
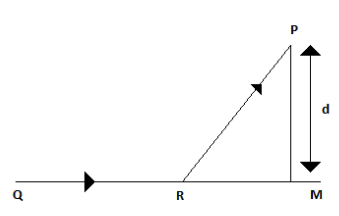
A man in a car at a location $Q$ on a straight highway is moving with speed $v$. He decides to reach a point \[P\] in a field at a distance d from the highway (point \[M\] ) as shown in the figure. The speed of the car in the field is half that on the highway. What should be the distance\[RM\] , so that the time taken to reach \[P\] is minimum?
$\left( A \right)\dfrac{d}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
$\left( B \right)\dfrac{d}{2}$
$\left( C \right)\dfrac{d}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
$(D)$ $d$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: By calculating the time \[{t_1}\] and \[\;{t_2}\], We will calculate the total time. By derivation of the time with respect to \[x\] we can find the minimum time taken to reach \[P\].
Complete step by step answer:
From point \[M\] at a distance, \[x\] the car turns off the highway. Then, \[RM = x\]
And if the speed of the car in the field is $v$ , then the time is taken by the car to cover the distance $QR = QM - x$
On the highway, \[{t_1}\] can be given by
${t_1} = \dfrac{{QM - x}}{{2v}}$
Time taken by the car to travel the distance \[RP\] can be given by,
${t_2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{d^2} + {x^2}} }}{v}$
The total time elapsed to move from Q to P
$t = {t_1} + {t_2}$
$ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{QM - x}}{{2v}} + \dfrac{{\sqrt {{d^2} + {x^2}} }}{v}$
If \[t\] is minimum,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}} = 0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}\left[ { - \dfrac{1}{2} + \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{d^2} + {x^2}} }}} \right] = 0$
$\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{d}{{\sqrt {4 - 1} }} = \dfrac{d}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Hence the right answer is in option $\left( A \right) \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{{\sqrt 3 }}$.
Additional information:
\[{\text{Speed = }}\dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{time}}}}\] : This formula describes distance traveled divided by the time taken to cover the distance.
Speed is Inversely proportional to Time and also directly Proportional to Distance.
Hence, \[{{Distance = Speed \times Time}}\], and \[{{Time = \;}}\dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{speed}}}}\;\], as the speed increases the time taken will decrease and vice versa.
Note: Distance, speed, and Time can be expressed in different units:
Time: seconds\[\left( s \right)\] , minutes\[\left( {min} \right)\] , hours \[\left( {hr} \right)\]
Distance: meters\[\left( m \right)\] , kilometers\[\left( {km} \right)\] , miles, feet
Speed: $m/s$ , $km/hr$
So if Distance = \[\left( {km} \right)\] and Time = \[\left( {hr} \right)\], then
${\text{Speed = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Distance}}}}{{{\text{time}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{km}}}}{{{\text{hr}}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
From point \[M\] at a distance, \[x\] the car turns off the highway. Then, \[RM = x\]
And if the speed of the car in the field is $v$ , then the time is taken by the car to cover the distance $QR = QM - x$
On the highway, \[{t_1}\] can be given by
${t_1} = \dfrac{{QM - x}}{{2v}}$
Time taken by the car to travel the distance \[RP\] can be given by,
${t_2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{d^2} + {x^2}} }}{v}$
The total time elapsed to move from Q to P
$t = {t_1} + {t_2}$
$ \Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{QM - x}}{{2v}} + \dfrac{{\sqrt {{d^2} + {x^2}} }}{v}$
If \[t\] is minimum,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dt}}{{dx}} = 0$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}\left[ { - \dfrac{1}{2} + \dfrac{x}{{\sqrt {{d^2} + {x^2}} }}} \right] = 0$
$\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{d}{{\sqrt {4 - 1} }} = \dfrac{d}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Hence the right answer is in option $\left( A \right) \Rightarrow \dfrac{d}{{\sqrt 3 }}$.
Additional information:
\[{\text{Speed = }}\dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{time}}}}\] : This formula describes distance traveled divided by the time taken to cover the distance.
Speed is Inversely proportional to Time and also directly Proportional to Distance.
Hence, \[{{Distance = Speed \times Time}}\], and \[{{Time = \;}}\dfrac{{{\text{distance}}}}{{{\text{speed}}}}\;\], as the speed increases the time taken will decrease and vice versa.
Note: Distance, speed, and Time can be expressed in different units:
Time: seconds\[\left( s \right)\] , minutes\[\left( {min} \right)\] , hours \[\left( {hr} \right)\]
Distance: meters\[\left( m \right)\] , kilometers\[\left( {km} \right)\] , miles, feet
Speed: $m/s$ , $km/hr$
So if Distance = \[\left( {km} \right)\] and Time = \[\left( {hr} \right)\], then
${\text{Speed = }}\dfrac{{{\text{Distance}}}}{{{\text{time}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{km}}}}{{{\text{hr}}}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




