
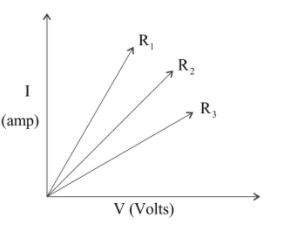
A student carries out an experiment and plots the V-I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistance ${R_1},{R_2},{R_3}$ respectively (see in figure). Which of the following is true?
A) ${R_1} = {R_2} = {R_3}$
B) ${R_1} = {R_2} = {R_3}$
C) ${R_1} < {R_2} < {R_3}$
D) ${R_2} > {R_3} > {R_1}$

Answer
538k+ views
Hint: This question can be solved by using ohm’s law and slope determining method as more the angle with the x-axis more will be the slope .As we know slope for any graph $ = \tan \theta $
Or in other words it is ratio of Y coordinate to the X coordinate
Hence, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{y}{x}$
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question given we have information from the graph as follows:
Resistance, Angle or slope for current and potential difference
As discussed above no calculative value is given so we will proceed with slope method
Always assumes of normal temperature if not given in the question because as temperature rises Ohms law will no longer be valid
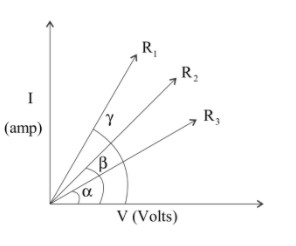
According to Ohm’s Law, $V = IR$ where v is the voltage, $I$ is the current and R is the resistance
Let’s study the graph above,
Slope $ = \tan \theta = \dfrac{V}{I} = \dfrac{1}{R}$
(by ohm's law)
As $\alpha > \beta > \gamma $
So, $\tan \gamma > \tan \beta > \tan \alpha $
That means $\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} > \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} > \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}$
On reciprocating we get,
${R_3} > {R_2} > {R_1}$
So, the conclusion is more the angle lesser will be the resistance only for this graph
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note: Ohm's law is only valid for normal temperatures, at high temperatures it fails as wire develops lots of heat due to which resistance automatically increases and the uniformity in ohm's Law destroys. In that case resistance changes depending on the nature of material that is metal, non-metal and semiconductors.
Or in other words it is ratio of Y coordinate to the X coordinate
Hence, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{y}{x}$
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question given we have information from the graph as follows:
Resistance, Angle or slope for current and potential difference
As discussed above no calculative value is given so we will proceed with slope method
Always assumes of normal temperature if not given in the question because as temperature rises Ohms law will no longer be valid

According to Ohm’s Law, $V = IR$ where v is the voltage, $I$ is the current and R is the resistance
Let’s study the graph above,
Slope $ = \tan \theta = \dfrac{V}{I} = \dfrac{1}{R}$
(by ohm's law)
As $\alpha > \beta > \gamma $
So, $\tan \gamma > \tan \beta > \tan \alpha $
That means $\dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} > \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} > \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}}$
On reciprocating we get,
${R_3} > {R_2} > {R_1}$
So, the conclusion is more the angle lesser will be the resistance only for this graph
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note: Ohm's law is only valid for normal temperatures, at high temperatures it fails as wire develops lots of heat due to which resistance automatically increases and the uniformity in ohm's Law destroys. In that case resistance changes depending on the nature of material that is metal, non-metal and semiconductors.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

CBSE Class 10 Sanskrit Set 4 52 Question Paper 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




