
A sugar solution with sugar molecules and water molecules is-
A. Weak electrolyte
B. Non-electrolyte
C. Metallic conductor
D. Strong electrolyte
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Sugar is sucrose and is composed of twelve carbon atoms, twenty two hydrogen atoms and eleven oxygen atoms which are bonded together by covalent bonds. Water is a polar molecule composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom which are also bonded together by covalent bond.
Step-by-Step Solution-
Sugar solution contains both sugar molecules and water molecules. Sugar molecules have a chemical formula ${C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}$ where all the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms are joined together by covalent bonds. Its structure is-
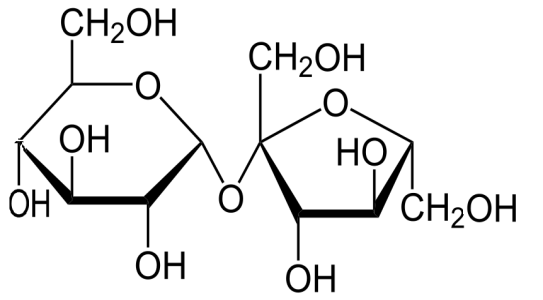
Since it is covalently bonded so it cannot decompose into ions which are necessary to conduct electricity in the solution.
Water molecule has formula ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ and it does dissociate into ions but its ionization constant is very low so the numbers of ions produced are not enough to conduct electricity. Since sugar and water molecules do not readily dissociate into ions when they are in their dissolved state and do not conduct electricity. Hence they are Non-electrolytes.
Non- electrolytes are typically joined by covalent bonds unlike electrolytes which are held together by ionic bonds so non- electrolytes do not easily break apart when placed in the aqueous solution.
Hence the correct answer is B.
Note: Electrolytes are totally opposite of non-electrolytes as they conduct electricity when they are in their dissolved state as they readily decompose into their ions. There are two types of electrolyte –
Weak Electrolyte- They do not dissociate completely in water only partially ionize in aqueous solution like hydrogen fluoride HF.
Strong Electrolyte-They completely dissociate into ions in the aqueous solution and completely ionize like sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Metallic conductor is a metal that conducts electricity due to flow of electrons like in copper, silver. There is only a physical change involved in it, no chemical changes occur.
Step-by-Step Solution-
Sugar solution contains both sugar molecules and water molecules. Sugar molecules have a chemical formula ${C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}$ where all the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms are joined together by covalent bonds. Its structure is-

Since it is covalently bonded so it cannot decompose into ions which are necessary to conduct electricity in the solution.
Water molecule has formula ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ and it does dissociate into ions but its ionization constant is very low so the numbers of ions produced are not enough to conduct electricity. Since sugar and water molecules do not readily dissociate into ions when they are in their dissolved state and do not conduct electricity. Hence they are Non-electrolytes.
Non- electrolytes are typically joined by covalent bonds unlike electrolytes which are held together by ionic bonds so non- electrolytes do not easily break apart when placed in the aqueous solution.
Hence the correct answer is B.
Note: Electrolytes are totally opposite of non-electrolytes as they conduct electricity when they are in their dissolved state as they readily decompose into their ions. There are two types of electrolyte –
Weak Electrolyte- They do not dissociate completely in water only partially ionize in aqueous solution like hydrogen fluoride HF.
Strong Electrolyte-They completely dissociate into ions in the aqueous solution and completely ionize like sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Metallic conductor is a metal that conducts electricity due to flow of electrons like in copper, silver. There is only a physical change involved in it, no chemical changes occur.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




