
A particle is moving unidirectionally on a horizontal plane under the action of a constant power-supplying energy source. Which of the following graphs accurately represents the motion of the particle in the displacement (s) – time (t) graph? (Graphs are drawn schematically and are not to scale)
A. 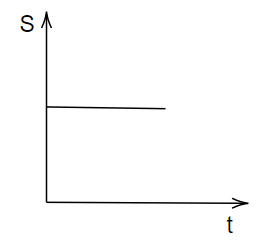
B. 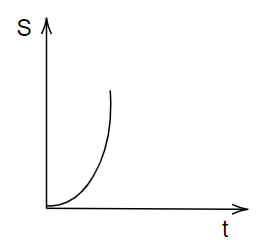
C. 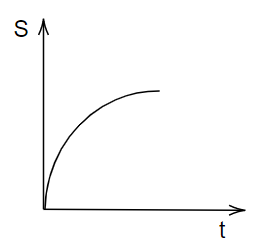
D. 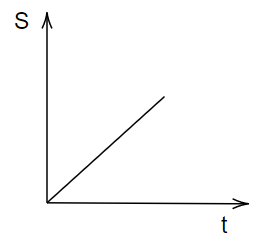
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:Before solving this problem let’s understand the term displacement. When a force is applied, the object changes its position which is known as displacement. Since it is a vector quantity it has both direction and magnitude. The power supplied to the particle is the product of the force applied and the velocity at which it travels.
Formula Used:
The power supplied to the particle is,
\[P = FV\]
Where, F is force applied and V is velocity.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a particle that is moving in one direction on a horizontal plane under the action of a constant power-supplying energy source. We need to find which of the following graphs accurately represents the motion of the particle in the displacement- time graph. We know that the power supplied to the particle is,
\[P = FV\]
We know that, \[F = m\dfrac{{dV}}{{dt}}\]
\[P = m\dfrac{{dV}}{{dt}} \times V\]
\[\Rightarrow VdV = \dfrac{P}{m}dt\]
On integrating we get the expression for V
\[\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{2} = \dfrac{P}{m}t\]
This clearly says that,
\[{V^2} \propto t\] or \[V \propto {t^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Here, velocity is,
\[V = \dfrac{\text{displacement}}{\text{time}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{S}{t}\]
Then,
\[\dfrac{S}{t} \propto {t^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
\[\therefore S \propto {t^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}\]
Therefore, we represent this equation in the displacement time graph as shown in option B.
Hence, Option B is the correct answer.
Note:The displacement-time graphs show how the displacement of a moving object changes with time. If a displacement-time graph is a sloping line then it shows that the object is moving. In this graph, the slope or gradient of the line is equal to the velocity of the object.
Formula Used:
The power supplied to the particle is,
\[P = FV\]
Where, F is force applied and V is velocity.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a particle that is moving in one direction on a horizontal plane under the action of a constant power-supplying energy source. We need to find which of the following graphs accurately represents the motion of the particle in the displacement- time graph. We know that the power supplied to the particle is,
\[P = FV\]
We know that, \[F = m\dfrac{{dV}}{{dt}}\]
\[P = m\dfrac{{dV}}{{dt}} \times V\]
\[\Rightarrow VdV = \dfrac{P}{m}dt\]
On integrating we get the expression for V
\[\dfrac{{{V^2}}}{2} = \dfrac{P}{m}t\]
This clearly says that,
\[{V^2} \propto t\] or \[V \propto {t^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
Here, velocity is,
\[V = \dfrac{\text{displacement}}{\text{time}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow V = \dfrac{S}{t}\]
Then,
\[\dfrac{S}{t} \propto {t^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}\]
\[\therefore S \propto {t^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}\]
Therefore, we represent this equation in the displacement time graph as shown in option B.
Hence, Option B is the correct answer.
Note:The displacement-time graphs show how the displacement of a moving object changes with time. If a displacement-time graph is a sloping line then it shows that the object is moving. In this graph, the slope or gradient of the line is equal to the velocity of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




