
A hydrocarbon ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ absorbs only one molecule of ${{H}_{2}}$ on catalytic hydrogenation. On ozonolysis, the hydrocarbon yields $CHO{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}CHO$. The hydrocarbon is:
(A) Cyclohexene
(B) 1,5-hexadiene
(C) 1,3-cyclohexadiene
(D) 1-methylcyclopentene
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: From the molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ , we can say that the hydrocarbon contains one double bond in its structure. On ozonolysis ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ giving a symmetrical dialdehyde ( $CHO{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}CHO$ ) as the product means the alkene should be symmetrical in nature.
Complete step by step solution:
-In the question, it is given that ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ absorbs one mole of hydrogen gas on catalytic hydrogenation, means the given hydrocarbon has unsaturation (one double bond) in its structure.
-It is given that on ozonolysis ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ yields $CHO{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}CHO$ as the product.
-Coming to the given options, option A, Cyclohexene.
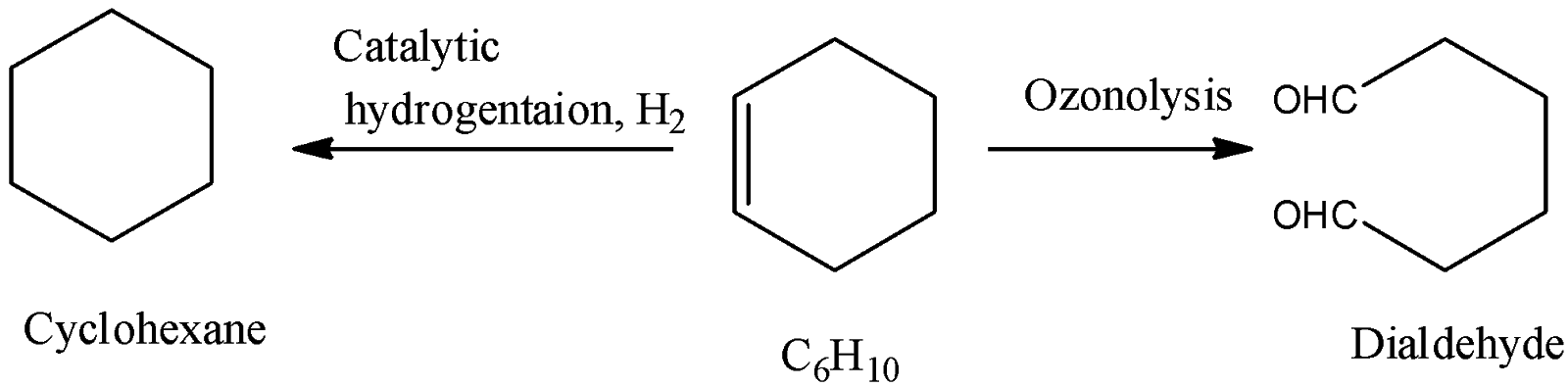
-Cyclohexene ( ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ ) on reaction with one mole of hydrogen and forms cyclohexane and on ozonolysis forms symmetrical dialdehyde as the product. So, option A is correct.
-Coming to option B, 1,5-hexadiene.
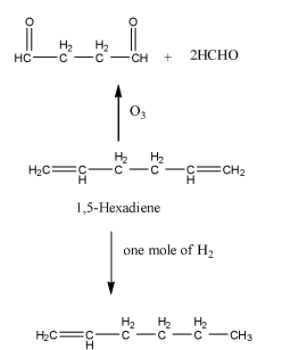
-Option B is wrong, because in the question it is given that on ozonolysis the hydrocarbon should give a single product. But on ozonolysis 1,5-Hexadiene gives two products. So, option B is wrong.
-Coming to option C, 1,3-cyclohexadiene.
