
If \[A\] and $B$ are two sets, then $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ is equal to
A. Only \[A\].
B. \[A\cup B\]
C. \[\left( A\cup B' \right)\]
D. None of these.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The union of two sets like $A\cup B$ which is read as “ $A$ union $B$” can be defined as the set of all the elements present in set $A$ and in set $B$whereas the intersection of two sets like $A\cap B$ which is read as “ $A$ intersection $B$” can be defined as the set of all the elements which is common in both set $A$ and in set $B$. $A-B$ is a set which contains all the elements that are present in set $A$ but not in set $B$.
So to solve this question we will first make the Venn diagrams of $A-B,\,B-A$and $A\cap B$. Then we will use union of all the three sets that is$(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ in the Venn diagram and determine from the shaded portion that $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$is equal to which of the options given.
Complete step by step solution: We are given two sets \[A\] and $B$ and we have to find the value of $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ .
First we will make the Venn diagram of $A-B$.
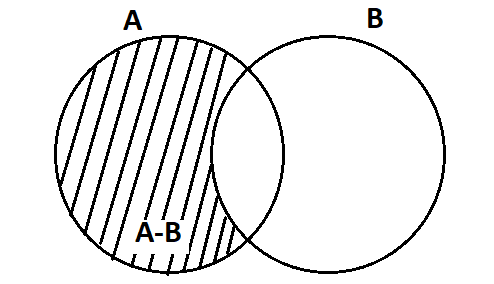
Now we will make the Venn diagram of $B-A$.
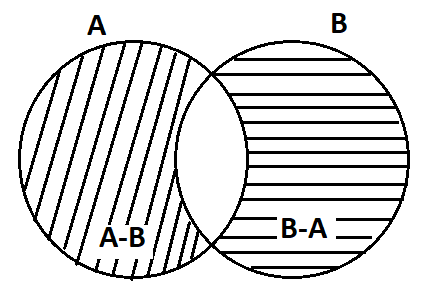
Now we will make the Venn diagram of $A\cap B$.
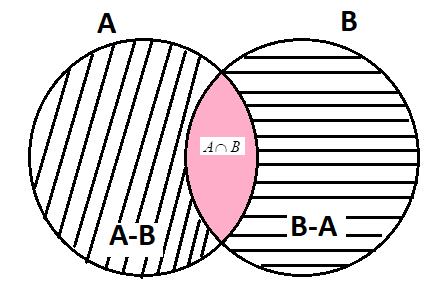
We will now use union in all the three sets $A-B,\,B-A$and $A\cap B$ that is $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$.
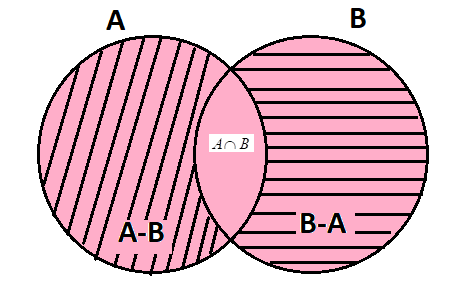
It means that $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ will contain all the elements present in all the three sets $A-B,\,B-A$and $A\cap B$. And as $A-B,\,B-A$and $A\cap B$ has all elements from the set \[A\] and $B$then it means $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ will contain all the elements of set \[A\] and $B$ that is \[A\cup B\]. Therefore $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ is equals to \[A\cup B\].
If \[A\] and $B$ are two sets, then $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ is equal to \[A\cup B\]
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: We can also solve this question without using Venn diagram. L
$A-B$ will contain all the elements that are present in set $A$ but not in set $B$ and $B-A$ will contain all the elements present in set $B$ but not in set $A$.
So union of both $A-B$ and $B-A$ that is $(A-B)\cup (B-A)$ will have only those elements which are only present in set $A$ and set $B$ but are not common in both.
Now $A\cap B$ will contain all elements that is common in both set. Now union of $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ will be,
$(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)=$Only $A\cup $ only $B\cup $ Common in both x and .
$=A\cup B$
So to solve this question we will first make the Venn diagrams of $A-B,\,B-A$and $A\cap B$. Then we will use union of all the three sets that is$(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ in the Venn diagram and determine from the shaded portion that $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$is equal to which of the options given.
Complete step by step solution: We are given two sets \[A\] and $B$ and we have to find the value of $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ .
First we will make the Venn diagram of $A-B$.

Now we will make the Venn diagram of $B-A$.

Now we will make the Venn diagram of $A\cap B$.

We will now use union in all the three sets $A-B,\,B-A$and $A\cap B$ that is $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$.

It means that $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ will contain all the elements present in all the three sets $A-B,\,B-A$and $A\cap B$. And as $A-B,\,B-A$and $A\cap B$ has all elements from the set \[A\] and $B$then it means $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ will contain all the elements of set \[A\] and $B$ that is \[A\cup B\]. Therefore $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ is equals to \[A\cup B\].
If \[A\] and $B$ are two sets, then $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ is equal to \[A\cup B\]
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: We can also solve this question without using Venn diagram. L
$A-B$ will contain all the elements that are present in set $A$ but not in set $B$ and $B-A$ will contain all the elements present in set $B$ but not in set $A$.
So union of both $A-B$ and $B-A$ that is $(A-B)\cup (B-A)$ will have only those elements which are only present in set $A$ and set $B$ but are not common in both.
Now $A\cap B$ will contain all elements that is common in both set. Now union of $(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)$ will be,
$(A-B)\cup (B-A)\cup (A\cap B)=$Only $A\cup $ only $B\cup $ Common in both x and .
$=A\cup B$
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Advanced 2026 Revision Notes for Vectors - Free PDF Download

JEE Advanced 2026 Revision Notes for Trigonometry - Free PDF Download

JEE Advanced 2026 Surface Chemistry Revision Notes - Free PDF Download

JEE Advanced Study Plan 2026: Expert Tips and Preparation Guide

JEE Advanced 2026 Revision Notes for Chemistry Solutions - Free PDF Download

Solutions Class 12 Notes JEE Advanced Chemistry [PDF]

Trending doubts
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Difference Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions Explained

IIT CSE Cutoff: Category‐Wise Opening and Closing Ranks

IIT Fees Structure 2025

Top IIT Colleges in India 2025

Other Pages
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter




