -1}$
Hence the equation for refraction at second boundary is
$\dfrac{\mu }{-u}+\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1-\mu }{\dfrac{R}{2}}$
On substituting the values, we get:
$\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{2(1-\mu )}{R}+\dfrac{\mu }{\dfrac{R}{\mu -1}}$
On further solving we get a quadratic equation in terms of refractive index (μ) as:
${{\mu }^{2}}-3\mu +1=0$
On solving this quadratic equation, we get refractive index as:
Refractive index, $\mu =\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}$
Therefore, the answer is $x=2$
Notes: Here on solving quadratic equations we get two values for the refractive index. But the refractive index is already given, we only have to find the denominator so we ignore another value. In this question we consider refraction at two surfaces.
Formula used:
Let refractive index be μ and v be image distance and if the light is falling parallel then we have the equation as:
$\dfrac{\mu }{v}-\dfrac{1}{\infty }=\dfrac{\mu }{\mu -1}$
Complete step by step solution:
We have a transparent sphere of radius R and it has a cavity with radius $\dfrac{R}{2}$. Refractive index of the sphere is given as $\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{x}$. This refractive index is measured when a parallel beam of light falling on the left surface focuses at point P. All conditions are given and we have to find the value of x. That is, we have to find a refractive index. When a parallel beam of light is falling on the left surface, then object distance will be infinity.
Let refractive index be μ and v be image distance and if the light is falling parallel then we have the equation as:
$\dfrac{\mu }{v}-\dfrac{1}{\infty }=\dfrac{\mu }{\mu -1}$
That is,
$v=\dfrac{\mu R}{\mu -1}$
For finding object distance at second boundary, we have:
$u=\dfrac{\mu R}{\mu -1}-R=\dfrac{R}{\mu -1}$
Hence the equation for refraction at second boundary is
$\dfrac{\mu }{-u}+\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{1-\mu }{\dfrac{R}{2}}$
On substituting the values, we get:
$\dfrac{1}{R}=\dfrac{2(1-\mu )}{R}+\dfrac{\mu }{\dfrac{R}{\mu -1}}$
On further solving we get a quadratic equation in terms of refractive index (μ) as:
${{\mu }^{2}}-3\mu +1=0$
On solving this quadratic equation, we get refractive index as:
Refractive index, $\mu =\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}$
Therefore, the answer is $x=2$
Notes: Here on solving quadratic equations we get two values for the refractive index. But the refractive index is already given, we only have to find the denominator so we ignore another value. In this question we consider refraction at two surfaces.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