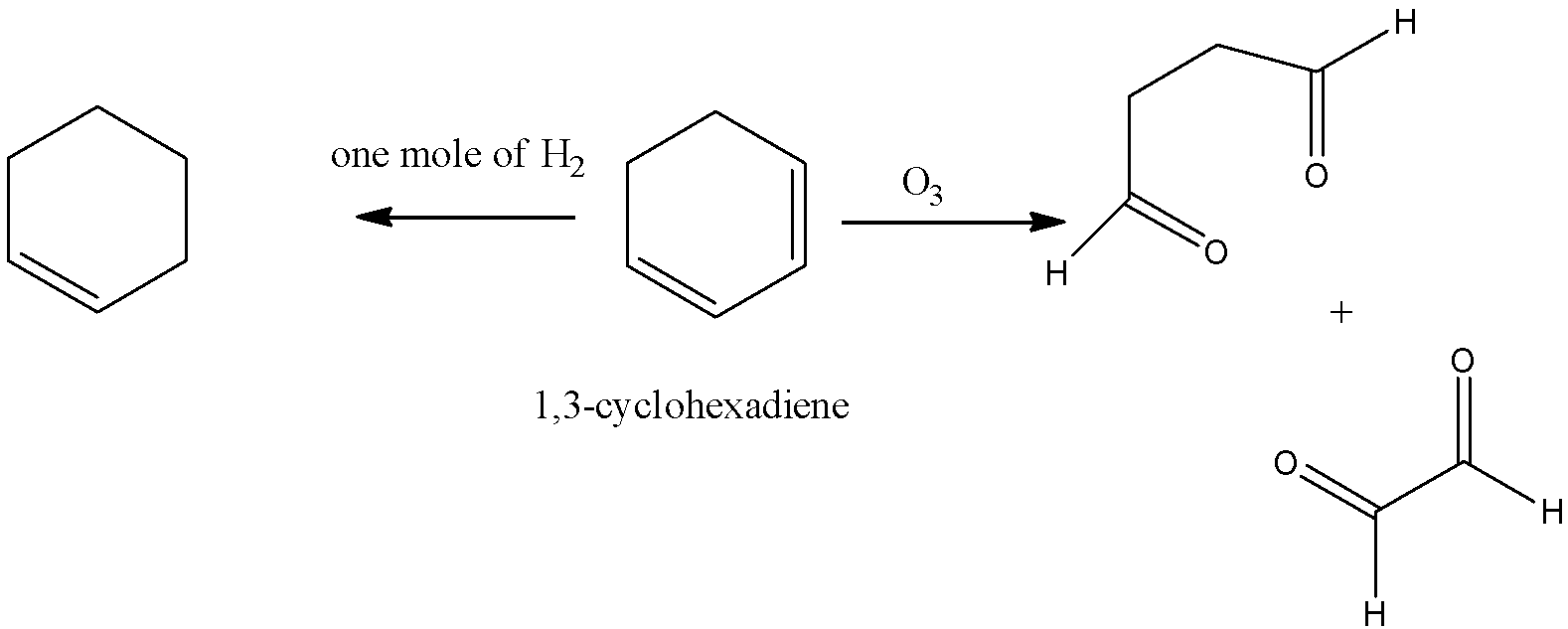
-In the question it is given that on ozonolysis the hydrocarbon should give only one product. But 1,3-cyclohexadiene is giving two products on ozonolysis. So, option C is wrong.
-Coming to option D, 1-methylcyclopentene.
