
A large tank is filled with water to a height H. A small hole is made at the base of the tank. It takes \[{T_1}\] time to decrease the height of water to \[\dfrac{H}{\eta }\]\[\left( {\eta > 1} \right)\] and \[{T_2}\] time to take out the rest of the water. If \[{T_1} = {T_2}\] then the value of \[\eta \] is ?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:The speed at which the water comes out of the hole is determined using Bernoulli’s theorem. The amount of water coming out of the tank per unit time will be equal to the amount of water decreasing in the tank per unit time.
Formula used:,
\[t = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt {{h_1}} - \sqrt {{h_2}} } \right]\]
where t is the time taken to decrease the height of water from \[{h_1}\] to \[{h_2}\] in a tank of cross-sectional area A through the hole at the bottom of cross-sectional area a.
Complete step by step solution:
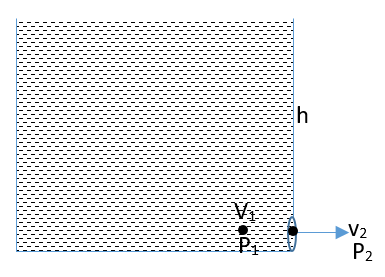
Image: Water tank
Taking two points 1 and 2, point 1 is just inside the tank and point 2 is just outside the tank with water of height h. Using Bernoulli’s equation between these two points, we get
\[{P_1} + \dfrac{{\rho v_1^2}}{2} + \rho g{h_1} = {P_2} + \dfrac{{\rho v_2^2}}{2} + \rho g{h_2}\]
The pressure outside point 2 is due to atmospheric pressure and the pressure at point 1 is due to the pressure of water and atmospheric pressure.
The velocity just inside the tank is zero and let the velocity of exit through the opening is \[{v_2}\]
Both the points are at same horizontal level, so \[{h_1} = {h_2}\]
Putting the values, we get
\[v = \sqrt {2gh} \]
The speed at which the water comes out of the tank is proportional to the square root of the height of water.
The time taken to decrease the height of water from \[{h_1}\] to \[{h_2}\] is given as,
\[t = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt {{h_1}} - \sqrt {{h_2}} } \right]\]
Here, A is the cross-section of the tank and a is the cross-section of the hole.
The initial height of the water is H and time taken to decrease it to \[\dfrac{H}{\eta }\] is given as \[{T_1}\].
\[{T_1} = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt H - \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} } \right]\]
When the rest of the water comes out, then height will become zero in time \[{T_2}\].
\[{T_2} = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} - \sqrt 0 } \right]\]
It is given that \[{T_1} = {T_2}\]. So, equating both the equations, we get
\[\dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt H - \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} } \right] = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} } \right] \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt H - \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} = \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt H = 2\sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt \eta = 2 \\ \]
\[\therefore \eta = 4\]
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: As the height of the water decreases the speed at which the water is coming out of the hole decreases. So, the time taken to empty the tank will increase as the height of the water in time decreases.
Formula used:,
\[t = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt {{h_1}} - \sqrt {{h_2}} } \right]\]
where t is the time taken to decrease the height of water from \[{h_1}\] to \[{h_2}\] in a tank of cross-sectional area A through the hole at the bottom of cross-sectional area a.
Complete step by step solution:

Image: Water tank
Taking two points 1 and 2, point 1 is just inside the tank and point 2 is just outside the tank with water of height h. Using Bernoulli’s equation between these two points, we get
\[{P_1} + \dfrac{{\rho v_1^2}}{2} + \rho g{h_1} = {P_2} + \dfrac{{\rho v_2^2}}{2} + \rho g{h_2}\]
The pressure outside point 2 is due to atmospheric pressure and the pressure at point 1 is due to the pressure of water and atmospheric pressure.
The velocity just inside the tank is zero and let the velocity of exit through the opening is \[{v_2}\]
Both the points are at same horizontal level, so \[{h_1} = {h_2}\]
Putting the values, we get
\[v = \sqrt {2gh} \]
The speed at which the water comes out of the tank is proportional to the square root of the height of water.
The time taken to decrease the height of water from \[{h_1}\] to \[{h_2}\] is given as,
\[t = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt {{h_1}} - \sqrt {{h_2}} } \right]\]
Here, A is the cross-section of the tank and a is the cross-section of the hole.
The initial height of the water is H and time taken to decrease it to \[\dfrac{H}{\eta }\] is given as \[{T_1}\].
\[{T_1} = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt H - \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} } \right]\]
When the rest of the water comes out, then height will become zero in time \[{T_2}\].
\[{T_2} = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} - \sqrt 0 } \right]\]
It is given that \[{T_1} = {T_2}\]. So, equating both the equations, we get
\[\dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt H - \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} } \right] = \dfrac{A}{a}\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{g}} \left[ {\sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} } \right] \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt H - \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} = \sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt H = 2\sqrt {\dfrac{H}{\eta }} \\ \]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt \eta = 2 \\ \]
\[\therefore \eta = 4\]
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: As the height of the water decreases the speed at which the water is coming out of the hole decreases. So, the time taken to empty the tank will increase as the height of the water in time decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




