
A massless equilateral triangle EFG of side ‘a’ (As shown in figure) has three particles of mass m situated at its vertices. The moment of inertia of the system about each line EX perpendicular to EG in the plane of EFG is (N/20) ma2 where N is an integer. The value of N is _____.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:The Parallel axis theorem determines the moment of inertia of anybody about an axis which is parallel to the body passing through its centre is equal to the sum of moment of inertia of any given body about the axis which is passing through the middle and the product of the mass of the body times the square of the distance between the two axes.
Formula used:
Parallel axis theorem is given as,
\[I = {I_C} + M{h^2}\]
Where, I is the moment of inertia of the given body, \[{I_C}\] is the moment of inertia about the centre, M is the mass and h is the distance.
Complete step by step solution:
The mass of a particle situated at the vertex is ‘m’.
Moment of inertia of the system, I=(N/20) $ma^2$
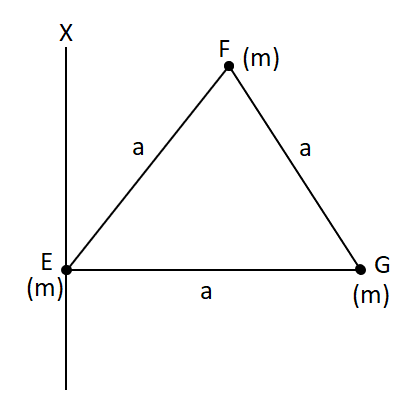
Image: moment of inertia of the system about the line EX
According to the parallel axis theorem,
I=moment of inertia of triangle along the medium + \[m{a^2}\]
\[I = m{\left( {\dfrac{a}{2}} \right)^2} + m{a^2}\]
Substituting the given value of moment of inertia of the system, we have
\[\dfrac{N}{{20}}m{a^2} = m{\left( {\dfrac{a}{2}} \right)^2} + m{a^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{N}{{20}}m{a^2} = \dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{4} + m{a^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{N}{{20}}m{a^2} = \dfrac{5}{4}m{a^2}\]
\[\therefore N = 25\]
Therefore, the value of N is 25.
Note: Parallel axis theorem and perpendicular axis theorems both are used in conjunction to find the moment of inertia of a given rigid body about any axis. Both the theorems can be used to determine the moment of inertia of an object that is in rotational motion.
Formula used:
Parallel axis theorem is given as,
\[I = {I_C} + M{h^2}\]
Where, I is the moment of inertia of the given body, \[{I_C}\] is the moment of inertia about the centre, M is the mass and h is the distance.
Complete step by step solution:
The mass of a particle situated at the vertex is ‘m’.
Moment of inertia of the system, I=(N/20) $ma^2$

Image: moment of inertia of the system about the line EX
According to the parallel axis theorem,
I=moment of inertia of triangle along the medium + \[m{a^2}\]
\[I = m{\left( {\dfrac{a}{2}} \right)^2} + m{a^2}\]
Substituting the given value of moment of inertia of the system, we have
\[\dfrac{N}{{20}}m{a^2} = m{\left( {\dfrac{a}{2}} \right)^2} + m{a^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{N}{{20}}m{a^2} = \dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{4} + m{a^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{N}{{20}}m{a^2} = \dfrac{5}{4}m{a^2}\]
\[\therefore N = 25\]
Therefore, the value of N is 25.
Note: Parallel axis theorem and perpendicular axis theorems both are used in conjunction to find the moment of inertia of a given rigid body about any axis. Both the theorems can be used to determine the moment of inertia of an object that is in rotational motion.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