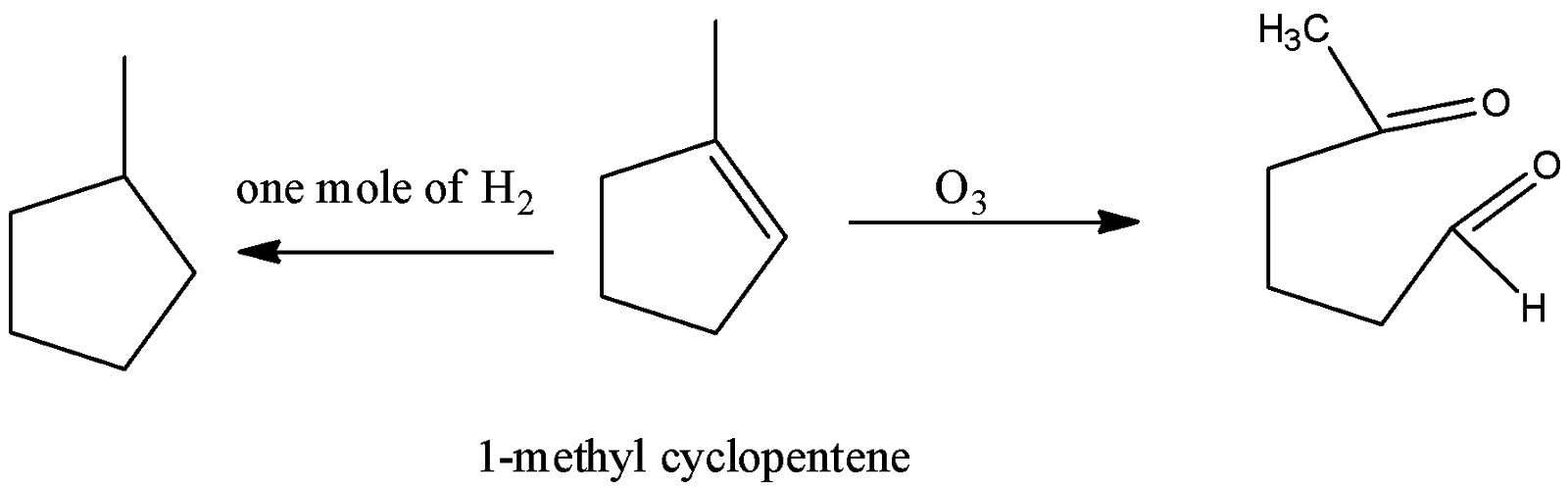
-In the question it is given that on ozonolysis the hydrocarbon should give a symmetrical dialdehyde.. But 1- methyl cyclopentene is giving an unsymmetrical product on ozonolysis. So, option D is wrong.
-Therefore, cyclohexene is going to match with the desired properties mentioned in the question.
So, the correct option is (A).
Note: Catalytic hydrogenation and ozonolysis are the best tests to identify the presence of unsaturation in the hydrocarbons. On hydrogenation alkenes gives alkanes and on ozonolysis alkenes gives respective carbonyl compounds as the products.
Complete step by step solution:
-In the question, it is given that ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ absorbs one mole of hydrogen gas on catalytic hydrogenation, means the given hydrocarbon has unsaturation (one double bond) in its structure.
-It is given that on ozonolysis ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ yields $CHO{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}CHO$ as the product.
-Coming to the given options, option A, Cyclohexene.

-Cyclohexene ( ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}$ ) on reaction with one mole of hydrogen and forms cyclohexane and on ozonolysis forms symmetrical dialdehyde as the product. So, option A is correct.
-Coming to option B, 1,5-hexadiene.

-Option B is wrong, because in the question it is given that on ozonolysis the hydrocarbon should give a single product. But on ozonolysis 1,5-Hexadiene gives two products. So, option B is wrong.
-Coming to option C, 1,3-cyclohexadiene.

-In the question it is given that on ozonolysis the hydrocarbon should give only one product. But 1,3-cyclohexadiene is giving two products on ozonolysis. So, option C is wrong.
-Coming to option D, 1-methylcyclopentene.

-In the question it is given that on ozonolysis the hydrocarbon should give a symmetrical dialdehyde.. But 1- methyl cyclopentene is giving an unsymmetrical product on ozonolysis. So, option D is wrong.
-Therefore, cyclohexene is going to match with the desired properties mentioned in the question.
So, the correct option is (A).
Note: Catalytic hydrogenation and ozonolysis are the best tests to identify the presence of unsaturation in the hydrocarbons. On hydrogenation alkenes gives alkanes and on ozonolysis alkenes gives respective carbonyl compounds as the products.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




