
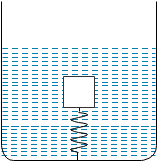
A block is submerged in a vessel filled with water by a spring attached to the bottom of the vessel. In equilibrium spring is compressed. The vessel now moves downwards with an acceleration a $(<\mathrm{g}) .$ The spring length
(a) will become zero
(b) may increase, decrease or remain constant
(c) will decrease
(d) will increase
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: We know that a body at rest in a fluid is acted upon by a force pushing upward called the buoyant force, which is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces. If the body is completely submerged, the volume of fluid displaced is equal to the volume of the body. If the body is only partially submerged, the volume of the fluid displaced is equal to the volume of the part of the body that is submerged. Based on this concept we have to answer this question.
Complete step by step answer
We know that when the vessel moves downwards, with acceleration, the block experiences a net pseudo force upwards. Hence, the apparent weight of the block decreases and the block moves upwards. Therefore, the length of the spring increases. Additional force on the block in upward direction-pseudo force on the block-decrease in buoyancy force.
at equilibrium
$k x+m g=F_{b}$
$k x_{1}=F_{b}-m g$
$x_{1}=\left(F_{b}-mg\right) / K$
When the vessel moves down,
$k x_{2}+mg=F_{b}+ma$
$k x_{2}=\left(F_{b}+ma\right)-mg$
$x_{2}=\dfrac{\left(F_{b}+ma\right)-mg}{K}$
${{x}_{2}}>{{x}_{1}}$
Hence, we can see that the length of spring increases.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: To answer such a question, it should be known to us that Archimedes' principle is very useful for calculating the volume of an object that does not have a regular shape. The oddly shaped object can be submerged, and the volume of the fluid displaced is equal to the volume of the object. It can also be used in calculating the density or specific gravity of an object.
Let us explain with the help of an example, for an object denser than water, the object can be weighed in air and then weighed when submerged in water. When the object is submerged, it weighs less because of the buoyant force pushing upward. The object's specific gravity is then the object's weight in air divided by how much weight the object loses when placed in water. But most importantly, the principle describes the behaviour of anybody in any fluid, whether it is a ship in water or a balloon in air.
Complete step by step answer
We know that when the vessel moves downwards, with acceleration, the block experiences a net pseudo force upwards. Hence, the apparent weight of the block decreases and the block moves upwards. Therefore, the length of the spring increases. Additional force on the block in upward direction-pseudo force on the block-decrease in buoyancy force.
at equilibrium
$k x+m g=F_{b}$
$k x_{1}=F_{b}-m g$
$x_{1}=\left(F_{b}-mg\right) / K$
When the vessel moves down,
$k x_{2}+mg=F_{b}+ma$
$k x_{2}=\left(F_{b}+ma\right)-mg$
$x_{2}=\dfrac{\left(F_{b}+ma\right)-mg}{K}$
${{x}_{2}}>{{x}_{1}}$
Hence, we can see that the length of spring increases.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: To answer such a question, it should be known to us that Archimedes' principle is very useful for calculating the volume of an object that does not have a regular shape. The oddly shaped object can be submerged, and the volume of the fluid displaced is equal to the volume of the object. It can also be used in calculating the density or specific gravity of an object.
Let us explain with the help of an example, for an object denser than water, the object can be weighed in air and then weighed when submerged in water. When the object is submerged, it weighs less because of the buoyant force pushing upward. The object's specific gravity is then the object's weight in air divided by how much weight the object loses when placed in water. But most importantly, the principle describes the behaviour of anybody in any fluid, whether it is a ship in water or a balloon in air.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




