
A man of height ‘ $h$ ’ is walking away from a street lamp with a constant speed ‘ $v$ ’. The height of the street lamp is $3h$ . The rate at which the length of the man’s shadow is increasing when he is at a distance of $10h$ from of the base of the street lamp is:
A. $\dfrac{v}{2}$
B. $\dfrac{v}{3}$
C. $2v$
D. $\dfrac{v}{6}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:Use the criteria of similarity of the triangle in this question. If two triangles possess the same ratio of corresponding sides and an equivalent pair of corresponding angles, they are similar. This will help in determining the value of a. Further, differentiate a w.r.t t.
Complete answer:
Given:
Height of the man = $h$
Speed of man (constant) = $v$
Height of street lamp = $3h$
Now, we just start the solution to find the length of the man’s shadow at a distance of $10h$,
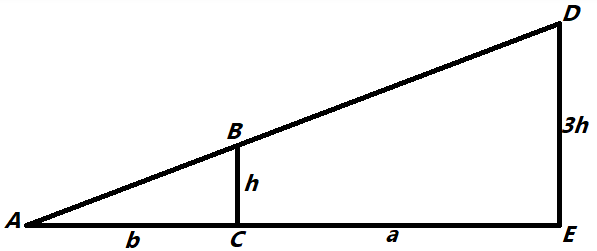
Let a be the horizontal separation between the lamp and the person, and b be the horizontal separation between the person and the shadow.
By seeing the figure, we get that,
$\Delta ABC$ is much similar to $\Delta ADE$,
By which we also say that,
$\dfrac{{DE}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}}$
Using all of the values in the aforementioned equation, we obtain,
$\dfrac{{3h}}{h} = \dfrac{{a + b}}{b}$
By using the cross multiplication method in the above equation, we get that,
$a = 2b$
By taking differentiation both sides with respect to t,
$\dfrac{{da}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{d}{{dt}}(2b)$
By doing further solutions, we get that,
$v_{man} = 2 \times {v_{shadow}}$
Because of the usage of velocity in the equation, we get that after which rearranging the values as suitable, we get that,
$v_{shadow} = \dfrac{v}{2}$
As in the above equation, we get the rate at which the man’s shadow is increasing when he is at a distance of $10h$ from the base of the street lamp.
Therefore, the correct answer is $v_{shadow} = \dfrac{v}{2}$ .
The correct option is (A).
Note:Instead of using similarity criteria of the triangle, we can also use the ratio of perpendicular to the base during the first few steps. Since the rate of length is mentioned in the question, we use differentiation w.r.t time for further calculations.
Complete answer:
Given:
Height of the man = $h$
Speed of man (constant) = $v$
Height of street lamp = $3h$
Now, we just start the solution to find the length of the man’s shadow at a distance of $10h$,
Let a be the horizontal separation between the lamp and the person, and b be the horizontal separation between the person and the shadow.
By seeing the figure, we get that,
$\Delta ABC$ is much similar to $\Delta ADE$,
By which we also say that,
$\dfrac{{DE}}{{BC}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}}$
Using all of the values in the aforementioned equation, we obtain,
$\dfrac{{3h}}{h} = \dfrac{{a + b}}{b}$
By using the cross multiplication method in the above equation, we get that,
$a = 2b$
By taking differentiation both sides with respect to t,
$\dfrac{{da}}{{dt}} = \dfrac{d}{{dt}}(2b)$
By doing further solutions, we get that,
$v_{man} = 2 \times {v_{shadow}}$
Because of the usage of velocity in the equation, we get that after which rearranging the values as suitable, we get that,
$v_{shadow} = \dfrac{v}{2}$
As in the above equation, we get the rate at which the man’s shadow is increasing when he is at a distance of $10h$ from the base of the street lamp.
Therefore, the correct answer is $v_{shadow} = \dfrac{v}{2}$ .
The correct option is (A).
Note:Instead of using similarity criteria of the triangle, we can also use the ratio of perpendicular to the base during the first few steps. Since the rate of length is mentioned in the question, we use differentiation w.r.t time for further calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




